Heavy Water - Thermophysical Properties
Thermodynamic properties of heavy water (D2O) like density, melting temperature, boiling temperature, latent heat of fusion, latent heat of evaporation, critical temperature and more.
Heavy water ( deuterium oxide , 2H2O , D2O ) is a form of water that contains a larger than normal amount of the hydrogen isotope deuterium (= heavy hydrogen = 2H = D), rather than the common hydrogen-1 isotope ( 1 H = H = protium) that makes up most of the hydrogen in normal water.
Thermodynamic properties of heavy water - D2O:
- Boiling temperature (at 101.325 kPa): 101.40 oC = 214.52 °F
- Bulk modulus elasticity (at 25°C): 2.10 x 109 Pa or N/m2
- Critical density: 0.356 g/cm3 = 0.691 slug/ft3 = 3.457 lbm /gal(US)
- Critical pressure : 213.88 atm = 220.98 bar = 21.671 MPa (MN/m2) = 3143 psi (=lbf /in2)
- Critical temperature : 370.697 oC = 699.255 °F
- Ionization constant , pK w (at 25°C): 14.951
- Latent heat of evaporation (at 101.4°C): 41.521 KJ/mol = 2073.20 kJ/kg = 891.32 Btu(IT)/lb
- Latent heat of fusion: 6.132 kJ/mol = 306.2 kJ/kg = 131.64 Btu(IT)/lb
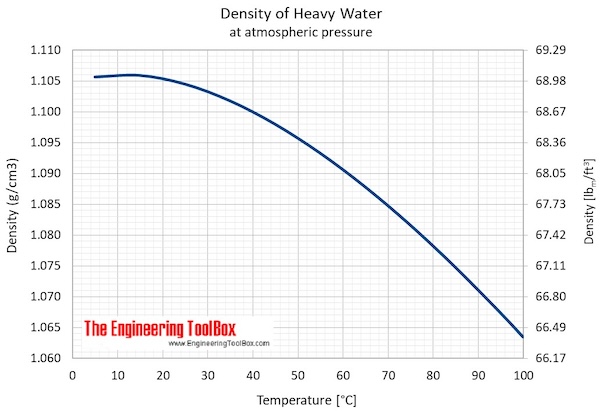
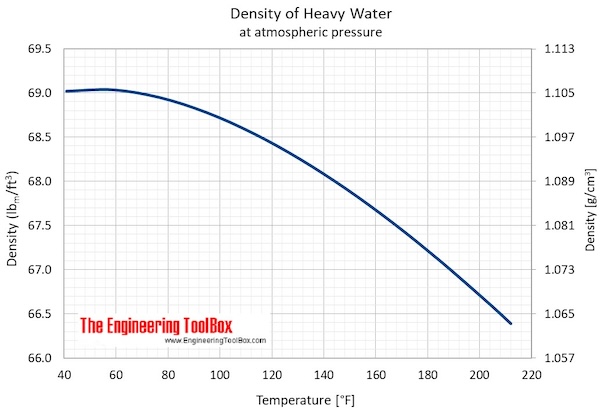
- Maximum density (at 11.23 oC): 1105.9 kg/m3 = 2.1460 slug/ft3 = 10.74048 lbm /gal(US)
- Melting temperature (at 101.325 kPa): 3.81 oC = 38.86 °F
- Molar mass: 20.02751 g/mol
- pD (~pH) (at 25°C): 7.43
- Specific heat (Cp ) water (at 20°C): 4.219 kJ/kgK = 1.008 Btu(IT)/(lbm °F) or kcal/(kg K)
- Specific weight (at 11.23 oC): 10.8452 kN/m3 = 69.0391 lbf /ft3
- Surface tension (at 25°C): 71.87 dyn/cm
- Triple point pressure: 0.00652 atm = 0.00661 bar = 661 Pa = 0.0959 psi (=lbf /in2)
- Triple point temperature: 3.82 °C = 38.88 °F
- Vapor pressure (at 25°C): 20.6 mmHg = 0.027 atm = 0.028 bar = 2750 Pa = 0.398 psi
- Viscosity (at 20°C): 1.251 cP or mPa s
Ionization Constant, pK w , of normal and heavy water with varying temperature .
See also more about atmospheric pressure , and STP - Standard Temperature and Pressure & NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure ,
as well as Thermophysical properties of: Acetone , Acetylene , Air , Ammonia , Argon , Benzene , Butane , Carbon dioxide , Carbon monoxide , Ethane , Ethanol , Ethylene , Helium , Hydrogen , Hydrogen sulfide , Methane , Methanol , Nitrogen , Oxygen , Pentane , Propane , Toluene and Water .
