Organic Sulfur Compounds - Physical Data
Boiling and melting points of thoils, sulfides, disulfides and thiophenes shown together with molecular structures, as well as molweights and density.
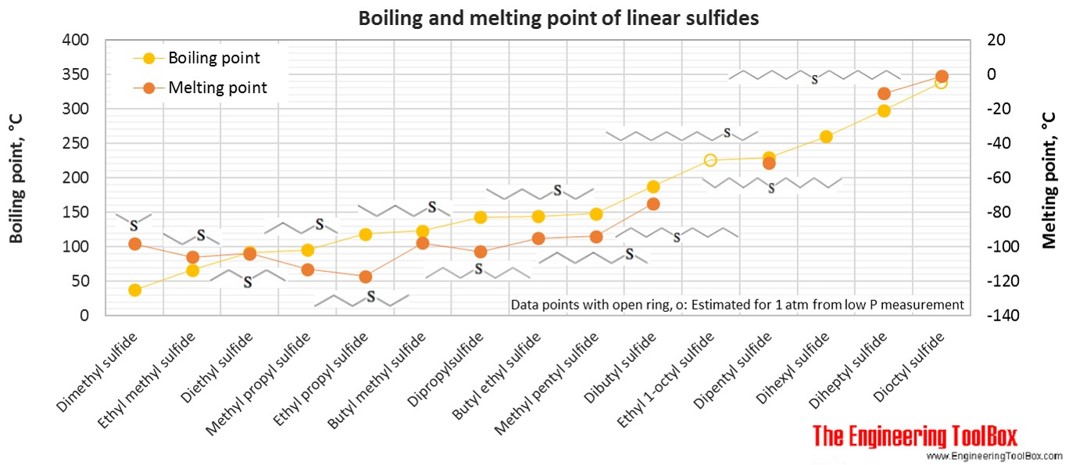
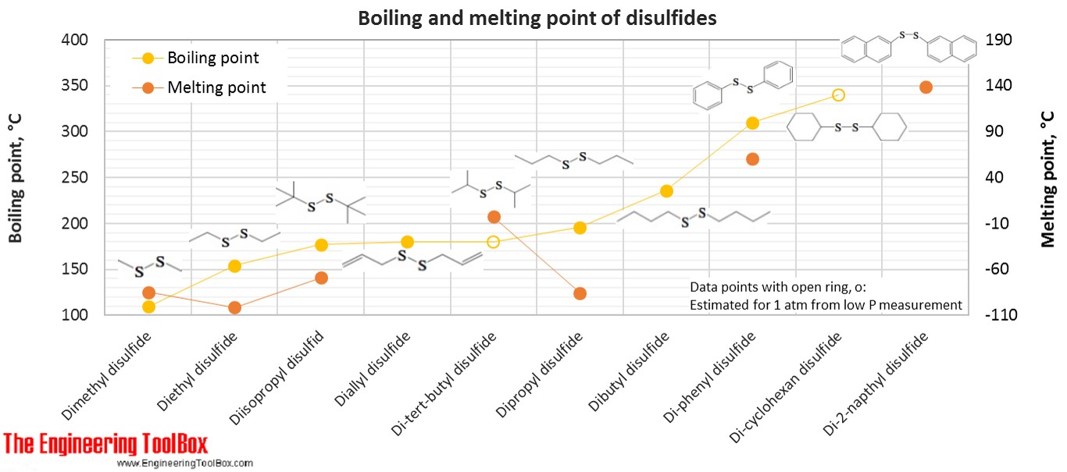
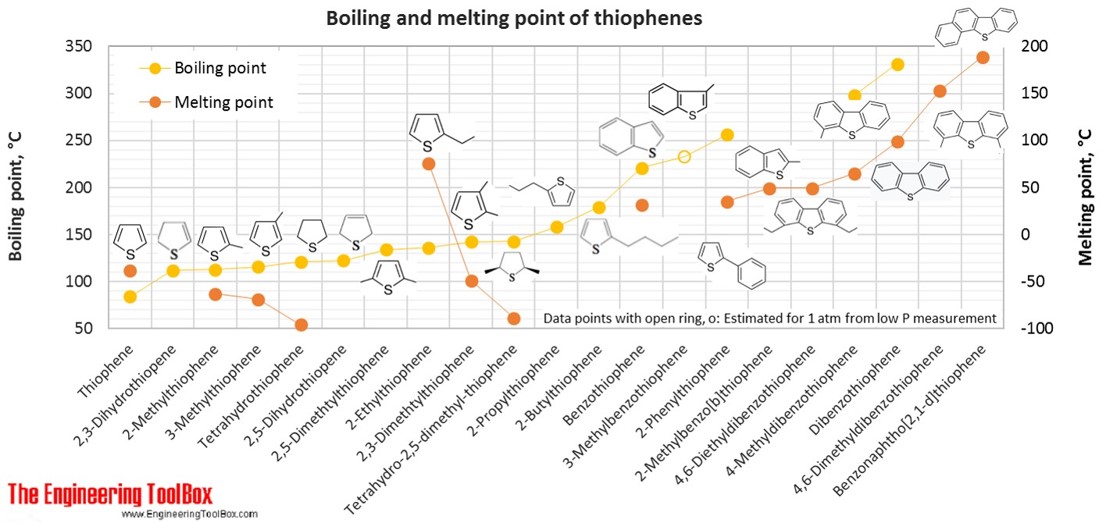
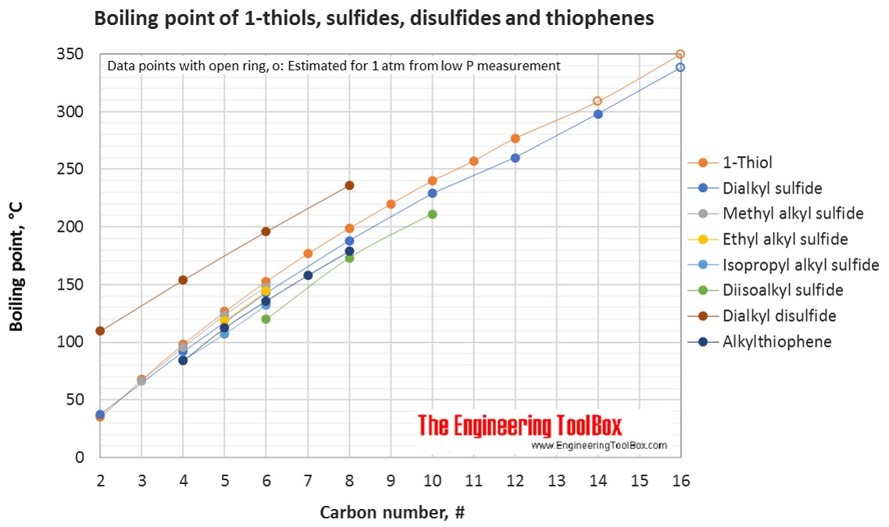
The figures below show the boiling and melting point for organic sulfur compounds as sulfides, disulfides, thiols (mercaptans) and thiophenes, together with the molecular structures of the different compounds. The table shows the same numbers together with the molecular weight and density, as well as the numbers of carbon, hydrogen and sulfur in the molecules. All numbers are given for boiling and melting at 1 atm (760 mm Hg). For some compounds