Amines, Diamines and Cyclic Organic Nitrogen Compounds - pKa Values
Values for the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant, pKa, of the conjugated acid of amines, diamines and cyclic organic nitrogen compounds, shown together with the molecular structure of the acids.
Definitions of the acid dissociation constant and pKa are given below the figures, together with the definition of some classes of organic acids .
In the table below, pKa1 and pKa2 is given together with boiling and melting point, density and molecular weight, as well as number of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms in each molecule.
See also boiling and melting point of different kinds of organic compounds, boiling and melting point of organic nitrogen compounds, pKa of phenols, alcohols and carboxylic acids and pKa of inorganic acids and bases, as well as acid and base pH indicators and Acid-base properties of aqueous solutions of salts with ions from both acids and bases .
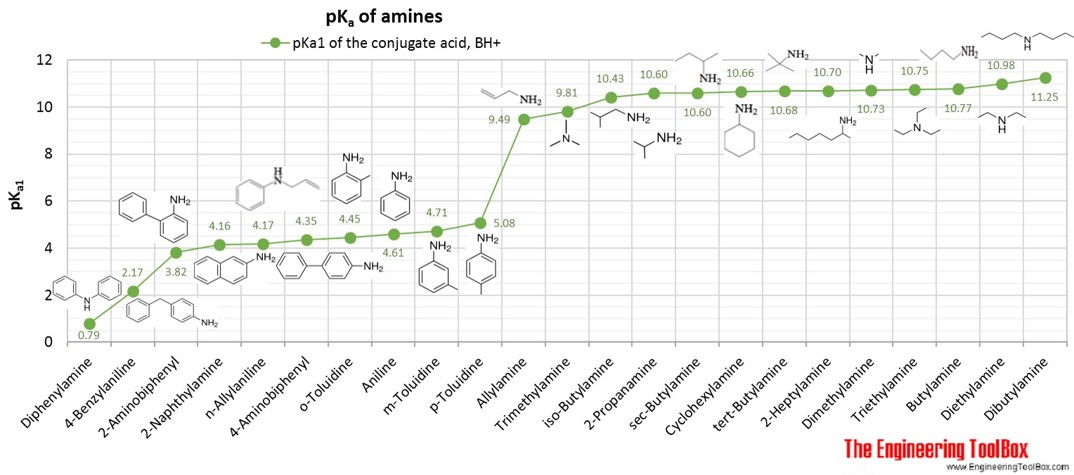
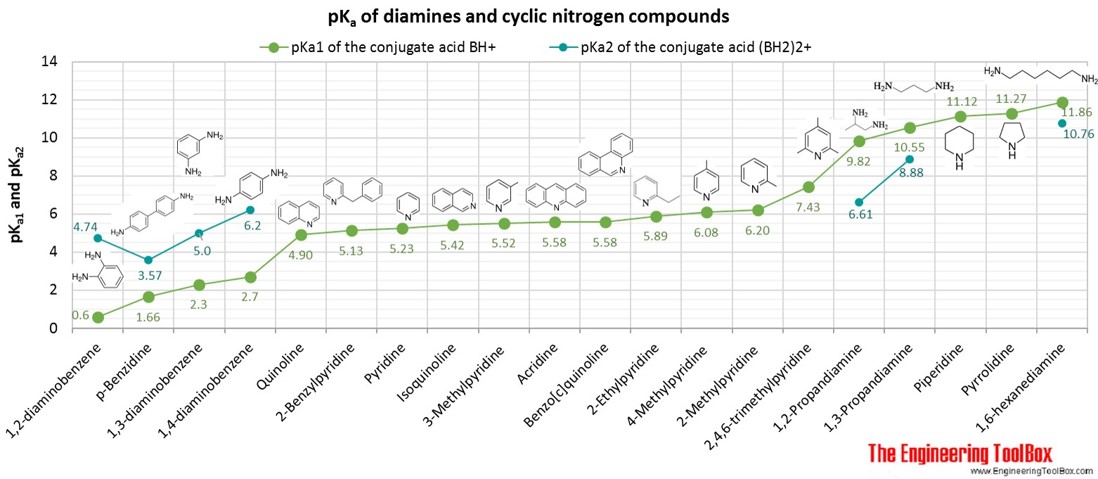
For full table with molweight, melting and boiling temperature and density - rotate the screen!
