Carbon Dioxide Concentration in Rooms Occupied with People
Carbon dioxide concentration in a room may indicate air quality and ventilation system efficiency.
The carbon dioxide concentration in a room can be used to indicate air quality.
The Carbon dioxide concentration in a room filled with persons after a time - t - can be calculated as
c = (q / (n V)) (1 - (1 / en t)) + (c0 - ci) (1 / en t) + ci (1)
where
c= carbon dioxide concentration in the room (m3/m3)
q= carbon dioxide supplied to the room (m3/h)
V= volume of the room (m3)
e= the constant 2.718.....
n= number of air shifts per hour (1/h)
t= time (hour, h)
ci= carbon dioxide concentration in the inlet ventilation air (m3/m3)
c0= carbon dioxide concentration in the room at start,t=0(m3/m3)
Note that this equation can be used to calculate the concentration of any pollution as long as the pollution substance is homogeneous mixed with the air.
CO2 Concentration Calculator
*) normal carbon dioxide concentration in outside air is aprox. 400 ppm (0.0004 m3/m3).
Example - Carbon Dioxide Concentration in a Cinema
With an approximately carbon dioxide emission per person in a cinema of 0.05 m3/h - the CO2 emission from 100 persons can be calculated to approximately 5 m3/h.
If the carbon dioxide concentration when people enters the room - and in the inlet air - is close to zero, the CO2 pollution concentration in a 500 m3 cinema after one hour and with one air shift per hour, can be calculated as:
c =((5 m3/h) / (1 h-1) (500 m3)) (1 - (1 / e((1 1/h) (1 h))) + ((0 m3/m3) - (0.0004 m3/m3)) (1 / e(1 1/h)(1 h)) + (0.0004 m3/m3)
= 0.0067 m3/m3 (6700 ppm)
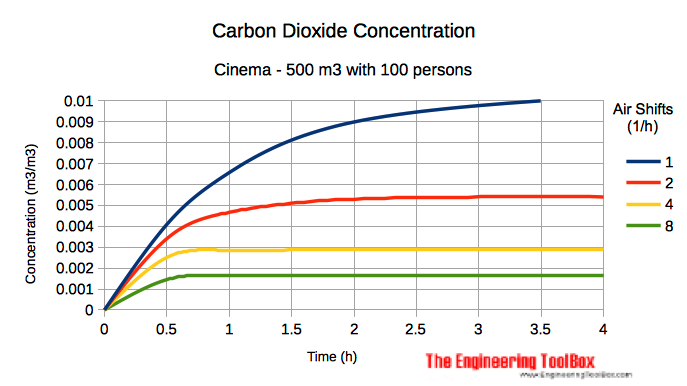
Note! - that with 6700 ppm(0.0067 m3/m3) of CO2 in the air - adverse health effects may be expected. One air shift per hour as used in this example is not enough.



