Organic Sulfur Compounds - Densities
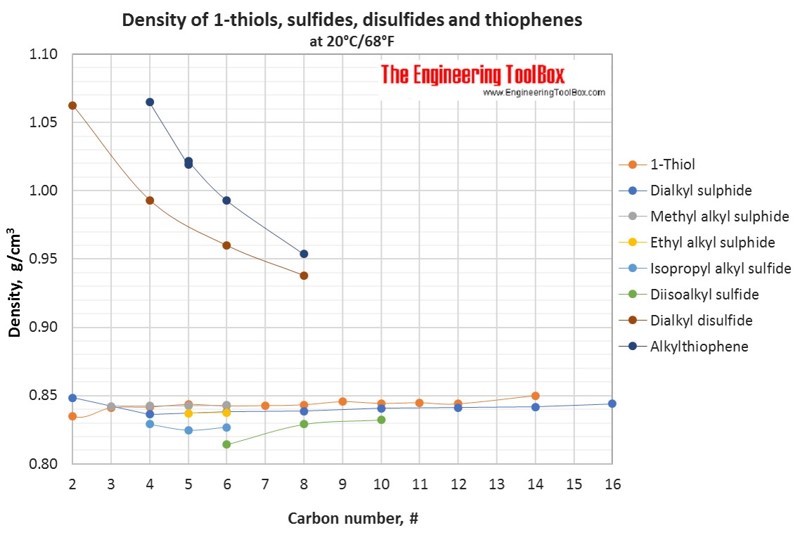
Liquid density of different kinds of organic sulfur compounds with varying carbon number (20°C/68°F). Comparison of thiols, sulfides, disulfides and thiophenes.
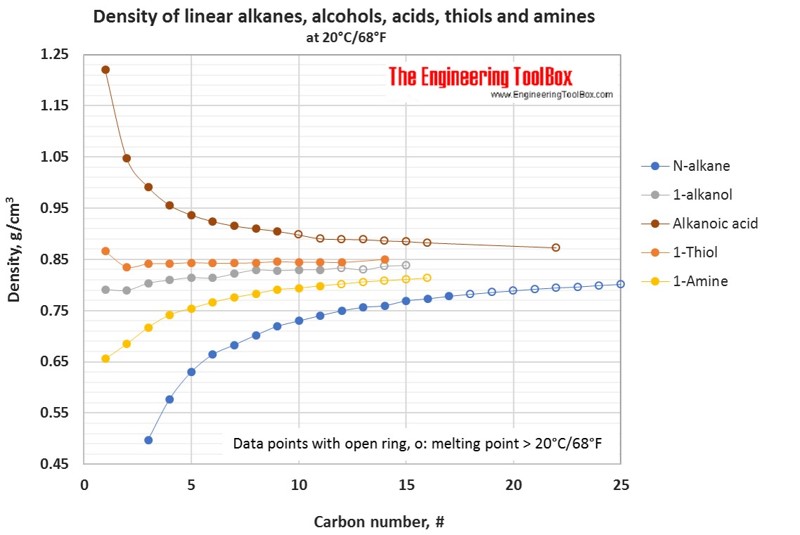
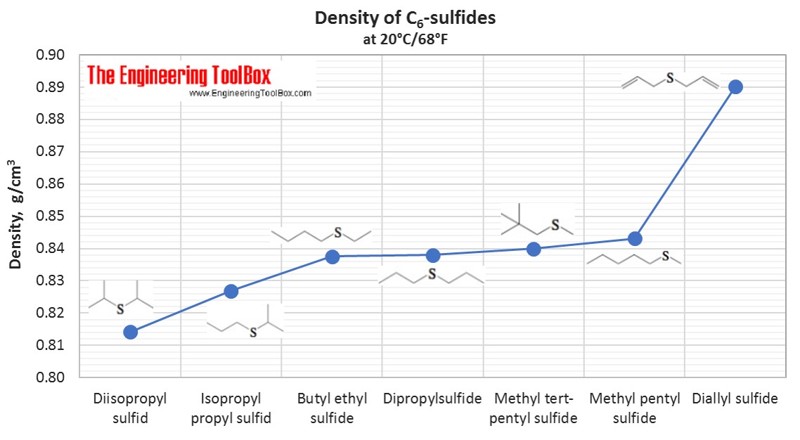
Tables and figures below show the liquid density at 20°C for different groups of organic sulfur compounds, compared to other kinds of organic classes as alkanes, alcohols, acids and amines. The density is shown as function of carbon number in the organic compounds.