the boiling point at 1 atm is not available. For these, the 1 atm boiling point is estimated from low pressure measurements, using a vaporization heat of 54- 70 kJ/mol (increasing with increasing BP). It is not known whether these compounds are stable at the 1 atm boiling temperature or not. Definitions of the organic classes are given below the figures.
- Boiling point - the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas
- Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid
See also similar figures and tables for organic nitrogen compounds and boiling and melting point of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids, as well as densities of organic sulfur compounds.

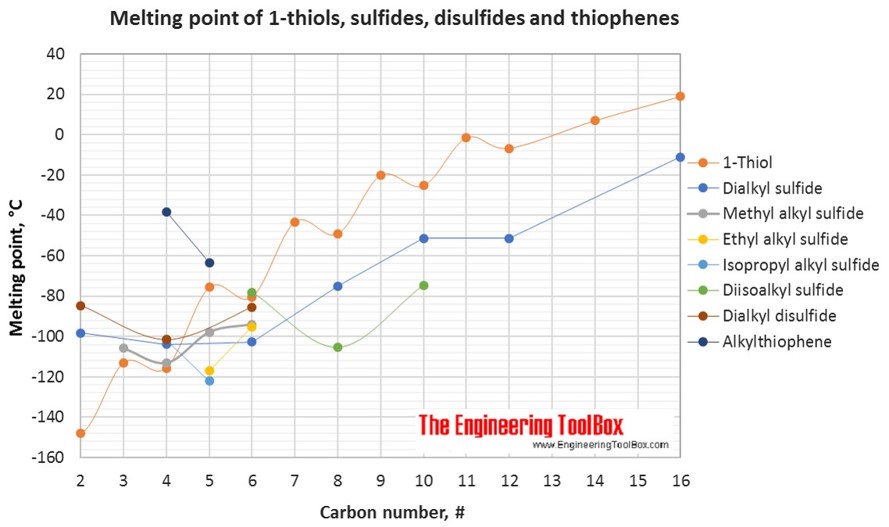
For full table with molweight and boling point - rotate the screen!
