Water - Dynamic (Absolute) and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Free online calculator - figures and tables with viscosity of water at temperatures ranging 0 to 360°C (32 to 675°F) - Imperial and SI Units.
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to gradual deformation by shear stress or tensile stress .
For further definitions, go to Absolute (dynamic) and kinematic viscosity . Absolute or dynamic viscosity is used to calculate Reynold's Number to determine if a fluid flow is laminar, transient or turbulent.
Online Water Viscosity Calculator
The calculator below can be used to calculate the liquid water dynamic or kinematic viscosity at given temperatures.
The output dynamic viscosity is given as cP, mPa*s, Pa*s, N*s/m2,lbf *s/ft2and lbm /(ft*h),
while the kinematic viscosity is given as cSt, m2/s, and ft2/s
Note! Temperature must be within the ranges 0-370 °C, 32-700 °F, 273-645 K and 492-1160 °R to get valid values.
See Water and Heavy Water - thermodynamic properties.
See also other properties of Water at varying temperature and pressure : Boiling points at high pressure , Boiling points at vacuum pressure , Density and specific weight , Enthalpy and entropy , Heat of vaporization , Ionization Constant, pK w , of normal and heavy water , Melting points at high pressure , Prandtl number , Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions , Saturation pressure , Specific gravity , Specific heat (heat capacity) , Specific volume , Thermal conductivity , Thermal diffusivity and Vapour pressure at gas-liquid equilibrium .
See also dynamic and kinematic viscosity of air , ammonia , benzene , butane , carbon dioxide , ethane , ethanol , ethylene , methane , methanol , nitrogen , oxygen and propane
The figures and tables below shows how water viscosity changes with temperature (°C and °F) at water saturation pressure (which for practicle use, gives the same result as atmospheric pressure at temperatures < 100 °C (212°F)). One figure showing relative viscosity with variations in pressure and temperature is also included.
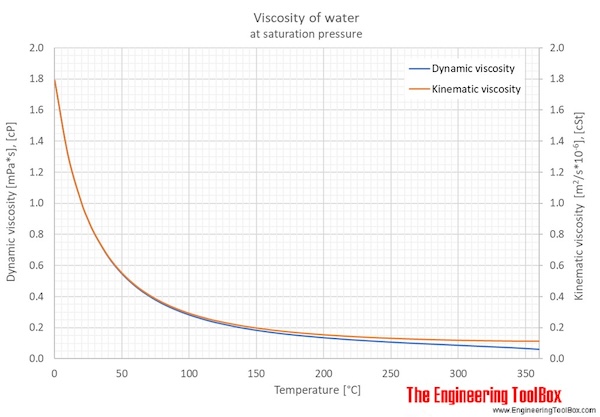
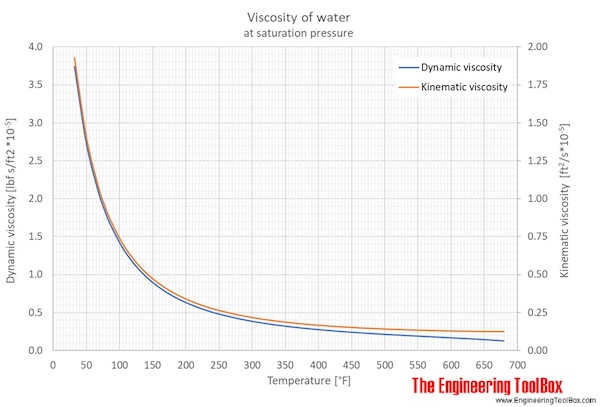
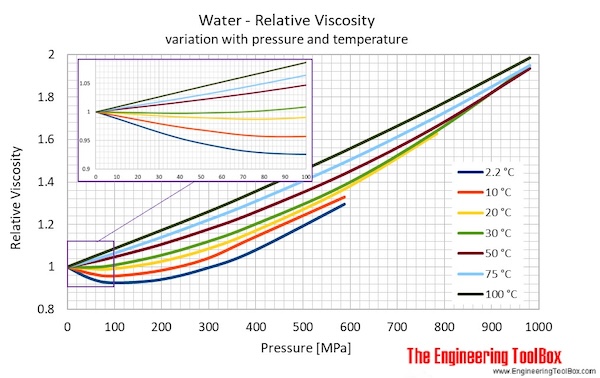
