Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids - Physical Data
Molweight, melting and boiling point, density, pKa-values, as well as number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in molecules are given for 150 different alcohols and acids.
Below the table, examples of molecule structures for the different classes of alcohols and acids are given, together with a definition of the different classes of organic compounds.
For figures showing trends for the different classes with increasing chain lengths, as well as molecular structures, see also
- Density of hydrocarbons and linear alcohols and acids
- Boiling points of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids
- Melting points of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids
- pKa of phenols, alcohols and carboxylic acids
For more tabulated values, see Physical data for hydrocarbons, Physical data for organic sulfur compounds and Physical data for organic nitrogen compounds
For full table - rotate the screen!
| Class of compound | IUPAC name | Common name | #C | #H | #O | Molweight g/mol | Melting point °C | Boiling point °C | Density @20°C* g/ml | pKa(1) | pKa(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-alkanol | Methanol | Methyl alcohol | 1 | 4 | 1 | 32.04 | -98 | 65 | 0.791 | 15.5 | |
| 1-alkanol | Ethanol | Ethyl alcohol | 2 | 6 | 1 | 46.07 | -114 | 78 | 0.789 | 15.5 | |
| 1-alkanol | 1-Propanol | Propyl alcohol | 3 | 8 | 1 | 60.09 | -124 | 97 | 0.804 | 16.1 | |
| 1-alkanol | 1-Butanol | Butyl alcohol | 4 | 10 | 1 | 74.12 | -89 | 118 | 0.810 | 16.1 | |
| 1-alkanol | 1-Pentanol | Amyl alcohol | 5 | 12 | 1 | 88.15 | -78 | 138 | 0.814 | ||
| 1-alkanol | 1-Hexanol | Caproyl alcohol | 6 | 14 | 1 | 102.17 | -46 | 157 | 0.814 | ||
| 1-alkanol | 1-Heptanol | Heptyl alcohol | 7 | 16 | 1 | 116.198 | -33 | 178 | 0.822 | ||
| 1-alkanol | 1-Octanol | Capryl alcohol | 8 | 18 | 1 | 130.22 | -15 | 195 | 0.829 | ||
| 1-alkanol | 1-Nonanol | Nonyl alcohol | 9 | 20 | 1 | 144.25 | -5 | 214 | 0.828 | ||
| 1-alkanol | 1-Decanol | Capric alcohol | 10 | 22 | 1 | 158.276 | 7 | 229 | 0.830 | ||
| 1-alkanol | 1-Undecanol | Undecyl alcohol | 11 | 24 | 1 | 172.30 | 1 | 246 | 0.830 | ||
| 1-alkanol | 1-Dodecanol | Lauryl alcohol | 12 | 26 | 1 | 186.33 | 24 | 264 | 0.833 | ||
| 1-alkanol | 1-Tridecanol | 13 | 28 | 1 | 200.35 | 31 | 287 | 0.82231 | |||
| 1-alkanol | 1-Tetradecanol | Tetra decylalcohol | 14 | 30 | 1 | 214.38 | 38 | 296 | 0.82438 | ||
| 1-alkanol | 1-Pentadecanol | 15 | 32 | 1 | 228.41 | 44 | 318 | 0.83525 | |||
| 1-alkanol | 1-Docosanol | 22 | 46 | 1 | 326.59 | 71 | |||||
| 2-alkanol | 2-Propanol | Isopropyl alcohol, isopropanol | 3 | 8 | 1 | 60.09 | -88 | 82 | 0.785 | 17.2 | |
| 2-alkanol | 2-Butanol | sec-Butyl alcohol | 4 | 10 | 1 | 74.12 | -88 | 99 | 0.806 | 17.6 | |
