Gases Solved in Water - Diffusion Coefficients
Diffusion flux [kg/m2s] tells how fast a substanse solved in another substance flows due to concentration gradients. Diffusion constants [m2/s] for several gases in water.
Fick's first law states that a substance will flow from region with high concentration to a region of low concentration . Fick's law can be expressed as
J = -D dφ/dx (1)
where
J = diffusion flux - the amount of substance that flows through an unit area per unit time (mass or mol /(m2s))
D = diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
dφ = change in concentration of substance (mass or mol/m3)
dx = change in length (m)
For simple one-dimensional transport, the diffusion coefficient describes the time–rate of change of concentration . The diffusion coefficient varies from substance to substance and with temperature.
See Water and Heavy Water - thermodynamic properties.
See also Water Boiling points at high pressure, Boiling points at vacuum pressure, Density, specific weight and thermal expansion coefficient, Dynamic and kinematic viscosity, Enthalpy and entropy, Heat of vaporization, Ionization Constant, pKw , of normal and heavy water, Melting points at high pressure, Saturation pressure, Specific gravity, Specific heat (heat capacity) and Specific volume for online calculatores, and similar figures and tables as shown below, as well as Air - Diffusion Coefficients of Gases in Excess of Air
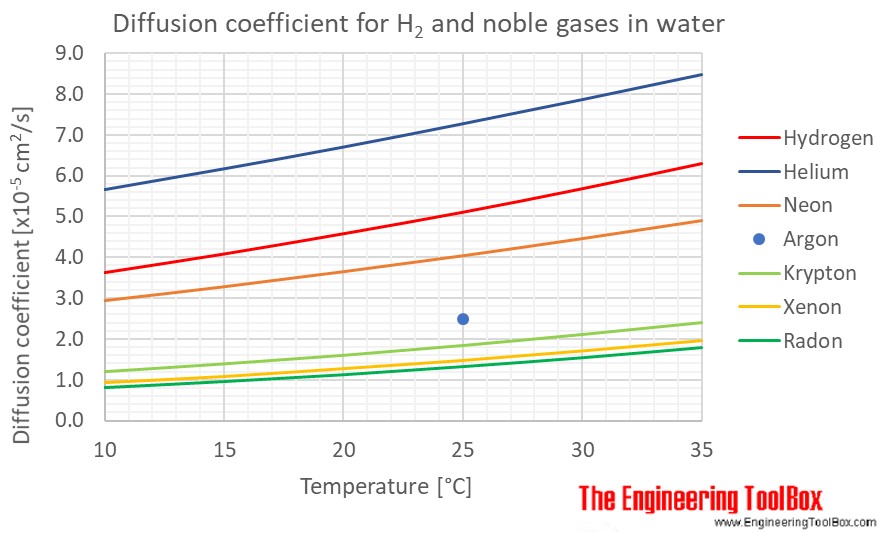
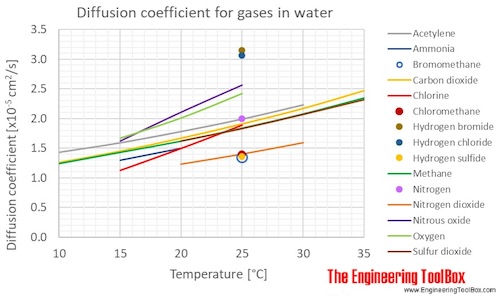
Diffusion coefficients for some common gases in water:
(Gas–liquid diffusion coefficients are difficult to measure, and since the values below are from different sources and different measuring methods, there is some uncertainty about the values)
| Gas in water | Diffusion coefficient, D, (×10-5cm2/s ) at atmospheric pressure and given temperatures | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 °C | 15 °C | 20 °C | 25 °C | 30 °C | 35 °C | ||
| Name | Formula | 50 °F | 59 °F | 68 °F | 77 °F | 86 °F | 95 °F |
| Acetylene | C2H2 | 1.43 | 1.59 | 1.78 | 1.99 | 2.23 | |
| Ammonia | NH3 | 1.30 | 1.50 | ||||
| Argon | Ar | 2.50 | |||||
| Bromomethane | CH3Br | 1.35 | |||||
| Carbon dioxide | CO2 | 1.26 | 1.45 | 1.67 | 1.91 | 2.17 | 2.47 |
| Chlorine | Cl2 | 1.13 | 1.50 | 1.89 | |||
| Chloromethane | CH3Cl | 1.40 | |||||
| Dichlorofluorumethane | CHCl2F | 1.80 | |||||
| Helium | He | 5.67 | 6.18 | 6.71 | 7.28 | 7.87 | 8.48 |
| Hydrogen | H2 | 3.62 | 4.08 | 4.58 | 5.11 | 5.69 | 6.31 |
| Hydrogen bromide | HBr | 3.15 | |||||
| Hydrogen chloride | HCl | 3.07 | |||||
| Hydrogen sulfide | H2S | 1.36 | |||||
| Krypton | Kr | 1.20 | 1.39 | 1.60 | 1.84 | 2.11 | 2.40 |
| Methane | CH4 | 1.24 | 1.43 | 1.62 | 1.84 | 2.08 | 2.35 |
| Neon | Ne | 2.93 | 3.27 | 3.64 | 4.03 | 4.45 | 4.89 |
| Nitrogen | N2 | 2.00 | |||||
| Nitrogen dioxide | NO2 | 1.23 | 1.40 | 1.59 | |||
| Nitrous oxide | N2O | 1.62 | 2.11 | 2.57 | |||
| Oxygen | O2 | 1.67 | 2.01 | 2.42 | |||
| Radon | Rn | 0.81 | 0.96 | 1.13 | 1.33 | 1.55 | 1.80 |
| Sulfur dioxide | SO2 | 1.62 | 1.83 | 2.07 | 2.32 | ||
| Xenon | Xe | 0.93 | 1.08 | 1.27 | 1.47 | 1.70 | 1.95 |