| Temperature | Pressure | Dynamic viscosity | Kinematic viscosity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [°C] | [MPa] | [Pa s], [N s/m2] | [cP], [mPa s] | [lbf s/ft2*10 -5 ] | [m2/s*10-6 ], [cSt]) |
| 0.01 | 0.000612 | 0.0017914 | 1.79140 | 3.7414 | 1.7918 |
| 10 | 0.0012 | 0.0013060 | 1.30600 | 2.7276 | 1.3065 |
| 20 | 0.0023 | 0.0010016 | 1.00160 | 2.0919 | 1.0035 |
| 25 | 0.0032 | 0.0008900 | 0.89004 | 1.8589 | 0.8927 |
| 30 | 0.0042 | 0.0007972 | 0.79722 | 1.6650 | 0.8007 |
| 40 | 0.0074 | 0.0006527 | 0.65272 | 1.3632 | 0.6579 |
| 50 | 0.0124 | 0.0005465 | 0.54650 | 1.1414 | 0.5531 |
| 60 | 0.0199 | 0.0004660 | 0.46602 | 0.9733 | 0.4740 |
| 70 | 0.0312 | 0.0004035 | 0.40353 | 0.8428 | 0.4127 |
| 80 | 0.0474 | 0.0003540 | 0.35404 | 0.7394 | 0.3643 |
| 90 | 0.0702 | 0.0003142 | 0.31417 | 0.6562 | 0.3255 |
| 100 | 0.101 | 0.0002816 | 0.28158 | 0.5881 | 0.2938 |
| 110 | 0.143 | 0.0002546 | 0.25461 | 0.5318 | 0.2677 |
| 120 | 0.199 | 0.0002320 | 0.23203 | 0.4846 | 0.2460 |
| 140 | 0.362 | 0.0001966 | 0.19664 | 0.4107 | 0.2123 |
| 160 | 0.618 | 0.0001704 | 0.17043 | 0.3559 | 0.1878 |
| 180 | 1.00 | 0.0001504 | 0.15038 | 0.3141 | 0.1695 |
| 200 | 1.55 | 0.0001346 | 0.13458 | 0.2811 | 0.1556 |
| 220 | 2.32 | 0.0001218 | 0.12177 | 0.2543 | 0.1449 |
| 240 | 3.35 | 0.0001111 | 0.11106 | 0.2320 | 0.1365 |
| 260 | 4.69 | 0.0001018 | 0.10181 | 0.2126 | 0.1299 |
| 280 | 6.42 | 0.0000936 | 0.09355 | 0.1954 | 0.1247 |
| 300 | 8.59 | 0.0000859 | 0.08586 | 0.1793 | 0.1206 |
| 320 | 11.3 | 0.0000783 | 0.07831 | 0.1636 | 0.1174 |
| 340 | 14.6 | 0.0000703 | 0.07033 | 0.1469 | 0.1152 |
| 360 | 18.7 | 0.0000603 | 0.06031 | 0.1260 | 0.1143 |
| Temperature | Pressure | Dynamic viscosity | Kinematic viscosity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [°F] | [psi] | [lbf s/ft2*10 -5 ] | [lbm /(ft h)] | [cP], [mPa s] | [ft2/s*10 -5 ] |
| 32.02 | 0.9506 | 3.7414 | 4.3336 | 1.7914 | 1.9287 |
| 34 | 0.0962 | 3.6047 | 4.1752 | 1.7259 | 1.8579 |
| 39.2 | 0.1180 | 3.2801 | 3.7992 | 1.5705 | 1.6906 |
| 40 | 0.1217 | 3.2340 | 3.7458 | 1.5484 | 1.6668 |
| 50 | 0.1781 | 2.7276 | 3.1593 | 1.3060 | 1.4063 |
| 60 | 0.2563 | 2.3405 | 2.7109 | 1.1206 | 1.2075 |
| 70 | 0.3634 | 2.0337 | 2.3556 | 0.9737 | 1.0503 |
| 80 | 0.5076 | 1.7888 | 2.0719 | 0.8565 | 0.9250 |