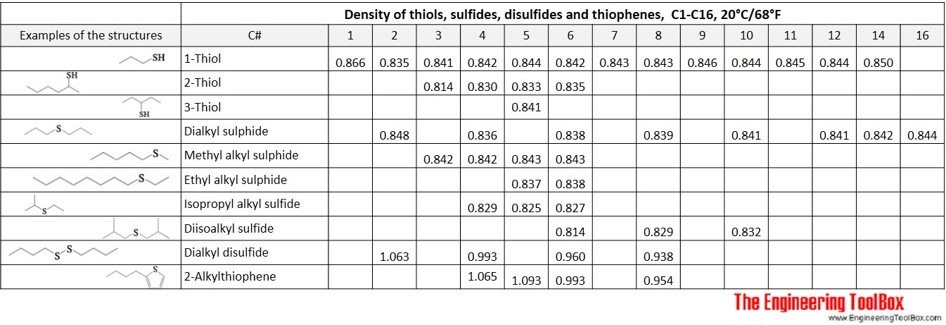
Also, examples of the structures of the sulfur compounds thiols, dialkyl sulfides, methylalkyl sulfides, ethyl alkyl sulfides, isopropyl alkyl sulfides, diisoalkyl sulfides, dialkyl disulfides and alkylthiophenes are shown in the table below. Definitions of the organic classes are given below the figures.
See also density for n-alkanes, alcohols and acids and density, boiling and melting points of nitrogen and sulfur compounds.
Definition of organic compounds
Hydrocarbon: An organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon.
Alkane: An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula CnH2n+2. Also called paraffin.
Alkyl: An alkyl group is an alkane substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula CnH2n+1
Alcohol: an organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom
Alkanol: An alcohol where the hydroxyl group is connected to an alkane
Carboxylic acid: an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group (C(=O)OH). The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R–COOH, with R referring to the rest of the molecule.
Alkanoic acid: A carboxylic acid where the R is an alkane.
Organic sulfur compounds:
Thiol: An organosulfur compound that contains a carbon-bonded sulfhydryl group (-SH), with the general formula R–SH (where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent). For thiols in this document the R represents an alkyl group, and in a 1-thiol the -SH group is located at the end of the alkyl chain. In a 2-thiol and a 3-thiol the -SH group is located at the second and third carbon atom in the alkyl chain, respectively. Also called mercaptan.
Sulfide: An organic compound of the form R’–S–R’’ (where R’ and R’’ represents an alkyl or other organic substituent).
Dialkyl sulfide: A sulphide where R’ and R’’ are linear alkyl groups, and of the same length.
Methyl alkyl sulfide: A sulphide where R’ is a methyl group and R’’ are any alkyl group.
Ethyl alkyl sulfide: A sulphide where R’ is an ethyl group and R’’ are any alkyl group.
Isopropyl alkyl sulphide: A sulphide where R’ is an isopropyl group and R’’ are any alkyl group.
Diisoalkyl sulphide: A sulphide where R’ and R’’ are isoalkyl groups, and of the same length.
Disulfide: An organic compound of the form R’–S-S–R’’ (where R’ and R’’ represents an alkyl or other organic substituent).
Thiophene: A heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a stable, flat five-membered ring.
Alkylthiophene: A monosubstituted thiophene with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of the thiophene ring, with the general formula CnH(2n+1)C4H3S
Organic nitrogen compounds:
Amine: A compound or functional group that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. It can be a primary (R-NH2), a secondary (R',R''-NH) or a tertiary amine (R',R'',R'''-N), where R represent an alkyl or other organic substituent. For 1-amines in this document the R represents an alkyl group, in which the NH2-group is placed at the end of the the alkane chain.



