Combustion Efficiency and Excess Air
Optimizing boilers efficiency is important to minimize fuel consumption and unwanted excess to the environment.
To ensure complete combustion of the fuel used combustion chambers are supplied with excess air. Excess air increase the amount of oxygen to the combustion and the combustion of fuel.
- when fuel and oxygen from the air are in perfect balance - the combustion is said to be stoichiometric
The combustion efficiency increases with increased excess air - until the heat loss in the excess air is larger than the heat provided by more efficient combustion.
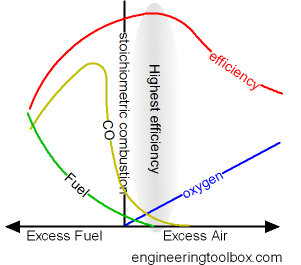
Typical excess air to achieve the highest possible efficiency for some common fuels:
- 5 - 10% for natural gas
- 5 - 20% for fuel oil
- 15 - 60% for coal
Carbon dioxide - CO2 - is a combustion product and the content of CO2 in a flue gas is an important indication of the combustion efficiency.
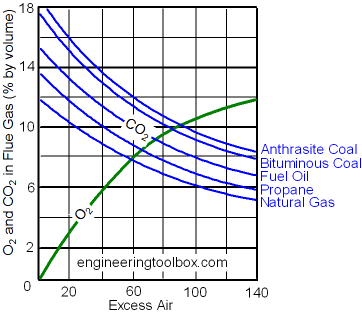
Optimal content of carbon dioxide CO2 after combustion is approximately 10% for natural gas and approximately 13% for lighter oils.
Normal combustion efficiency for natural gas at different combinations of excess air and flue gas temperatures are indicated below:
| Excess (%) | Combustion Efficiency (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net Stack Temperature1) (oF) | ||||||
| Air | Oxygen | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 |
| 9.5 | 2.0 | 85.4 | 83.1 | 80.8 | 78.4 | 76.0 |
| 15 | 3.0 | 85.2 | 82.8 | 80.4 | 77.9 | 75.4 |
| 28.1 | 5.0 | 84.7 | 82.1 | 79.5 | 76.7 | 74.0 |
| 44.9 | 7.0 | 84.1 | 81.2 | 78.2 | 75.2 | 72.1 |
| 81.6 | 10.0 | 82.8 | 79.3 | 75.6 | 71.9 | 68.2 |
1) "Net stack temperature" is temperature difference between flue gas temperature inside the chimney and room temperature outside the burner.
Flue Gas Loss with Oil Combustion
The efficiency loss in the flue gas related to
- temperature difference in flue gas and supply air
- CO2 concentration in the flue gas
with oil combustion is indicated below:
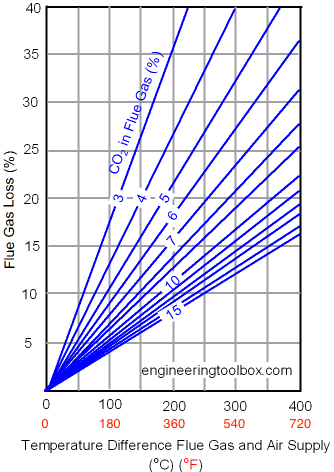
Example - Oil Combustion and Heat Loss in the Flue Gas
If
- the temperature difference between the flue gas leaving a boiler and the ambient supply temperature is 300 oC, and
- the carbon dioxide measured in the flue gas is 10% - then,
from the diagram above
- the flue gas loss can be estimated to approximately 16%.



