Benzene - Thermophysical properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of benzene, also called benzol. Phase diagram included.
Benzene, C6H6, is a clear colorless to light-yellow liquid, flammable with a petroleum-like, aromatic odor.
Benzene is less dense than water and is slightly soluble in water . Hence it floats on water . Benzene vapor is heavier than air. Benzene causes central nervous system damage acutely and bone marrow damage chronically and is carcinogenic. It was formerly used as parasiticide.
Benzene is present in crude oils and is a product of oil-refining processes. There are limitations on the content of benzene in gasoline. In industry benzene is used as a solvent, as a chemical intermediate, and is used in the synthesis of numerous chemicals.
The phase diagram of benzene is shown below the table.
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of benzene :
Values are given for liquid at 25 oC /77 oF / 298 K and 1 bara, if not other phase, temperature or pressure given.
For full table with Imperial Units - rotate the screen!
| Property | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | Value | Unit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autoignition temperature | 771 | K | 498 | °C | 928 | °F | |||||
| Boiling Point | 353.2 | K | 80.08 | °C | 176.1 | °F | |||||
| Critical density | 4.00 | mol/dm3 | 312 | kg/m3 | 0.606 | slug/ft3 | 19.5 | lb/ft3 | |||
| Critical pressure | 4.89 | MPa=MN/m2 | 48.9 | bar | 48.3 | atm | 709 | psi=lbf/in2 | |||
| Critical temperature | 562.0 | K | 288.9 | °C | 551.9 | °F | |||||
| Critical volume | 250 | cm3 /mol | 0.00320 | m3 /kg | 1.65 | ft3 /slug | 0.0513 | ft3 /lb | |||
| Density | 11185 | mol/m3 | 873.7 | kg/m3 | 1.695 | slug/ft3 | 54.54 | lb/ft3 | |||
| Flammable, gas and liquid | yes | ||||||||||
| Flash point | 262 | K | -11 | °C | 12 | °F | |||||
| Gas constant , individual, R | 106.4 | J/kg K | 0.02957 | Wh/(kg K) | 636.5 | [ft lbf/slug °R] | 19.78 | [ft lbf/lb °R] | |||
| Gibbs free energy of formation (gas) | 130 | kJ/mol | 1664 | kJ/kg | 716 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of combustion (liquid) | -3267.6 | kJ/mol | -41832 | kJ/kg | -18.0 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of formation (gas) | 82.9 | kJ/mol | 1061 | kJ/kg | 456 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of formation (liquid) | 49 | kJ/mol | 627 | kJ/kg | 270 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of fusion at 42°F/5.85°C | 9.9 | kJ/mol | 127 | kJ/kg | 54.49 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of sublimation, at 42°F/5.85°C | 45 | kJ/mol | 576 | kJ/kg | 248 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Heat (enthalpy) of evaporation | 33.8 | kJ/mol | 433 | kJ/kg | 186 | Btu/lb | |||||
| Specific heat capacity , Cp (gas) | 82.4 | J/mol K | 1.05 | kJ/kg K | 0.252 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | |||||
| Specific heat capacity, Cp (liquid) | 133 | J/mol K | 1.70 | kJ/kg K | 0.407 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | |||||
| Specific heat capacity, Cp (solid) at 32°F/0°C | 118 | J/mol K | 1.51 | kJ/kg K | 0.361 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | |||||
| Specific heat capacity, Cv (liquid) | 92.8 | J/mol K | 1.19 | kJ/kg K | 0.284 | Btu/lb°F or cal/g K | |||||
| Ionization potential | 9.24 | eV | |||||||||