| Group | Compound name | Common name | #C | #H | #N | pKa1 of the conjugate acid BH+ | pKa2 of the conjugate acid BH2 2+ | Mole weight g/mol | Melting temp °C | Boiling temp °C | Density@20°C g/ml |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Amine | Methylamine | Methanamine | 1 | 5 | 1 | 10.59 | 31.06 | -93 | -6 | 0.660 | |
| 1-Amine | Ethylamine | Ethanamine | 2 | 7 | 1 | 10.67 | 45.08 | -81 | 17 | 0.685 | |
| 1-Amine | Propylamine | 1-Propanamine | 3 | 9 | 1 | 10.69 | 59.11 | -85 | 47 | 0.717 | |
| 1-Amine | Butylamine | 1-Butanamine | 4 | 11 | 1 | 10.61 | 73.14 | -49 | 77 | 0.741 | |
| 1-Amine | Pentylamine | Amylamine | 5 | 13 | 1 | 10.63 | 87.16 | -51 | 105 | 0.754 | |
| 1-Amine | Hexylamine | 1-Hexanamine | 6 | 15 | 1 | 10.56 | 101.19 | -21 | 132 | 0.766 | |
| 1-Amine | Heptylamine | 1-Heptanamine | 7 | 17 | 1 | 10.67 | 115.22 | -23 | 153 | 0.775 | |
| 1-Amine | Octylamine | 1-Octanamine | 8 | 19 | 1 | 10.65 | 129.24 | 0 | 179 | 0.783 | |
| 1-Amine | Nonylamine | 1-Nonanamine | 9 | 21 | 1 | 10.64 | 143.27 | -1 | 198 | 0.791 | |
| 1-Amine | Decylamine | 1-Decanamine | 10 | 23 | 1 | 10.64 | 157.30 | 15 | 217 | 0.794 | |
| 1-Amine | Undecylamine | 1-Undecanamine | 11 | 25 | 1 | 10.63 | 171.32 | 15 | 229 | 0.798 | |
| 1-Amine | Dodecylamine | 1-Dodecanamine | 12 | 27 | 1 | 10.63 | 185.35 | 28 | 255 | 0.802 | |
| 1-Amine | (Tridecyl)amine | 1-Tridecanamine | 13 | 29 | 1 | 10.63 | 199.38 | 27 | 273 | 0.806 | |
| 1-Amine | Tetradecylamine | 1-Tetradecanamine | 14 | 31 | 1 | 10.62 | 213.40 | 39 | 289 | 0.808 | |
| 1-Amine | Pentadecylamine | Pentadecanamine | 15 | 33 | 1 | 10.61 | 227.43 | 37 | 312 | 0.810 | |
| 1-Amine | Hexadecylamine | 1-Hexadecanamine | 16 | 35 | 1 | 10.63 | 241.46 | 46 | 321 | 0.813 | |
| 1-Amine | Octadecylamine | 1-Octadecanamine | 18 | 39 | 1 | 10.60 | 269.51 | 53 | 350 | 0.862 | |
| Amine | Dimethylamine | Methyl methylamine | 2 | 7 | 1 | 10.73 | 45.08 | -92 | 7 | 0.654 | |
| Amine | Allylamine | 2-propen-1-amine | 3 | 7 | 1 | 9.49 | 57.09 | -88 | 54 | 0.758 | |
| Amine | Trimethylamine | Dimethyl methylamine | 3 | 9 | 1 | 9.81 | 59.11 | -117 | 3 | 0.631 | |
| Amine | 2-Propanamine | 3 | 9 | 1 | 10.60 | 59.11 | -95 | 32 | 0.682 | ||
| Amine | sec-Butylamine | 2-Butanamine | 4 | 11 | 1 | 10.60 | 73.14 | -105 | 63 | 0.725 | |
| Amine | tert-Butylamine | 2-Methyl-2-propanamine | 4 | 11 | 1 | 10.68 | 73.14 | -67 | 46 | 0.696 | |
| Amine | Butylamine | 1-Butanamine | 4 | 11 | 1 | 10.77 | 73.14 | -49 | 77 | 0.741 | |
| Amine | Diethylamine | Ethyl ethylamine | 4 | 11 | 1 | 10.98 | 73.14 | -50 | 56 | 0.706 | |
| Amine | iso-Butylamine | 2-Methyl-1-propanamine | 5 | 12 | 1 | 10.43 | 86.16 | -85 | 68 | 0.730 | |
| Amine | Aniline | 6 | 7 | 1 | 4.61 | 93.13 | -6 | 184 | 1.025 | ||
| Amine | Cyclohexylamine | 6 | 13 | 1 | 10.66 | 99.17 | -18 | 134 | 0.819 | ||
| Amine | Triethylamine | Diethyl ethylamine | 6 | 15 | 1 | 10.75 | 101.19 | -115 | 90 | 0.727 | |
| Amine | o-Toluidine | 2-Aminotoluene, 2-Methylaniline | 7 | 9 | 1 | 4.45 | 107.15 | -28 | 199 | 1.010 | |
| Amine | m-Toluidine | 3-Aminotoluene, 3-Methylaniline | 7 | 9 | 1 | 4.71 | 107.15 | -30 | 203 | 1.001 | |
