Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) Properties & Characteristics: Density, Thermal Data & More
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of carbon dioxide. Phase diagram included.
Carbon dioxide, CO2, is a colourless and odorless gas. It is relatively nontoxic and noncombustible, but it is heavier than air and may asphyxiate by the displacement of air.
When CO2is solved in water, the mild carbonic acid , is formed. Cooled CO2in solid form is called dry ice.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of carbon dioxide : Values are given for gas phase at 25 oC (77 oF, 298 K) and 1 atm, if not other phase, temperature or pressure given.
For full table with Imperial Units - rotate the screen!
| Property | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acidity (pKa1) | 6.35 | ||||||||||
| Acidity (pKa2) | 10.33 | ||||||||||
| Boiling Point - sublimation point | 194.686 | K | -78.464 | °C | -109.24 | °F | |||||
| Critical density | 10.63 | mol/dm3 | 467.6 | kg/m3 | 0.9073 | slug/ft3 | 29.19 | lb/ft3 | |||
| Critical pressure | 7.38 | MPa=MN/m2 | 73.8 | bar | 72.8 | atm | 1070 | psi=lbf/in2 | |||
| Critical temperature | 304.13 | K | 30.98 | °C | 87.76 | °F | |||||
| Critical volume | 94.12 | cm3/mol | 0.00214 | m3/kg | 1.102 | ft3/slug | 0.03426 | ft3/lb | |||
| Density | 40.8 | mol/m3 | 1.795 | kg/m3 | 0.00348 | slug/ft3 | 0.1121 | lb/ft3 | |||
| Density, gas at 32°F/0°C 1 atm | 44.9 | mol/m3 | 1.977 | kg/m3 | 0.00384 | slug/ft3 | 0.1234 | lb/ft3 | |||
| Density, liquid at -34.6 °F/-37°C, saturation pressure | 25017 | mol/m3 | 1101 | kg/m3 | 2.136 | slug/ft3 | 68.73 | lb/ft3 | |||
| Density, solid at -109.3 °F/-78.5°C, 1 atm | 35492 | mol/m3 | 1562 | kg/m3 | 3.031 | slug/ft3 | 97.51 | lb/ft3 | |||
| Flammable | no | ||||||||||
| Gas constant - R (individual) | 188.92 | J/kg K | 0.0525 | Wh/(kg K) | 1130 | (ft lbf/slug °R) | 35.114 | (ft lbf/lb °R) | |||
| Gibbs free energy of formation | -394.00 | kJ/mol | -8953 | kJ/kg | -3849 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of combustion | 0 | kJ/mol | 0 | kJ/kg | 0 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of formation | -393.50 | kJ/mol | -8941 | kJ/kg | -3844 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of fusion | 9.02 | kJ/mol | 205 | kJ/kg | 88.11 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of sublimation, at 180 K | 26 | kJ/mol | 591 | kJ/kg | 254 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of vaporization at 15°C | 179.5 | kJ/kg | 77.2 | Btu/lb | |||||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of vaporization at triple point | 15.55 | kJ/mol | 353.4 | kJ/kg | 151.93 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Specific heat capacity, Cp (isobaric) | 37.35 | J/mol K | 0.849 | kJ/kg K | 0.203 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | |||||
| Specific heat capacity, Cv (isochoric) | 28.96 | J/mol K | 0.658 | kJ/kg K | 0.157 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | |||||
| Ionization potential | 13.77 | eV | |||||||||
| Molecular Weight | 44.0095 | g/mol | 0.09702 | lb/mol | |||||||
| pH of saturated aqueous solution | 3.7 | ||||||||||
| Solubility in water | 0.148 | g/100 g | 1.48 | g/l=mg/ml | |||||||
| Sound velocity in gas | 269 | m/s | |||||||||
| Specific Gravity (density relativ to density of air) | 1.53 | ||||||||||
| Specific Heat Ratio - Cp/Cv | 1.29 | ||||||||||
| Specific Volume | 0.0245 | m3/mol | 0.557 | m3/kg | 287.1 | ft3/slug | 8.92 | ft3/lb | |||
| Standard molar entropy, S° | 213.8 | J/mol K | 4.86 | kJ/kg K | 1.16 | Btu/lb °F | |||||
| Sublimation Point | 194.686 | K | -78.464 | °C | -109.24 | °F | |||||
| Surface tension at melting point | 16.2 | dynes/cm | |||||||||
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.01663 | W/m°C | 0.009609 | Btu/hr ft °F | |||||||
| Triple point pressure | 0.5180 | MPa=MN/m2 | 5.180 | bar | 5.112 | atm | 75.12 | psi=lbf/in2 | |||
| Triple point temperature | 216.58 | K | -56.57 | °C | -69.81 | °F | |||||
| Vapor (saturation) pressure | 6.45 | MPa=MN/m2 | 48379 | mm Hg | 63.66 | atm | 935.5 | psi=lbf/in2 | |||
| Viscosity, dynamic (absolute) | 1.495 | cP | 1004.6 | (lbm/ft s ×10-6) | 31.22 | (lbf s/ft2 ×10-6) | |||||
| Viscosity, kinematic | 0.834 | cSt | 8.977 | (ft2/s ×10-6) |
Follow the links below to get values for the listed properties of carbon dioxide at varying pressure and temperature :
- Density and specific weight
- Dynamic and kinematic viscosity
- Prandtl number
- Specific heat (heat capacity)
- Thermal conductivity
See also more about atmospheric pressure, and STP - Standard Temperature and Pressure & NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure,
as well as Thermophysical properties of: Acetone, Acetylene, Air, Ammonia, Argon, Benzene, Butane, Carbon monoxide, Ethane, Ethanol, Ethylene, Helium, Hydrogen, Hydrogen sulfide, Methane, Methanol, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Pentane, Propane, Toluene, Water and Heavy water, D2O.
Carbon dioxide is a gas at standard conditions. However, at low temperature and/or high pressures the gas becomes a liquid or a solid.
The phase diagram for carbon dioxide shows the phase behavior with changes in temperature and pressure. The curve between the critical point and the triple point shows the carbon dioxide boiling point with changes in pressure. The curve between the triple point downwards to zero pressure shows the sublimation point with changes in pressure (Sublimation: transformation from solid phase directly to gas phase). Carbon dioxide in solid phase is called dry ice.
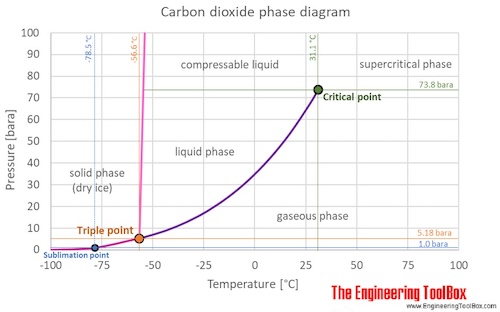
At the critical point there is no change of state when pressure is increased or if heat is added.
The triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
Atmospheric CO2Concentration