| log KOW (Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient) | 2.13 | ||||||||||
| Melting point | 278.708 | K | 5.6 | °C | 42.0 | °F | |||||
| Molecular Weight | 78.112 | g/mol | 0.17221 | lb/mol | |||||||
| Solubility in water, at 25°C | 1.79 | mg/ml | |||||||||
| Sound velocity | 1330 | m/s | 4362 | ft/s | 2979 | mi/h | |||||
| Specific Gravity (gas) (relativ to air) | 2.77 | ||||||||||
| Specific Gravity (liquid) (relativ to water) | 0.88 | ||||||||||
| Specific Heat Ratio (liquid) - CP/CV | 1.43 | ||||||||||
| Specific Volume | 0.0000894 | m3 /mol | 0.00114 | m3 /kg | 0.590 | ft3 /slug | 0.0183 | ft3 /lb | |||
| Standard molar entropy , S° (gas) | 269 | J/mol K | 3.44 | kJ/kg K | 0.82 | Btu/lb °F | |||||
| Standard molar entropy, S° (liquid) | 173 | J/mol K | 2.21 | kJ/kg K | 0.53 | Btu/lb °F | |||||
| Standard molar entropy, S° (solid), at 1 bara | 45.56 | J/mol K | 0.58 | kJ/kg K | 0.14 | Btu/lb °F | |||||
| Surface tension | 28.2 | dynes/cm | 0.02822 | N/m | |||||||
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.143 | W/m°C | 0.0826 | Btu/hr ft °F | |||||||
| Triple point pressure | 4.80E-03 | MPa=MN/m2 | 4.80E-02 | bar | 4.74E-02 | atm | 6.96E-01 | psi=lbf /in2 | |||
| Triple point temperature | 278.7 | K | 5.6 | °C | 41.99 | °F | |||||
| Vapor (saturation) pressure | 0.0128 | MPa=MN/m2 | 96 | mm Hg | 0.126 | atm | 1.86 | psi=lbf /in2 | |||
| Viscosity , dynamic (absolute) | 0.6040 | cP | 405.9 | [lbm /ft s*10-6 ] | 12.61 | [lbf s/ft2*10-6 ] | |||||
| Viscosity, kinematic | 0.691 | cSt | 7.4 | [ft2/s*10-6 ] |
See also the following documents for changes in benzene properties with changes in pressure and temperature:
See also more about atmospheric pressure , and STP - Standard Temperature and Pressure & NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure ,
as well as Thermophysical properties of: Acetone , Acetylene , Air , Ammonia , Argon , Butane , Carbon dioxide , Carbon monoxide , Ethane , Ethanol , Ethylene , Helium , Hydrogen , Hydrogen sulfide , Methane , Methanol , Nitrogen , Oxygen , Pentane , Propane , Toluene , Water and Heavy water, D2O .
Benzene is a liquid at standard conditions. However, if heated it becomes a gas, and when cooled it becomes a solid. The phase diagram for benzene shows the phase behavior with changes in temperature and pressure. The curve between the critical point and the triple point shows the benzene boiling point with changes in pressure. It also shows the saturation pressure with changes in temperature.
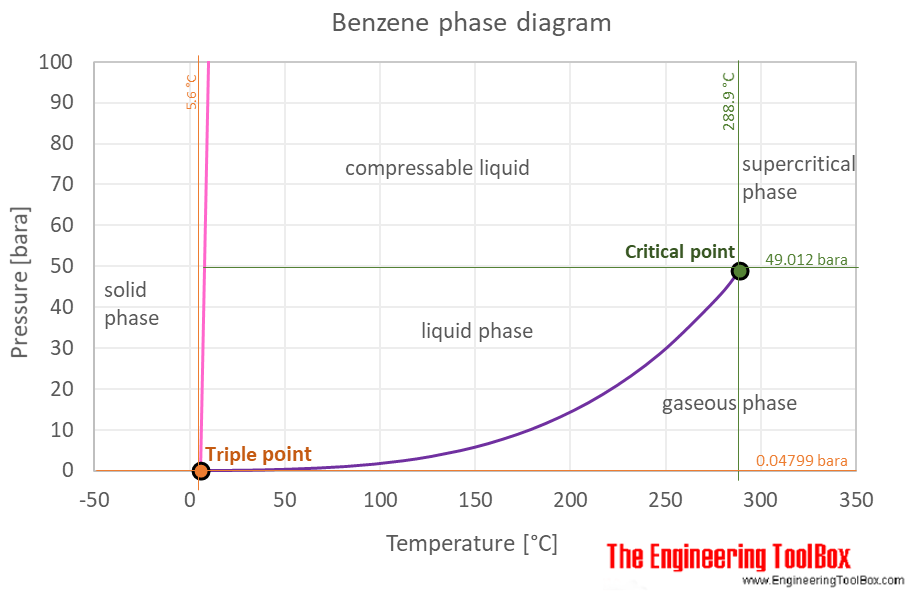
At the critical point there is no change of state when pressure is increased or if heat is added.
The triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
Related Topics
-
Boiling Points of Fluids
Boiling points of elements, products and chemical species at varying conditions. -
Densities
Densities of solids, liquids and gases. Definitions and convertion calculators. -
Fluid Mechanics
The study of fluids - liquids and gases. Involving velocity, pressure, density and temperature as functions of space and time. -
Material Properties
Properties of gases, fluids and solids. Densities, specific heats, viscosities and more. -
Melting and Freezing Points
Melting and freezing points of elements and chemical species at varying conditions. -
Thermodynamics
Work, heat and energy systems. -
Viscosities
Viscosities of products and chemical species at varying conditions.