| Amine | p-Toluidine | 4-Aminotoluene, 4-Methylaniline | 7 | 9 | 1 | 5.08 | 107.15 | 44 | 201 | 0.975 | |
| Amine | 2-Heptylamine | 2-Heptanamine, 1-Methylhexylamine | 7 | 17 | 1 | 10.70 | 115.22 | 143 | 0.766 | ||
| Amine | Dibutylamine | 8 | 19 | 1 | 11.25 | 129.24 | -62 | 162 | 0.767 | ||
| Amine | n-Allylaniline | Allylphenylamine | 9 | 11 | 1 | 4.17 | 133.19 | 219 | 0.977 | ||
| Amine | 2-Naphthylamine | 2-Aminonaphthalene, beta-naphthylamine | 10 | 9 | 1 | 4.16 | 143.19 | 112 | 306 | 1.063 | |
| Amine | Diphenylamine | N-phenyl-aminobenzene | 12 | 11 | 1 | 0.79 | 169.22 | 51 | 302 | 1.160 | |
| Amine | 2-Aminobiphenyl | 2-Biphenylylamine, 2-Phenylaniline | 12 | 11 | 1 | 3.82 | 169.22 | 48 | 299 | ||
| Amine | 4-Aminobiphenyl | 4-Phenylaniline, Xenylamine | 12 | 11 | 1 | 4.35 | 169.22 | 53 | 348 | ||
| Amine | 4-Benzylaniline | 13 | 13 | 1 | 2.17 | 183.25 | 35 | 300 | 1.038 | ||
| Diamine | 1,2-Propandiamine | 3 | 10 | 2 | 9.82 | 6.61 | 74.12 | 118 | 0.875 | ||
| Diamine | 1,3-Propandiamine | 3 | 10 | 2 | 10.55 | 8.88 | 74.12 | -11 | 139 | 0.887 | |
| Diamine | 1,3-diaminobenzene | m-phenylenediamine | 6 | 8 | 2 | 2.3 | 5.0 | 108.14 | 65 | 282 | |
| Diamine | 1,2-diaminobenzene | o-phenylenediamine | 6 | 8 | 2 | 0.6 | 4.74 | 108.14 | 102 | 256 | |
| Diamine | 1,4-diaminobenzene | p-Phenylenediamine | 6 | 8 | 2 | 2.7 | 6.2 | 108.14 | 140 | 267 | |
| Diamine | 1,6-hexanediamine | 6 | 16 | 2 | 11.86 | 10.76 | 116.20 | ||||
| Diamine | p-Benzidine | 1,1-biphenyl-4,4-diamine | 12 | 12 | 2 | 1.66 | 3.57 | 184.24 | 127 | 401 | |
| Piperidine | Piperidine | 5 | 11 | 1 | 11.12 | 85.15 | -13 | 106 | 0.862 | ||
| Pyridine | Pyridine | Azine | 5 | 5 | 1 | 5.23 | 79.10 | -42 | 115 | 0.982 | |
| Pyridine | 3-Methylpyridine | 6 | 7 | 1 | 5.52 | 93.13 | -18 | 144 | 1.504 | ||
| Pyridine | 4-Methylpyridine | 6 | 7 | 1 | 6.08 | 93.13 | 4 | 145 | 1.504 | ||
| Pyridine | 2-Methylpyridine | 6 | 7 | 1 | 6.20 | 93.13 | -67 | 129 | 1.499 | ||
| Pyridine | 2-Ethylpyridine | 7 | 9 | 1 | 5.89 | 107.15 | -63 | 149 | 0.952 | ||
| Pyridine | 2,4,6-trimethylpyridine | 2,4,6-Collidine | 8 | 11 | 1 | 7.43 | 121.18 | -44 | 170 | 0.917 | |
| Pyridine | 2-Benzylpyridine | 12 | 11 | 1 | 5.13 | 169.22 | 13 | 277 | 1.059 | ||
| Pyrrole | Pyrrolidine | Azacyclopentane, tetrahydropyrrole | 4 | 9 | 1 | 11.27 | 71.12 | -58 | 87 | 0.859 | |
| Quinoline | Quinoline | 1-Azanapthalene | 9 | 7 | 1 | 4.90 | 129.16 | -15 | 237 | 1.096 | |
| Quinoline | Isoquinoline | 9 | 7 | 1 | 5.42 | 129.16 | 27 | 242 | 1.101 | ||
| Quinoline | Acridine | Dibenzo(b,e)pyridine | 13 | 9 | 1 | 5.58 | 179.22 | 111 | 347 | 1.005 | |
| Quinoline | Benzo(c)quinoline | Phenanthridine | 13 | 9 | 1 | 5.58 | 179.22 | 107 | 350 | ||
An acid dissociation constant, Ka , is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction known as dissociation of acid–base reactions. In aqueous solution, the equilibrium of acid dissociation can be written symbolically as:
HA + H2O = A-+H3 O+
where HA is an acid that dissociates into A-, (known as the conjugate base of the acid) and a hydrogen ion which combines with a water molecule to make a hydronium ion.