| 90 | 0.6992 | 1.5896 | 1.8411 | 0.7611 | 0.8234 |
| 100 | 0.9506 | 1.4243 | 1.6497 | 0.6820 | 0.7392 |
| 110 | 1.277 | 1.2847 | 1.4880 | 0.6151 | 0.6682 |
| 120 | 1.695 | 1.1652 | 1.3496 | 0.5579 | 0.6075 |
| 130 | 2.226 | 1.0620 | 1.2300 | 0.5085 | 0.5551 |
| 140 | 2.893 | 0.9733 | 1.1273 | 0.4660 | 0.5102 |
| 150 | 3.723 | 0.8950 | 1.0366 | 0.4285 | 0.4706 |
| 160 | 4.747 | 0.8279 | 0.9589 | 0.3964 | 0.4367 |
| 170 | 6.000 | 0.7698 | 0.8916 | 0.3686 | 0.4074 |
| 180 | 7.520 | 0.7192 | 0.8330 | 0.3444 | 0.3820 |
| 190 | 9.349 | 0.6745 | 0.7813 | 0.3230 | 0.3596 |
| 200 | 11.537 | 0.6300 | 0.7297 | 0.3016 | 0.3371 |
| 212 | 14.710 | 0.5881 | 0.6812 | 0.2816 | 0.3163 |
| 220 | 17.203 | 0.5619 | 0.6508 | 0.2690 | 0.3032 |
| 240 | 25.001 | 0.5050 | 0.5850 | 0.2418 | 0.2750 |
| 260 | 35.263 | 0.4575 | 0.5299 | 0.2191 | 0.2515 |
| 280 | 49.286 | 0.4176 | 0.4837 | 0.2000 | 0.2320 |
| 300 | 67.264 | 0.3840 | 0.4448 | 0.1839 | 0.2157 |
| 350 | 134.73 | 0.3202 | 0.3708 | 0.1533 | 0.1853 |
| 400 | 247.01 | 0.2750 | 0.3185 | 0.1317 | 0.1648 |
| 450 | 422.32 | 0.2404 | 0.2785 | 0.1151 | 0.1504 |
| 500 | 680.56 | 0.2126 | 0.2463 | 0.1018 | 0.1398 |
| 550 | 1045.0 | 0.1888 | 0.2187 | 0.0904 | 0.1322 |
| 600 | 1542.1 | 0.1673 | 0.1937 | 0.0801 | 0.1270 |
| 625 | 1851.2 | 0.1562 | 0.1809 | 0.0748 | 0.1252 |
| 650 | 2207.8 | 0.1438 | 0.1666 | 0.0689 | 0.1239 |
| 675 | 2618.7 | 0.1292 | 0.1496 | 0.0619 | 0.1230 |
Unit conversion
Viscosity Dynamic, Absolute
centipoise [cP], gram/(centimetre second) [g/(cm s)] = poise [P], kilogram/metre second [kg/m s]=newton second/square metre [N s/m2]= pascal second [Pa s], pound/(foot hour) [lb/(ft h)], pound/(foot second) [lb/(ft s)], reyn [reyn]
- 1 cP = 0.001 Pa s = 0.01 P = = 0.01 g/(cm sec) = 6.72197x10-4 lb/(ft s) = 2.4191 lb/(ft h)
- 1 lb/(ft h) = 0.00027778 lb/(ft s) = 0.00041338 Pa s = 0.0041338 P = 0.41338 cP
- 1 lb/(ft s) = 3600 lb/(ft h) = 1.48816 Pa s = 14.8816 P = 1488.16 cP
- 1 kg/(m s ) = 1 (N s)/m2= 1 Pa s = 10 P = 1000 cP = 0.672197 lb/(ft s) = 2419.09 lb/(ft h)
- 1 (N s)/m2= 1 kg/(m s ) = 1 Pa s = 10 P = 1000 cP = 0.672197 lb/(ft s) = 2419.09 lb/(ft h)
- 1 P = 1 g/(cm s) = 0.1 Pa s = 100 cP = 0.067197 lb/(ft s) = 241.909 lb/(ft h)