Related Documents
-
Acetone - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of acetone, also called 2-propanone, dimethyl ketone and pyroacetic acid. Phase diagram included. -
Acetylene - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Acetylene. -
Air - Thermophysical Properties
Thermal properties of air at different temperatures - density, viscosity, critical temperature and pressure, triple point, enthalpi and entropi, thermal conductivity and diffusivity and more. -
Ammonia - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Ammonia. Phase diagram included. -
Argon - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Argon. -
Benzene - Density and Specific Weight vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and table showing density and specific weight of benzene, C6H6, at temperatures ranging from 5 to 325 °C (42 to 620 °F) at atmospheric and higher pressure - Imperial and SI Units. -
Benzene - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and table showing dynamic and kinematic viscosity of benzene, C6H6, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units. -
Benzene Gas - Specific Heat vs. Temperature
Specific heat of Benzene Gas - C6H6 - at temperatures ranging 250 - 900 K. -
Benzene Liquid - Thermal Properties
Properties like density, specific heat, thermal conductivity, dynamic viscosity and Prandtl number. -
Butane - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of n-Butane. -
Carbon Dioxide - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of carbon dioxide. Phase diagram included. -
Carbon Monoxide - CO - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Carbon Monoxide - CO. -
Conductive Heat Transfer
Conductive heat transfer takes place in a solid if there is a temperature gradient. -
Critical Temperatures and Pressures for some Common Substances
Critical temperatures and pressures for some common substances like air, alcohol, ether, oxygen and more. -
Density vs. Specific Weight and Specific Gravity
An introduction to density, specific weight and specific gravity. -
Ethane - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Ethane - C2H6. -
Ethanol - Thermophysical properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of ethanol (also called alcohol or ethyl alcohol). Phase diagram included. -
Heat Capacity
The amount of heat required to change the temperature of a substance by one degree. -
Heavy Water - Thermophysical Properties
Thermodynamic properties of heavy water (D2O) like density, melting temperature, boiling temperature, latent heat of fusion, latent heat of evaporation, critical temperature and more. -
Helium - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Helium - He. -
Hydrocarbons - Physical Data
Molweight, melting and boiling point, density, flash point and autoignition temperature, as well as number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in each molecule for 200 different hydrocarbons. -
Hydrocarbons - Autoignition Temperatures and Flash Points
Autoignition temperatures and flash points (°C and °F) of different types of hydrocarbons with varying carbon numbers up to C12. -
Hydrocarbons, Alcohols and Acids - Boiling points
Boiling temperatures (°C and °F) with varying carbon numbers up to C33. -
Hydrocarbons, Linear Alcohols and Acids - Densities
Density of hydrocarbons like alcohols and acids as function of carbon number at 20°C / 68°. -
Hydrogen - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Hydrogen - H2. -
Hydrogen sulfide - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of hydrogen sulfide, H2S, also called hydrosulfuric acid, sewer gas and stink damp. Phase diagram included. -
Liquids - Latent Heat of Evaporation
Latent heat of vaporization for fluids like alcohol, ether, nitrogen, water and more. -
Liquids - Vapor Pressures
Vapor and saturation pressure for some common liquids. -
Methane - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Methane - CH4. Phase diagram included. -
Methanol - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of methanol, CH3OH (also called carbinol, wood alcohol, hydroxy methyl and methyl alcohol). Phase diagram included. -
Molecular Weight of Substances
Definition and molecular weight (molar mass) of some common substances. -
Nitrogen - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Nitrogen - N2. -
Oxygen - Thermophysical properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Oxygen - O2. -
Pentane - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of pentane, also called n-pentane. Phase diagram included. -
Pressure
Introduction to pressure - online pressure units converter. -
Propane - Thermophysical properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of propane gas - C3H8. -
Solubility
The amount of a solute that can be dissolved in a solvent. -
Speed of Sound - Equations
Calculate the speed of sound (the sonic velocity) in gases, fluids or solids. -
Standard State and Enthalpy of Formation, Gibbs Free Energy of Formation, Entropy and Heat Capacity
Definition and explanation of the terms standard state and standard enthalpy of formation, with listing of values for standard enthalpy and Gibbs free energy of formation, as well as standard entropy and molar heat capacity, of 370 inorganic compounds. -
STP - Standard Temperature and Pressure and NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure
The definition of STP - Standard Temperature and Pressure and NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure. -
Substances Triple Points
Triple points for common substances. -
Surface Tension
Surface tension of liquids like water, mercury, oils and more. -
Universal and Individual Gas Constants
The Universal and Individual Gas Constants in fluid mechanics and thermodynamics. Individual gas constants for the most common gases. -
Viscosity - Absolute (Dynamic) vs. Kinematic
Vicosity is a fluid's resistance to flow and can be valued as dynamic (absolute) or kinematic. -
Water - Thermophysical Properties
Thermal properties of water at different temperatures like density, freezing temperature, boiling temperature, latent heat of melting, latent heat of evaporation, critical temperature and more.