| 2-alkanol | 2-Pentanol | sec-Amyl alcohol | 5 | 12 | 1 | 88.15 | -73 | 119 | 0.809 | 17.8 | |
| 2-alkanol | 2-Hexanol | 6 | 14 | 1 | 102.17 | -23 | 138 | 0.816 | |||
| 2-alkanol | 2-Heptanol | 7 | 16 | 1 | 116.20 | 159 | 0.817 | ||||
| 2-alkanol | 2-Octanol | sec-Caprylic alcohol | 8 | 18 | 1 | 130.22 | -31.6 | 179 | 0.819 | ||
| 2-alkanol | 2-Nonanol | 9 | 20 | 1 | 144.25 | -35 | 194 | 0.83 | |||
| 2-alkanol | 2-Decanol | 10 | 22 | 1 | 158.28 | -5 | 212 | 0.825 | |||
| 2-alkanol | 2-Undecanol | 11 | 24 | 1 | 172.30 | 0 | 231 | 0.825 | |||
| 2-alkanol | 2-Dodecanol | 12 | 26 | 1 | 186.33 | 19 | 249 | 0.829 | |||
| 3-alkanol | 3-Pentanol | Diethyl carbinol | 5 | 12 | 1 | 88.15 | -73 | 115 | 0.820 | 18.2 | |
| 3-alkanol | 3-Hexanol | 6 | 14 | 1 | 102.17 | -57 | 143 | 0.818 | |||
| 3-alkanol | 3-Heptanol | Ethylbutylcarbinol | 7 | 16 | 1 | 116.20 | -70 | 163 | 0.823 | ||
| 3-alkanol | 3-Octanol | 8 | 18 | 1 | 130.22 | -45 | 175 | 0.826 | |||
| 3-alkanol | 3-Nonanol | 9 | 20 | 1 | 144.25 | 22 | 193 | 0.825 | |||
| 3-alkanol | 3-Decanol | 10 | 22 | 1 | 158.28 | -5 | 212 | 0.827 | |||
| 3-alkanol | 3-Undecanol | 11 | 24 | 1 | 172.30 | 230 | 0.088 | ||||
| 3-alkanol | 3-Dodecanol | 12 | 26 | 1 | 186.33 | 25 | 246 | 0.829 | |||
| 4-alkanol | 4-Heptanol | Dipropylcarbinol | 7 | 16 | 1 | 116.12 | -41 | 161 | 0.818 | ||
| 4-alkanol | 4-Octanol | 8 | 18 | 1 | 130.22 | -41 | 176 | 0.819 | |||
| 4-alkanol | 4-Nonanol | 9 | 20 | 1 | 144.25 | -7 | 193 | 0.828 | |||
| 4-alkanol | 4-Decanol | 10 | 22 | 1 | 158.28 | -11 | 214 | 0.826 | |||
| Branched alcohol | 2-Methyl-2-propanol | 4 | 10 | 1 | 74.12 | 25.7 | 83 | 0.789 | |||
| Branched alcohol | 2-Methyl-1-propanol | Isobutanol, isobutyl alcohol | 4 | 10 | 1 | 74.12 | 108 | 0.802 | |||
| Branched alcohol | 2-Methyl-2-butanol | 5 | 12 | 1 | 88.15 | -8 | 102 | 0.810 | |||
| Branched alcohol | 3-Methyl-2-butanol | 5 | 12 | 1 | 88.15 | 114 | 0.818 | ||||
| Branched alcohol | 2-Methyl-1-butanol | 5 | 12 | 1 | 88.15 | 129 | 0.818 | ||||
| Branched alcohol | 3-Methyl-1-butanol | 5 | 12 | 1 | 88.15 | -117 | 131 | 0.810 | |||
| Cycloalcohol | Cyclohexanol | 6 | 12 | 1 | 100.16 | 25 | 161 | 0.962 | |||
| Phenols | Phenol | Hydroxybenzene | 6 | 6 | 1 | 94.11 | 41 | 181 | 1.05545 | 9.98 | |
| Phenols | 2-Methylphenol | o-Cresol, 2-methylhydroxybenzene | 7 | 8 | 1 | 108.13 | 31 | 191 | 1.03335 | 10.29 | |
| Phenols | 4-Methylphenol | p-Cresol, 4-methylhydroxybenzene | 7 | 8 | 1 | 108.13 | 35 | 202 | 1.01940 | 10.26 | |
| Phenols | 3-Methylphenol | m-Cresol, 3-methylhydroxybenzene | 7 | 8 | 1 | 108.13 | 12 | 202 | 1.034 | 10.09 | |
| Phenols | 2-Methoxyphenol | Guaiacol | 7 | 8 | 2 | 124.13 | 28 | 204 | 1.12921 | 9.98 | |
| Phenols | 3-Methoxyphenol | Resorcinol, monomethyl ether | 7 | 8 | 2 | 124.13 | -18 | 244 | 1.13125 | 9.65 | |
