Surface Tension
Surface tension of liquids like water, mercury, oils and more.
Surface tension is caused by the inward attraction of molecules at a boundary.
Surface tension is the energy required to stretch a unit change of surface area - and the surface tension will form a drop of liquid to a sphere since the sphere offers the smallest area for a definite volume.

Surface tension can be defined as
σ = Fs / l (1)
where
σ = surface tension (N/m)
Fs = stretching force (N)
l = unit length (m)
Alternative Units
Alternatively, surface tension is typically measured in dynes/cm, which is
- the force in dynes required to break a film of length 1 cm
or as surface energy J/m2 or alternatively ergs per square centimeter.
- 1 dynes/cm (dyn/cm) = 0.001 N/m = 0.0000685 lbf/ft = 0.571×10-5 lbf/in = 0.0022 poundal/ft = 0.00018 poundal/in = 1.0 mN/m = 0.001 J/m2 = 1.0 erg/cm2 = 0.00010197 kgf/m
Common Imperial units used are lb/ft and lb/in.
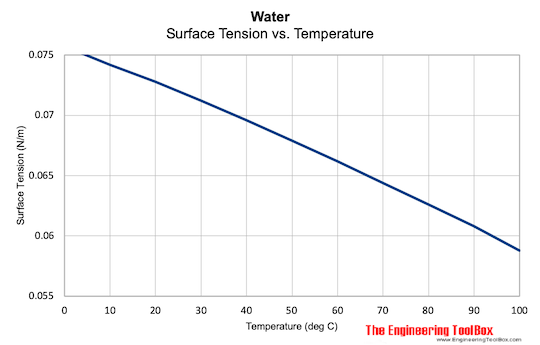
Surface Tension of Water
Surface tension of water at some temperatures:
| Temperature (oC) | Surface Tension - σ - (N/m) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0757 |
| 10 | 0.0742 |
| 20 | 0.0728 |
| 30 | 0.0712 |
| 40 | 0.0696 |
| 50 | 0.0679 |
| 60 | 0.0662 |
| 70 | 0.0644 |
| 80 | 0.0626 |
| 90 | 0.0608 |
| 100 | 0.0588 |
Surface Tension Common Fluids
Surface tension of fluids at 25 oC (77 oF).
| Fluid | Surface Tension (N/m) |
|---|---|
| Acetaldehyde | 0.021 |
| Acetic acid, Ethanoic acid | 0.027 |
| Acetic anhydride, Acetyl acetat | 0.032 |
| Acetone, 2-Propanone | 0.024 |
| Acetonitrile, Methyl cyanide | 0.287 |
| Allyl alcohol | 0.025 |
| Ammonia, R-717 | 0.021 |
| Aniline, Benzenamine | 0.042 |
| Anisole, Methoxybenzene | 0.035 |
| Benzene, Annulene | 0.028 |
| Benzonitrile, Phenyl cyanide | 0.039 |
| Benzylamine | 0.039 |
| Bromine | 0.041 |
| Bromobenzene | 0.035 |
| Bromoethane | 0.024 |
| n-Butane | 0.023 |
| 1-Butanol, Butyl alcohol | 0.025 |
| Butyl acetat | 0.025 |
| Butylamine | 0.023 |
| Diethyl ether | 0.017 |
| Carbon dioxide | 0.00056 |
| Carbon disulfide | 0.032 |
| Carbon tetrachloride | 0.027 |
| Clorobenzene, Phenyl chloride | 0.033 |
| Chlorodifluoromethane, HCFC-22 | 0.008 |
| Chloroform | 0.0271 |
| 1-Chlorohexane, Hexyl chloride | 0.026 |
| 1-Chloropentane | 0.024 |
| p-Cresol | 0.035 |
| Cyclohexane | 0.024 |
| Cyclohexanol | 0.033 |
| Cyclohexene | 0.026 |
| Cyclopentane | 0.022 |
| Decane | 0.024 |
| Dibutylamine | 0.024 |
| Dichlorodifluoromethane, CFC-12 | 0.0086 |
| Diethylene glycol | 0.045 |
| Diethyl ether, Ethyl ether | 0.017 |
| Diethyl sulfide, Ethyl sulfide | 0.025 |
| Ethane | 0.00048 |
| Ethanol, Ethyl Alcohol, Pure Alcohol, Grain Alcohol, Drinking Alcohol | 0.022 |
| Ethanolamine, glycinol | 0.048 |
| Ethyl acetate | 0.024 |
| Ethylamine, Ethanamine | 0.019 |
| Ethylbenzene, Phenylethane | 0.029 |
| Ethyl benzoate | 0.035 |
| Ethyl bromide | 0.025 |
| Ethyl mercaptan | 0.024 |
| Ethylene glycol | 0.0477 |
| Formamide | 0.057 |
| Formixc acis, Methanoic acid | 0.037 |
| Furfural | 0.043 |
| n-Heptane | 0.020 |
| Heptanoic acid, Enanthic acid | 0.028 |
| Hexadekane, Cetane | 0.027 |
| n-Hexane | 0.018 |
| Hexanenitrile, Capronitrile | 0.027 |
| 1-Hexanol, Caproyl alcohol | 0.026 |
| 1-Hexene | 0.018 |
| Hydrazine | 0.066 |
| Glycerol | 0.064 |
| Isobenzene, Phenyl iodide | 0.039 |
| Isobutane, 2-Methylpropane | 0.010 |
| Isobutyl acetat. 2-Methylpropyl acetat | 0.023 |
| Isobutyric acid | 0.025 |
| Isopropanol, 2-propanol, Isopropyl Alcohol, Rubbing Alcohol, Sec-propyl Alcohol, s-Propanol | 0.022 |
| Mercury, Quicksilver | 0.485 |
| Methanol, Methyl alcohol | 0.022 |
| Methyl acetat | 0.025 |
| Methyl formate | 0.025 |
| Nitrobenzene (50 oC) | 0.041 |
| Nitromethane, Nitrocarbol | 0.036 |
| Nonane | 0.022 |
| Octane | 0.021 |
| Pentane | 0.015 |
| Pentyl acetat | 0.025 |
| Propane, LPG | 0.007 |
| 1-Propanol, Propyl alcohol | 0.023 |
| n-Propyl alcohol | 0.024 |
| n-Propyl benzene | 0.030 |
| Pyridine | 0.037 |
| Trichloromethane, Chloroform | 0.023 |
| Toluene, Methylbenzene | 0.028 |
| Trifluormethane, Fluoroform | 0.00003 |
| Undecane, Hendecane | 0.025 |
| Water at 20 oC | 0.072 |
| Water, soapy at 20 oC | 0.0250 - 0.0450 |
| Water-d2, Heavy Water | 0.071 |
| Xenon (10 oC) | 0.00044 |
| o-Xylene | 0.029 |
| m-Xylene | 0.028 |
| p-Xylene | 0.028 |
Surface Active Agents
Soaps, detergents or surfactants - also called surface-active agents - added to to water even in small substances decreases the surface tension of water to a considerable extent. Due to decreased surface tension water with soap can remove oil or grease where clean water can not.