- 1 Pa s = 1 kg/(m s) = 1 (N s)/m2= 10 P = 1000 cP = 0.672197 lb/(ft s) = 2419.08 lb/(ft h) = 0.00014504 reyn
- 1 reyn = 6894.76 Pa s
See also Absolute or Dynamic Viscosity Unit Converter
Viscosity Kinematic
centistoke [cSt] = square millimetre/second [mm2/s], square foot/hour [ft2/h], square foot/second [ft2/s], square inch/second [in2/s], square metre/hour [m2/h], square metre/second [m2/s], stoke [St] = square centimetre/second [cm2/s]
- 1 cm2/s = 1 St = 100 mm2/s = 100 cSt = 1x10-4 m2/s = 0.36 m2/h = 1.07639x10-3 ft2/s = 3.875008 ft2/h = 0.1550003 in2/s
- 1 cSt = 1 mm2/s = 0.01 St = 1x10-6 m2/s = 0.0036 m2/h = 1.07639x10 -5 ft2/s = 0.03875008 ft2/h = 0.001550003 in2/s
- 1 ft2/h = 2.7778x10-4 ft2/s = 0.04 in2/s = 2.58064x10 -5 m2/s = 0.09290304 m2/h = 25.8064 cS = 0.258064 St
- 1 ft2/s = 3600 ft2/h = 144 in2/s = 0.09290304 m2/s = 334.451 m2/h = 92903.04 cSt = 929.0304 St
- 1 in2/s = 0.0069444 ft2/s = 25 ft2/h = 0.00064516 m2/s = 2.322576 m2/h = 645.16 cSt = 6.4516 St
- 1 m2/h = 1/3600 m2/s = 2.7778x10-4 m2/s = 2.7778 cm2/s = 277.78 mm2/s = 277.78 cSt = 2.7778 St = 0.00298998 ft2/s = 10.7639 ft2/h = 0.430556 in2/s
- 1 m2/s = 3600 m2/h = 1x104 cm2/s = 1x104 St = 1x106 mm2/s = 1x106 cSt = 10.7639 ft2/s = 38750.08 ft2/h = 1550003 in2/s
- 1 mm2/s = 1 cSt = 1x10-6 m2/s = 0.0036 m2/h = 0.01 cm2/s = 0.01 St = 1.07639x10 -5 ft2/s = 0.03875008 ft2/h = 0.001550003 in2/s
- 1 St = 1 cm2/s = 100 cSt = 100 mm2/s = 1x10-4 m2/s = 0.36 m2/h = 1.076x10-3 ft2/s = 3.875008 ft2/h = 0.1550003 in2/s
See also Kinematic Viscosity Unit Converter
Related Mobile Apps from The Engineering ToolBox 
- free apps for offline use on mobile devices.
Related Topics
-
Fluid Mechanics
The study of fluids - liquids and gases. Involving velocity, pressure, density and temperature as functions of space and time. -
Material Properties
Properties of gases, fluids and solids. Densities, specific heats, viscosities and more. -
Steam and Condensate
Design of steam & condensate systems with properties, capacities, sizing of pipe lines, system configuration and more. -
Viscosities
Viscosities of products and chemical species at varying conditions. -
Water Systems
Design of hot and cold water service and utility systems with properties, capacities, sizing of pipe lines and more.