| Phenols | 4-Methoxyphenol | 7 | 8 | 2 | 124.13 | 55 | 253 | 10.21 | |||
| Phenols | 2-Ethylphenol | 2-Ethylhydroxybenzene | 8 | 10 | 1 | 122.16 | -3 | 205 | 1.017 | 10.2 | |
| Phenols | 4-Ethylphenol | 4-Ethylhydroxybenzene | 8 | 10 | 1 | 122.16 | 45 | 218 | 1.05025 | 10 | |
| Phenols | 3-Ethylphenol | 3- Ethylhydroxybenzene | 8 | 10 | 1 | 122.16 | -4 | 218 | 1.028 | 9.9 | |
| Phenols | 2-Propylphenol | o-Propylphenol | 9 | 12 | 1 | 136.19 | 7 | 223 | 1.015 | 10.47 | |
| Phenols | 4-Propylphenol | p-Propylphenol | 9 | 12 | 1 | 136.19 | 22 | 232 | 1.009 | 10.34 | |
| Diol | 1,2-Ethanediol | Ethylene glycol | 2 | 6 | 2 | 62.07 | -14 | 198 | 1.114 | ||
| Diol | 1,2-Benzenediol | Catechol, pyrocatechol | 6 | 6 | 2 | 110.11 | 102 | 245 | 1.34425 | 9.45 | 12.8 |
| Diol | 1,3-Benzenediol | Resorcinol | 6 | 6 | 2 | 110.11 | 110 | 277 | 1.278 | 9.2 | 11.3 |
| Diol | 1,4-Benzenediol | Hydroquinone,,4-Dihydroxybenzene | 6 | 6 | 2 | 110.11 | 172 | 285 | 10.9 | 11.4 | |
| Diol | 4-Methyl-1,2-benzenediol | 4-Methylcatechol | 7 | 8 | 2 | 124.13 | 68 | 251 | 1.12925 | 9.55 | |
| Triol | 1,3,5-Benzenetriol | Phloroglucinol, 1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene |
6 | 6 | 3 | 126.11 | 216 | sub | 1.4625 | 8.45 | |
| Alkanoic acid | Formic acid | Methanoic acid | 1 | 2 | 2 | 46.03 | 8 | 101 | 1.22 | 3.74 | |
| Alkanoic acid | Acetic acid | Ethanoic acid | 2 | 4 | 2 | 60.05 | 17 | 118 | 1.048 | 4.76 | |
| Alkanoic acid | Propanoic acid | Propionic acid | 3 | 6 | 2 | 74.08 | -21 | 142 | 0.991 | 4.87 | |
| Alkanoic acid | Butanoic acid | Butyric acid | 4 | 8 | 2 | 88.10 | -5 | 164 | 0.956 | 4.82 | |
| Alkanoic acid | Pentanoic acid | Valeric acid | 5 | 10 | 2 | 102.13 | -34 | 186 | 0.937 | 4.86 | |
| Alkanoic acid | Hexanoic acid | Caproic acid | 6 | 12 | 2 | 116.16 | -4 | 202 | 0.924 | 4.87 | |
| Alkanoic acid | Heptanoic acid | Enanthic acid | 7 | 14 | 2 | 130.18 | -7 | 222 | 0.916 | 4.89 | |
| Alkanoic acid | Octanoic acid | Caprylic acid | 8 | 16 | 2 | 144.21 | 17 | 240 | 0.911 | 4.89 | |
| Alkanoic acid | Nonanoic acid | Pelargonic acid | 9 | 18 | 2 | 158.23 | 12 | 256 | 0.905 | 4.96 | |
| Alkanoic acid | Dodecanoic acid | Lauric acid | 12 | 24 | 2 | 200.31 | 44 | 296 | 0.86850 | ||
| Alkanoic acid | Decanoic acid | Capric acid | 13 | 26 | 2 | 214.34 | 31 | 270 | 0.88640 | ||
| Alkanoic acid | Tridecanoic acid | Tridecylic acid | 14 | 28 | 2 | 228.36 | 42 | 308 | 0.84680 | ||
| Alkanoic acid | Undecanoic acid | 15 | 30 | 2 | 242.39 | 28.5 | 280 | 0.891 | |||
| Alkanoic acid | Tetradecanoic acid | Myristic acid | 16 | 32 | 2 | 256.42 | 54 | 350** | 0.86254 | ||
| Alkanoic acid | Pentacanoic acid | Pentadecylic acid | 17 | 34 | 2 | 270.44 | 52 | 360** | 0.84280 | ||