Related Topics
-
Densities
Densities of solids, liquids and gases. Definitions and convertion calculators. -
Material Properties
Properties of gases, fluids and solids. Densities, specific heats, viscosities and more. -
Steam and Condensate
Design of steam & condensate systems with properties, capacities, sizing of pipe lines, system configuration and more. -
Thermodynamics
Work, heat and energy systems. -
Water Systems
Design of hot and cold water service and utility systems with properties, capacities, sizing of pipe lines and more.
Related Documents
-
Acetone - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of acetone, also called 2-propanone, dimethyl ketone and pyroacetic acid. Phase diagram included. -
Air - Thermophysical Properties
Thermal properties of air at different temperatures - density, viscosity, critical temperature and pressure, triple point, enthalpi and entropi, thermal conductivity and diffusivity and more. -
Ammonia - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Ammonia. Phase diagram included. -
Benzene - Thermophysical properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of benzene, also called benzol. Phase diagram included. -
Bulk Modulus and Fluid Elasticities
Introduction to - and definition of - Bulk Modulus Elasticity commonly used to characterize the compressibility of fluids. -
Carbon Dioxide - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of carbon dioxide. Phase diagram included. -
Critical Temperatures and Pressures for some Common Substances
Critical temperatures and pressures for some common substances like air, alcohol, ether, oxygen and more. -
Density vs. Specific Weight and Specific Gravity
An introduction to density, specific weight and specific gravity. -
Ethylene - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of ethylene, also called ethene, acetene and olefiant gas. Phase diagram included. -
Gases Solved in Water - Diffusion Coefficients
Diffusion flux [kg/m2s] tells how fast a substanse solved in another substance flows due to concentration gradients. Diffusion constants [m2/s] for several gases in water. -
Heat Capacity
The amount of heat required to change the temperature of a substance by one degree. -
Ice and Water - Melting Points vs. Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables with melting points of ice to water at pressures ranging from 0 to 29000 psia (0 to 2000 bara). Temperature given as °C, °F, K and °R. -
Liquids - Latent Heat of Evaporation
Latent heat of vaporization for fluids like alcohol, ether, nitrogen, water and more. -
Methane - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Methane - CH4. Phase diagram included. -
Methanol - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of methanol, CH3OH (also called carbinol, wood alcohol, hydroxy methyl and methyl alcohol). Phase diagram included. -
Pentane - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of pentane, also called n-pentane. Phase diagram included. -
Viscosity - Absolute (Dynamic) vs. Kinematic
Vicosity is a fluid's resistance to flow and can be valued as dynamic (absolute) or kinematic. -
Water - Boiling Points at Higher Pressures
Online calculator, figures and tables showing boiling points of water at pressures ranging from 14.7 to 3200 psia (1 to 220 bara). Temperature given as °C, °F, K and °R. -
Water - Boiling Points at Vacuum Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables giving the boiling temperatures of water in varying vacuum, SI and Imperial units. -
Water - Density, Specific Weight and Thermal Expansion Coefficients
Definitions, online calculator and figures and tables with water properties like density, specific weight and thermal expansion coefficient of liquid water at temperatures ranging 0 to 360°C (32 to 680°F). -
Water - Dynamic (Absolute) and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Free online calculator - figures and tables with viscosity of water at temperatures ranging 0 to 360°C (32 to 675°F) - Imperial and SI Units. -
Water - Ionization Constant, pKw, of Normal and Heavy Water
Ionization constant (= dissociation constant = self-ionization constant = ion product = autoprotolysis constant ) of water and heavy water, given as function of temperature (°C and °F) in figures and tables. -
Water - Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions
Figures and tables showing how the properties of water changes along the boiling/condensation curve (vapor pressure, density, viscosity, thermal conductivity, specific heat, Prandtl number, thermal diffusivity, entropy and enthalpy). -
Water - Saturation Pressure vs. Temperature
Online calculator, figures and tables with water saturation (vapor) pressure at temperatures ranging 0 to 370 °C (32 to 700°F) - in Imperial and SI Units. -
Water - Specific Heat vs. Temperature
Online calculator, figures and tables showing specific heat of liquid water at constant volume or constant pressure at temperatures from 0 to 360 °C (32-700 °F) - SI and Imperial units. -
Water - Specific Volume vs. Temperature
Online calculator, figures and tables showing Specific Volume of water at temperatures ranging from 0-370 °C and 32 - 700 °F - Imperial and IS Units. -
Water - Thermal Conductivity vs. Temperature
Figures and tables showing thermal conductivity of water (liquid and gas phase) with varying temperature and pressure, SI and Imperial units. -
Water - Thermal Diffusivity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Figures and tables with thermal diffusivity of liquids and gaseous water at varying temperarures and pressures - SI and Imperial units. -
Water - Thermophysical Properties
Thermal properties of water at different temperatures like density, freezing temperature, boiling temperature, latent heat of melting, latent heat of evaporation, critical temperature and more. -
Water vs. Steam - Critical and Triple Points
Critical point is where vapor and liquid are indistinguishable and triple point is where ice, water and vapor coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.