Pressure
Introduction to pressure - online pressure units converter.
The pressure in a fluid is defined as
"the normal force per unit area exerted on a imaginary or real plane surface in a fluid or a gas"
The equation for pressure can be expressed as:
p = F / A (1)
where
p = pressure (lb/in2(psi), lb/ft2(psf), N/m2, kg/ms2(Pa))
F = force (N) 1)
A = area (in2, ft2, m2)
1) In the Imperial - English Engineering System special care must be taken for the force unit. The basic unit for mass is slug and the unit for force is pound ( lb ) or pound force ( lbf ).
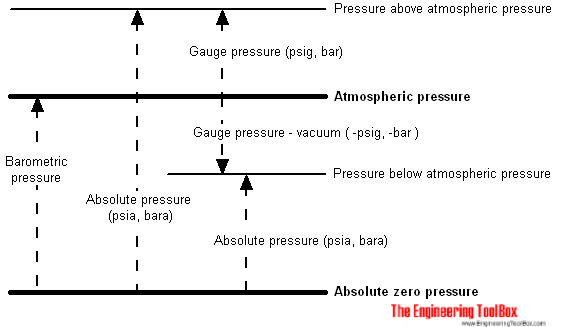
Absolute Pressure
The absolute pressure - p abs - is measured relative to the absolute zero pressure - the pressure that would occur at absolute vacuum. All calculations involving the gas law requires pressure (and temperature) to be in absolute units.
Gauge Pressure
A gauge is often used to measure the pressure difference between a system and the surrounding atmosphere. This pressure is often called the gauge pressure and can be expressed as
p g = p s - p atm (2)
where
p g = gauge pressure (Pa, psi)
p s = system pressure (Pa, psi)
p atm = atmospheric pressure (Pa, psi)
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the pressure in the surrounding air at - or "close" to - the surface of the earth. The atmospheric pressure varies with temperature and altitude above sea level.
Standard Atmospheric Pressure
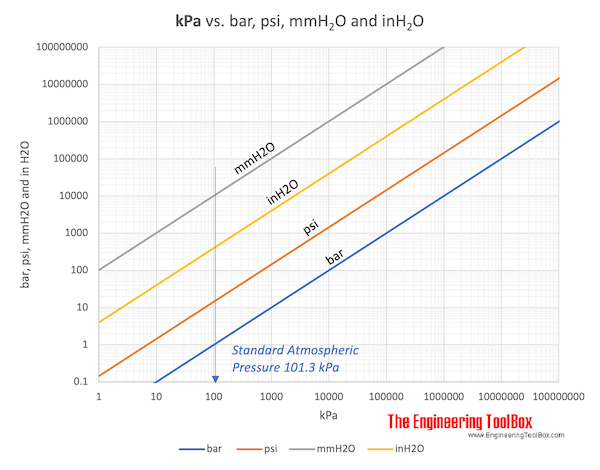
The Standard Atmospheric Pressure ( atm ) is normally used as the reference when listing gas densities and volumes. The Standard Atmospheric Pressure is defined at sea-level at 273 o K (0 oC) and is 1.01325 bar or 101325 Pa (absolute) . The temperature of 293 o K (20 oC) is sometimes used.
In imperial units the Standard Atmospheric Pressure is 14.696 psi.
- 1 atm = 1.01325 bar = 101.3 kPa = 1.013 105 Pa = 14.696 psi (lbf /in2)= 760 mmHg =10.33 mH2O = 760 torr = 29.92 inHg = 1013 mbar = 1.0332 kgf /cm2= 33.90 ftH2O
Pressure Units
Since 1 Pa is a small pressure unit the unit hectoPascal (hPa) is widely used, especially in meteorology. The unit kiloPascal (kPa) is commonly used in the design of technical applications - like HVAC systems, piping systems and similar.