| Alkanoic acid | Hexadecanoic acid | Palmitic acid | 16 | 32 | 2 | 256.42 | 63 | 351 | 0.85362 | ||
| Alkanoic acid | Octadecanoic acid | Stearic acid | 18 | 36 | 2 | 284.48 | 69 | d361 | 0.941 | ||
| Alkanoic acid | Docosanoic acid | Behenic acid | 22 | 44 | 2 | 340.57 | 81 | >400** | 0.82290 | ||
| Branched alkanoic acid | 2-Methylpropanoic acid | Isobutyric acid | 4 | 8 | 2 | 88.104 | -46 | 155 | 0.945 | 4.84 | |
| Branched alkanoic acid | 2-Methylbutanoic acid | 5 | 10 | 2 | 102.13 | <-80 td=""> | 177 | 0.934 | 4.8 | ||
| Branched alkanoic acid | 3-Methylbutanoic acid | Isovaleric acid | 5 | 10 | 2 | 102.13 | -30 | 176 | 0.925 | 4.77 | |
| Branched alkanoic acid | 2,2-Dimethylpropanoic acid | Trimethylacetic acid | 5 | 10 | 2 | 102.13 | 35 | 164 | 0.90550 | 4.78 | |
| Branched alkanoic acid | 2-Methylpentanoic acid | 6 | 12 | 2 | 116.16 | 195 | 0.923 | ||||
| Branched alkanoic acid | 3-Methylpentanoic acid | 3-Methylvaleric acid | 6 | 12 | 2 | 116.16 | -42 | 197 | 0.926 | ||
| Branched alkanoic acid | 4-Methylpentanoic acid | 4-Methylvaleric acid, Isocaproic acid | 6 | 12 | 2 | 116.16 | -33 | 200 | 0.923 | 4.84 | |
| Branched alkanoic acid | 2-Methylhexanoic acid | 7 | 14 | 2 | 130.18 | 209 | 0.92 | ||||
| Branched alkanoic acid | 4-Methylhexanoic acid | 7 | 14 | 2 | 130.18 | 11010 | 0.921 | ||||
| Branched alkanoic acid | 2-Propylpentanoic acid | Valproic acid | 8 | 16 | 2 | 144.21 | 223 | 0.906 | 4.6 | ||
| Benzoic acids | Benzoic acid | Benzenecarboxylic acid | 7 | 6 | 2 | 122.12 | 122 | 249 | 1.26615 | 4.2 | |
| Benzoic acids | 2-Methyl-benzoic acid | o-Toluic acid | 8 | 8 | 2 | 136.14 | 107 | 258 | 1.062115 | 3.91 | |
| Benzoic acids | 3-Methyl-benzoic acid | m-Toluic acid | 8 | 8 | 2 | 136.14 | 111 | 1.054112 | 4.25 | ||
| Benzoic acids | 4-Methyl-benzoic acid | p-Toluic acid | 8 | 8 | 2 | 136.14 | 182 | 275 | 4.37 | ||
| Benzoic acids | 2-Phenylbenzoic acid | 13 | 10 | 2 | 198.21 | 112 | 344 | 3.46 | |||
| Benzoic acids | 4-Phenylbenzoic acid | 13 | 10 | 2 | 210 | s | |||||
| Cinnamic acid | trans-o-Methylcinnamic acid | 10 | 10 | 2 | 162.18 | 175 | 4.5 | ||||
| Cinnamic acid | trans-p-Methylcinnamic acid | 10 | 10 | 2 | 199 | 4.56 | |||||
| Phenyl-alkanoic acid | Phenylethanoic acid | α-Tolylic acid, Benzeneacetic | 8 | 8 | 2 | 136.14 | 77 | 266 | 1.2286 | 4.31 | |
| Phenyl-alkanoic acid | 2-Phenylbutyric acid | a-Ethyl-a-toluic acid | 10 | 12 | 2 | 47.5 | 4.66 | ||||
| Hydroxy acids | Hydroxyethanoic acid | Glycolic acid | 2 | 4 | 3 | 76.05 | 80 | d | 3.88 | ||
| Hydroxy acids | Hydroxyethanoic acid | Glycolic acid | 2 | 4 | 3 | 76.05 | 80 | d | 3.88 | ||
| Hydroxy acids | 2-Hydroxy-benzoic acid | Salicylic acid | 7 | 6 | 3 | 138.12 | 159 | 1.443 | 2.97 | 13.59 | |
| Hydroxy acids | 3-Hydroxy-benzoic acid | 7 | 6 | 3 | 138.12 | 202 | 4.8 | 9.9 | |||