The chemical species HA, A-and H3 O+are said to be in equilibrium when their concentrations do not change with the passing of time. The dissociation constant is usually written as a quotient of the equilibrium concentrations (in mol/L), denoted by (HA), (A-) and (H3 O+)
Ka = (A-)*(H3 O+) / (HA)*(H2O)
In all, but the most concentrated, aqueous solutions of an acid the concentration of water can be taken as constant and can be ignored. The definition can then be written more simply
HA = A-+ H+and Ka = (A-)*(H+) / (HA)
This is the definition in common usage. For many practical purposes it is more convenient to discuss the logarithmic constant, pKa
pKa = -log10 Ka
The larger the value of pKa , the smaller the extent of dissociation at any given pH - that is, the weaker the acid.
A weak acid has a pKa value in the approximate range -2 to 12 in water.
Strong acids has pKa values of less than about -2; the dissociation of a strong acid is effectively complete such that concentration of the undissociated acid is too small to be measured. pKa values for strong acids can, however, be estimated by theoretical means.
After rearranging the expression defining Ka , and putting pH = -log10 (H+), one obtains
pH = pKa + (A-) / (HA) and further
pH - pKa = log(A-) / (HA)
Then, a solution with 50% dissociation has pH equal to the pKa of the acid.
Polyprotic acids are acids that can lose more than one proton. Then we have more than one dissiciation constant; Ka1 , Ka2 , etc.. and similar pKa1 , pKa2 , etc.
All data given in the figures apply to dilute aqueous solutions at ambient temperature.
For amines, the pka value is given for the conjugate bases BH+and BH2 2+.
BH+= B + H+
The pKb for a base may be calculated from the pKa value of its conjugate acid:
pKw = pKa + pKb
At 25°C the pKw is 14 and
pKb = 14 - pKa
Definition of organic compounds
Hydrocarbon: An organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon.
Alkane: An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula Cn H2n+2 . Also called paraffin.
Aromatic hydrocarbon : A cyclic (ring-shaped), planar (flat) molecule with a ring of resonance bonds that exhibits more stability than other geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms. The simplest of the aromatics have 6 carbon atoms and contains 3 double bounds. A one ring aromatic without any substituents is called benzene, with the formula C6H6.
Alkyl: An alkyl group is an alkane substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula Cn H2n+1.
Phenyl: An phenyl group is a benzene substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula C6 H5.
Amine: A compound or functional group that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. It can be a primary (R-NH2), a secondary (R',R''-NH) or a tertiary amine (R',R'',R'''-N), where R represent an alkyl or other organic substituent. For 1-amines in this document the R represents an alkyl group, in which the NH2-group is placed at the end of the the alkane chain.
Diamine: An amine with two amino groups.
Pyrrole: A heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with two double bounds, with the formula C4H4NH. Substituted derivatives are called pyrroles.
Dihydropyrrole: A compound formally derived from the aromate pyrrole by partial hydrogenation, containing one double bound. Also called pyrroline.
Pyridine: A heterocyclic six-membered ring compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally similar to benzene, with one methine group (=CH-) replaced by a nitrogen atom.
Piperidine: A heterocyclic amine consisting of a six-membered ring containing five methylene bridges (–CH2–) and one amine bridge (–NH–). The molecular formula is (CH2)5NH.
Quinoline: A heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, consisting of a benzene ring fused to a pyridine ring, with the molecular formula C9H7N and the nitrogen atom in position 1.
Isoquinoline: An analog to quinoline with the nitrogen atom in position 2.



