Critical Temperatures and Pressures for some Common Substances
Critical temperatures and pressures for some common substances like air, alcohol, ether, oxygen and more.
Gases can be converted to liquids by compressing the gas at a suitable temperature. However, they become more difficult to liquefy as the temperature increases because the kinetic energies of the particles that make up the gas also increase. At the critical temperature they cannot longer be liquified.
- Critical Temperature: The temperature which above, a substance can not exist as a liquid, no matter how much pressure is applied. Every substance has a critical temperature.
- Critical Pressure: The pressure required to liquify a substance vapor at its critical temperature
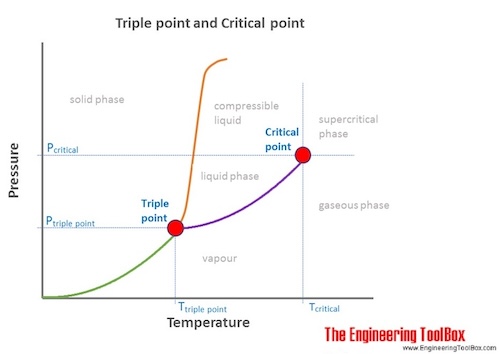
- Critical point: The end point of the pressure-temperature curve that designates conditions under which a liquid and its vapor can coexist. At higher temperatures, the gas cannot be liquefied by pressure alone. At the critical point, defined by the critical temperature Tc and the critical pressure pc, phase boundaries vanish.
- Triple point: The temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of a substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
The table below shows critical temperature and pressure for some common substances, together with boiling temperature.
See Triple point for listing of triple point values for common substances.
| Substance | Critical temperature | Critical pressure | Boiling temperature (1 atm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°F) | (°C) | (psi), (lb/in2) | (bar) | (°F) | (°C) | |
| Air | -220.94 | -140.52 | 549.08 | 37.858 | - | - |
| Ammonia (NH3) | 270 | 132.4 | 1636 | 112.8 | -27.4 | -33 |
| Argon | -188 | -122 | 705.6 | 48.7 | -302.5 | -185.8 |
| Butane | 305.6 | 152 | 550.4 | 38 | 32 | 0 |
| Carbon-dioxide (CO2) | 87.8 | 31.2 | 1071.6 | 73.8 | -110 | -79 |
| Carbon-monoxide (CO) | -220.5 | -140.3 | 507.5 | 35 | -310 | -190 |
| Chlorine | 291 | 144 | 1118.7 | 77.1 | -29.3 | -34 |
| Decane | 653 | 345 | 301.7 | 20.8 | 345 | 174 |
| Dowtherm A | 465 | 32.1 | ||||
| Ethane | 90.0 | 32.2 | 708 | 48.9 | -127.4 | -88.5 |
| Ethanol (alcohol) | 467 | 242 | 914 | 63 | 173 | 78.4 |
| Ethylether | 381 | 194 | 522 | 36 | 94.2 | 34.6 |
| Ethylene | 48.9 | 9.4 | 735 | 50.7 | -272.6 | -169.2 |
| Fluorine | -200 | -129 | 808.5 | 55.8 | -307 | -188 |
| Helium | -456 | -271 | 33.2 | 2.3 | -452 | -269 |
| Hydrogen (H) | -400 | -240 | 188.2 | 13.0 | -423 | -253 |
| Hydrogen Chloride | 125 | 51.6 | 1198 | 82.7 | -121.1 | -85.1 |
| Isobutane | 274 | 135 | 529.2 | 36.5 | 10.9 | -11.7 |
| Isobutylene | 293 | 145 | 580 | 40.0 | 19.6 | -6.9 |
| Isononane | 590 | 310 | 335.1 | 23.1 | 303 | 151 |
| Methane | -117 | -82.6 | 673.3 | 46.5 | -259 | -162 |
| Nitrogen (N) | -232.6 | -147 | 492.4 | 34.0 | -321 | -195 |
| Nitrous Oxide (N2O) | 97.4 | 36.4 | 1047.6 | 72.3 | -127 | -88.5 |
| Oxygen (O2) | -181.5 | -118.6 | 732 | 50.5 | -297 | -183 |
| Phosgene | 823.2 | 56.8 | 46.9 | 8.3 | ||
| Propane | 206.1 | 96.7 | 617.4 | 42.6 | -44 | -42 |
| Propylbenzene | 689 | 365 | 464.2 | 32 | 319 | 159 |
| Propylene | 198 | 92.4 | 670.3 | 46.3 | -54 | -48 |
| Refrigerants | ||||||
| Undecane | 691 | 366 | 287.2 | 19.8 | 385 | 196 |
| Water | 705 | 374 | 3206.2 | 220.5 | 212 | 100 |