- 1 hectoPascal = 100 Pascal = 1 millibar
- 1 kiloPascal = 1000 Pascal
Some Pressure Levels
- 10 Pa - the pressure below 1 mm of water
- 1 kPa - approximately the pressure exerted by a 10 g of mass on a 1 cm2 area
- 10 kPa - the pressure below 1 m of water, or the drop in air pressure when moving from sea level to 1000 m elevation
- 10 MPa - nozzle pressure in a "high pressure" washer
- 10 GPa - pressure enough to form diamonds
Some Alternative Units of Pressure
- 1 bar - 100,000 Pa
- 1 millibar - 100 Pa
- 1 atmosphere - 101325 Pa
- 1 mm Hg - 133 Pa
- 1 inch Hg - 3386 Pa
A torr (often used in vacuum applications) is named after Torricelli and is the pressure produced by a column of mercury 1 mm high - equals to 1 / 760 th of an atmosphere.
- 1 atm = 760 torr = 14.696 psi = 1.013 bar
Pounds per square inch (psi) was commonly used in the U.K. but is now replaced in almost every country except in the US by SI units. Since atmospheric pressure is 14.696 psi - a column of air on a area of one square inch area from the Earth's surface to the space - weights 14.696 pounds .
The bar (bar) is commonly used in the industry. One bar is 100,000 Pa , and for most practical purposes can be approximated to one atmosphere even if
1 bar = 0.9869 atm = 14.5 psi
There are 1000 millibar (mbar) in one bar , a unit common in meteorology and weather applications.
1 millibar = 0.001 bar = 0.750 torr = 100 Pa
Download kPa to bar, psi, mmH2O and inH2O chart
Related Mobile Apps from The Engineering ToolBox 
- free apps for offline use on mobile devices.
Related Topics
-
Basics
Basic engineering data. SI-system, unit converters, physical constants, drawing scales and more. -
Fluid Mechanics
The study of fluids - liquids and gases. Involving velocity, pressure, density and temperature as functions of space and time. -
Gases and Compressed Air
Properties of air, LNG, LPG and other common gases. Pipeline capacities and sizing of relief valves. -
Process Control Systems
Instrumentation, design and documentation of process control systems.
Related Documents
-
ABS Pipes - Pressure Ratings
Pressure ratings of ABS 1208, ABS 1210, ABS 1316 and ABS 2112. -
Acetone - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of acetone, also called 2-propanone, dimethyl ketone and pyroacetic acid. Phase diagram included. -
Air - Specific Heat vs. Pressure at Constant Temperature
Figures and tables with isobaric (Cp) and isochoric (Cv) specific heat of air at constant temperature and pressure ranging 0.01 to 10000 bara. -
Atmospheric Pressure vs. Elevation above Sea Level
Elevation above sea level - in feet and meter - with barometric and atmospheric pressure - inches mercury, psia, kg/cm2 and kPa. -
Barometer - Altitude Compensation
Elevation compensating manometer. -
Benzene - Thermophysical properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of benzene, also called benzol. Phase diagram included. -
Compression and Expansion of Gases
Isothermal and isentropic gas compression and expansion processes. -
Duct Systems - Pressure Classifications
Duct systems are commonly divided into three pressure classifications. -
Hydraulic Force vs. Pascal's Law
Pascal's law and the hydraulic force acting in fluids. -
Hydrostatic Pressure vs. Depth
Depth and hydrostatic pressure. -
International Standard Atmosphere
International standard atmosphere in elevation -2000 to 30000 metre - pressure, temperature, density, viscosity, thermal conductivity and velocity of sound. -
Pressure Energy
Calculate the potential of pressure energy in a incompressible fluid. -
Pressure to Head Unit Converter
Pressure vs. head units - like lb/in2, atm, inches mercury, bars, Pa and more. -
Pressure Units - Online Converter
Convert between pressure units like Pa, bar, atmosphere, pound square feet, psi and more. -
Pressure Units Converter
Convert from kPa to psi and inches of Water and Mercury. -
SI System
An introduction to the SI metric system. -
Steam Flash Generation (bar)
The amount of flash steam generated depends on steam pressure and pressure in the condensate lines. -
Steam Pipes - Online Pressure drop Calculator
Calculate pressure drops in steam distribution pipe lines. -
U.S. Standard Atmosphere vs. Altitude
Properties of the US standard atmosphere ranging -5000 to 250000 ft altitude. -
Unit Converter with commonly used Units
Common converting units for Acceleration, Area, Density, Energy, Energy per unit mass, Force, Heat flow rate, Heat flux, Heat generation per unit volume and many more.