| Hydroxy acids | 4-Hydroxy-benzoic acid | 7 | 6 | 3 | 138.12 | 215 | 4.58 | 9.4 | |||
| Alkanedioic acid | Ethanedioic acid | Oxalic acid | 2 | 2 | 4 | 90.04 | d190 | s157 | 1.917 | 1.25 | 4.29 |
| Alkanedioic acid | Propanedioic acid | Malonic acid | 3 | 4 | 4 | 104.06 | 136 | d140 | 1.61916 | 2.85 | 5.69 |
| Alkanedioic acid | Butanedioic acid | Succinic acid | 4 | 6 | 4 | 118.09 | 185 | d235 | 1.57225 | 4.21 | 5.64 |
| Alkanedioic acid | Pentanedioic acid | Glutaric acid | 5 | 8 | 4 | 132.11 | 96 | 302** | 3.22 | 4.82 | |
| Alkanedioic acid | Hexanedioic acid | Adipic acid | 6 | 10 | 4 | 146.14 | 153 | 265** | 4.34 | 5.41 | |
| Alkanedioic acid | Heptanedioic acid | Pimelic acid | 7 | 12 | 4 | 160.17 | 104 | 212** | 4.71 | 5.58 | |
| Alkanedioic acid | Octanedioic acid | Suberic acid | 8 | 14 | 4 | 174.19 | 142 | 230** | 4.52 | 5.498 | |
| Alkanedioic acid | Nonanedioic acid | Azelaic acid | 9 | 16 | 4 | 188.29 | 110 | 286** | 4.53 | 5.33 | |
| Alkanedioic acid | Decanedioic acid | Sebacic acid | 10 | 18 | 4 | 202.24 | 131 | 374** | 1.271 | 4.59 | 5.59 |
| Alkanedioic acid | Undecanedioic acid | 1,9-Nonanedicarboxylic acid | 11 | 20 | 4 | 216.27 | 109 | 4.65 | |||
| Alkanedioic acid | Dodecanedioic acid | Decane-1,10-dicarboxylic acid | 12 | 22 | 4 | 230.30 | 128 | 245** | 4.65 | ||
| Alkanedioic acid | Tridecanedioic acid | Brassylic acid | 13 | 24 | 4 | 244.32 | 113 | 4.65 | |||
| Alkenedioic acids | cis-Butenedioic acid | Maleic | 4 | 4 | 4 | 116.07 | 139 | d | 1.5925 | 1.92 | 6.22 |
| Alkenedioic acids | trans-Butenedioic acid | Fumaric | 4 | 4 | 4 | 116.07 | s300 | 1.635 | 3.02 | 4.39 | |
| Alkenedioic acids | 2-Octenedioic acid | 8 | 12 | 4 | 172.18 | 4.15 | |||||
| Branched dioic acids | 2-Methylpropanedioic acid | Methylmalonic acid | 4 | 6 | 4 | 118.09 | 129 | 1.455 | 3.07 | 5.76 | |
| Branched dioic acids | 3-Methylpentanedioic acid | 3-Methylglutaric acid | 6 | 10 | 4 | 146.14 | 83 | 4.24 | |||
| Aromatic dioic acids | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid | o-Phthalic acid | 8 | 6 | 4 | 166.13 | d210 | 4.42 | 5.41 | ||
| Aromatic dioic acids | 2,6-Naphthalenedicarboxylic acid | 12 | 8 | 4 | 216.18 | >300 | |||||
| Aromatic dioic acids | 1,4-Naphthalenedicarboxylic acid | 12 | 8 | 4 | 216.18 | >301 | |||||
| Aromatic dioic acids | Biphenyl-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid | 14 | 10 | 4 | 242.22 | >300 | |||||
| * Note that some of the substances have a melting point above 20°C, and that the given densities then are given for solid state. Superscript notations give measurement temperature(in °C) different from 20°C. | |||||||||||
| ** Boiling point is estimated from low pressure measurements. It is not known whether the substance is chemically stable at the given1 atm boiling temperature. | |||||||||||