Related Documents
-
Absolute or Dynamic Viscosity Online Converter
Convert between dynamic or absolute viscosity units - Poiseuille, Poise, centPoise and more. -
Benzene - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and table showing dynamic and kinematic viscosity of benzene, C6H6, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units. -
Butane - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculators, figures and tables with dynamic and kinematic viscosity of liquid and gaseous butane, C4H10, at varying temperarure and pressure, SI and Imperial units. -
Dynamic (Absolute) Viscosity - Converting Chart
Convert dynamic viscosity values between units like Poiseuille - Poise - centiPoise and more. -
Ethanol - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables showing dynamic and kinematic viscosity of ethanol, C2H5OH, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units. -
Ethylene - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables showing dynamic and kinematic viscosity of ethylene, C2H4, also called ethene or acetene, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units. -
Gases Solved in Water - Diffusion Coefficients
Diffusion flux [kg/m2s] tells how fast a substanse solved in another substance flows due to concentration gradients. Diffusion constants [m2/s] for several gases in water. -
Heavy Water - Thermophysical Properties
Thermodynamic properties of heavy water (D2O) like density, melting temperature, boiling temperature, latent heat of fusion, latent heat of evaporation, critical temperature and more. -
Ice and Water - Melting Points vs. Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables with melting points of ice to water at pressures ranging from 0 to 29000 psia (0 to 2000 bara). Temperature given as °C, °F, K and °R. -
Kinematic Viscosity - Online Converter
Convert between kinematic viscosity units like centistokes, poise, lentor and more. -
Kinematic Viscosity - Unit Converter
Convert between Centistokes, Saybolt and Redwood seconds. -
Methane - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables showing dynamic and kinematic viscosity of methane, CH4, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units. -
Methanol - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables showing dynamic and kinematic viscosity of liquid methanol,CH3OH, at varying temperature - Imperial and SI Units. -
Oxygen - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables showing dynamic and kinematic viscosity of oxygen, O2, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units. -
Propane - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculators, figures and tables showing dynamic and kinematic viscosity of liquid and gaseous propane at varying temperarure and pressure, SI and Imperial units. -
Sewage Sludge - Viscosities
Viscosity of sewage sludge vs. content of solids. -
Steel Pipes - Viscous Liquid Flow and Friction Loss
Friction loss in schedule 40 steel pipe with viscous liquids - viscosities ranging from water to oil. -
Sugar Water Solutions - Viscosities
Dynamic viscosities of sucrose water solutions vs. temperature. -
Viscosity - Absolute (Dynamic) vs. Kinematic
Vicosity is a fluid's resistance to flow and can be valued as dynamic (absolute) or kinematic. -
Viscosity Converting Chart
Convert between viscosity units like Centiposes, milliPascal, CentiStokes and SSU. -
Viscous Liquids - Friction Loss vs. Viscosity and Flow
Friction loss in steel pipes for fluids with viscosities ranging 32 - 80000 SSU. -
Water - Absolute (Dynamic) Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Absolute viscosity for water in centipoises for temperatures between 32 - 200oF. -
Water - Boiling Points at Vacuum Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables giving the boiling temperatures of water in varying vacuum, SI and Imperial units. -
Water - Density, Specific Weight and Thermal Expansion Coefficients
Definitions, online calculator and figures and tables with water properties like density, specific weight and thermal expansion coefficient of liquid water at temperatures ranging 0 to 360°C (32 to 680°F). -
Water - Enthalpy and Entropy vs. Temperature
Figures and tables showing the enthalpy and entropy of liquid water as function of temperature - SI and Imperial Units. -
Water - Heat of Vaporization vs. Temperature
Online calculator, figures and tables showing heat of vaporization of water, at temperatures from 0 - 370 °C (32 - 700 °F) - SI and Imperial units. -
Water - Ionization Constant, pKw, of Normal and Heavy Water
Ionization constant (= dissociation constant = self-ionization constant = ion product = autoprotolysis constant ) of water and heavy water, given as function of temperature (°C and °F) in figures and tables. -
Water - Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions
Figures and tables showing how the properties of water changes along the boiling/condensation curve (vapor pressure, density, viscosity, thermal conductivity, specific heat, Prandtl number, thermal diffusivity, entropy and enthalpy). -
Water - Saturation Pressure vs. Temperature
Online calculator, figures and tables with water saturation (vapor) pressure at temperatures ranging 0 to 370 °C (32 to 700°F) - in Imperial and SI Units. -
Water - Specific Heat vs. Temperature
Online calculator, figures and tables showing specific heat of liquid water at constant volume or constant pressure at temperatures from 0 to 360 °C (32-700 °F) - SI and Imperial units. -
Water - Specific Volume vs. Temperature
Online calculator, figures and tables showing Specific Volume of water at temperatures ranging from 0-370 °C and 32 - 700 °F - Imperial and IS Units. -
Water - Thermal Conductivity vs. Temperature
Figures and tables showing thermal conductivity of water (liquid and gas phase) with varying temperature and pressure, SI and Imperial units. -
Water - Thermal Diffusivity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Figures and tables with thermal diffusivity of liquids and gaseous water at varying temperarures and pressures - SI and Imperial units. -
Water vs. Steam - Critical and Triple Points
Critical point is where vapor and liquid are indistinguishable and triple point is where ice, water and vapor coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.