| s = sublimates d = decomposes | |||||||||||
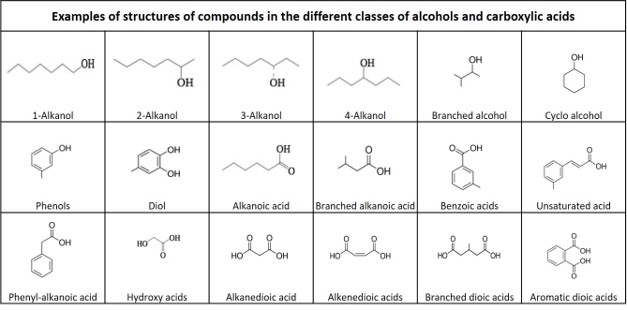
Definitions of organic compounds
Hydrocarbon: An organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon.
Main groups of hydrocarbons:
Alkane: An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula Cn H2n+2 . Also called paraffin .
Alkene: An unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond, with the general formula Cn H2n . Also called olefine .
Cycloalkane: A one-ring (monocyclic) saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula Cn H2n . Also called naphthene .
Aromatic hydrocarbon : A cyclic (ring-shaped), planar (flat) molecule with a ring of resonance bonds that exhibits more stability than other geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms. The simplest of the aromatics have 6 carbon atoms and contains 3 double bounds. A one ring aromatic without any substituents is called benzene, with the formula C6 H6.
Some under-groups of hydrocarbons given in this document:
Alkyl: An alkane substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula Cn H2n+1
Branched alkyl: An alkyl with one or several side chains of carbon atoms connected to the main carbon atom chain.
Phenyl: An phenyl group is a benzene substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula C6H5.
Classes of alcohols:
Alcohol: an organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom
Alkanol: An alcohol where the hydroxyl group is bound to an alkyl. If the hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom at the end of the alkyl, it is a 1-alkanol, if it is bound to the second carbon, it is a 2-alkanol, etc.
Branched alcohol: An alcohol where the hydroxyl group is bound to a branched alkyl.
Cyclo alcohol: An alcohol where the hydroxyl group is bound to a cycloalkane.
Phenol: An alcohol where the hydroxyl group is bound to a phenyl group, with the formula C6H5OH.
Phenols: A group of compounds consisting of a phenol molecule with one or more substiuents.
Diol: An organic compound containing two hydroxyl groups, R(-OH)2.
Triol : An organic compound containing three hydroxyl groups, R(-OH)3.
Classes of carboxylic acids:
Carboxylic acid: an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group (C(=O)OH). The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R–COOH, with R referring to the rest of the molecule.
Alkanoic acid: A carboxylic acid where the R is an alkyl.
Branched alkanoic acid: A carboxylic acid where the R is a branched alkyl.
Phenyl-alkanoic acid: An alkanoic acid bound to a phenyl.
Benzoic acid: A carboxylic acid where the acid group is substituted to one carbon of a benzene ring.
Hydroxy acid: A carboxylic acid containing an additional hydroxyl group.
Dioic acid: A carboxylic acid with two acid groups, R(-COOH)2