| Group | Compound name | Common name | #C | #H | #S | Molweight (g/mol) | Melting point (°C) | Boiling point (°C) | Density @20°C (g/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Thiol | Methanethiol | Methyl mercaptan | 1 | 4 | 1 | 48.11 | -123 | 6 | 0.866 |
| 1-Thiol | Ethanethiol | Ethyl mercaptan | 2 | 6 | 1 | 62.13 | -148 | 35 | 0.835 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Propanethiol | Propyl mercaptan | 3 | 8 | 1 | 76.16 | -113 | 68 | 0.841 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Butanethiol | Butyl mercaptan | 4 | 10 | 1 | 90.19 | -116 | 98 | 0.842 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Pentanethiol | Pentyl mercaptan | 5 | 12 | 1 | 104.21 | -76 | 127 | 0.844 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Hexanethiol | Hexyl mercaptan | 6 | 14 | 1 | 118.24 | -81 | 153 | 0.842 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Heptanethiol | Heptyl mercaptan | 7 | 16 | 1 | 132.27 | -43 | 177 | 0.843 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Octanethiol | Octyl mercaptan | 8 | 18 | 1 | 146.29 | -49 | 199 | 0.843 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Nonanethiol | Nonyl mercaptan | 9 | 20 | 1 | 160.32 | -20 | 220 | 0.846 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Decanethiol | Decyl mercaptan | 10 | 22 | 1 | 174.35 | -25 | 240 | 0.844 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Undecanethiol | Undecyl mercaptan | 11 | 24 | 1 | 188.37 | -2 | 257 | 0.845 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Dodecanethiol | Dodecyl mercaptan | 12 | 26 | 1 | 202.40 | -7 | 277 | 0.844 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Tetradecanethiol | Tetradecyl mercaptan | 14 | 30 | 1 | 230.45 | 7 | 309* | 0.850 |
| 1-Thiol | 1-Hexadecanethiol | Cetyl mercaptan | 16 | 34 | 1 | 258.51 | 19 | 350* | |
| Branched thiol | 2-Propanethiol | Isopropyl mercaptan | 3 | 8 | 1 | 76.16 | -131 | 53 | 0.814 |
| Branched thiol | 2-Butanethiol | sec-Butyl mercaptan | 4 | 10 | 1 | 90.19 | -165 | 85 | 0.830 |
| Branched thiol | 2-Pentanethiol | sec-Pentyl mercaptan | 5 | 12 | 1 | 104.21 | -169 | 113 | 0.833 |
| Branched thiol | 3-Pentanethiol | 3-Pentyl mercaptan | 5 | 12 | 1 | 104.21 | -111 | 116 | 0.841 |
| Branched thiol | Benzenethiol | Phenyl mercaptan | 6 | 6 | 1 | 110.18 | -15 | 169 | 1.078 |
| Branched thiol | 2-Hexanethiol | 7 | 8 | 1 | 118.24 | -147 | 139 | 0.835 | |
| Linear sulfide | Dimethyl sulfide | 2-Thiapropane | 2 | 6 | 1 | 62.13 | -98 | 37 | 0.848 |
| Linear sulfide | Ethyl methyl sulfide | 3 | 8 | 1 | 76.16 | -106 | 67 | 0.842 | |
| Linear sulfide | Diethyl sulfide | Ethyl sulfide | 4 | 10 | 1 | 90.19 | -104 | 92 | 0.836 |
| Linear sulfide | Methyl propyl sulfide | 4 | 10 | 1 | 90.19 | -113 | 96 | 0.842 | |
| Linear sulfide | Ethyl propyl sulfide | 5 | 12 | 1 | 104.21 | -117 | 119 | 0.837 | |
| Linear sulfide | Butyl methyl sulfide | 5 | 12 | 1 | 104.21 | -98 | 123 | 0.843 | |
| Linear sulfide | Dipropylsulfide | 6 | 14 | 1 | 118.24 | -103 | 143 | 0.838 | |
| Linear sulfide | Butyl ethyl sulfide | 6 | 14 | 1 | 118.24 | -95 | 144 | 0.838 | |
| Linear sulfide | Methyl pentyl sulfide | 6 | 14 | 1 | 118.24 | -94 | 148 | 0.843 | |
| Linear sulfide | Dibutyl sulfide | Butyl sulfide | 8 | 18 | 1 | 146.29 | -75 | 188 | 0.839 |
| Linear sulfide | Ethyl 1-octyl sulfide | 1-(Ethylthio)octane | 10 | 22 | 1 | 174.35 | 225* | ||
| Linear sulfide | Dipentyl sulfide | 10 | 22 | 1 | 174.35 | -51 | 229 | 0.841 | |
| Linear sulfide | Dihexyl sulfide | Hexyl sulfide | 12 | 26 | 1 | 202.40 | 260 | 0.841 | |
| Linear sulfide | Diheptyl sulfide | Heptyl sulfide | 14 | 30 | 1 | 230.45 | -11 | 298 | 0.842 |
| Linear sulfide | Dioctyl sulfide | Octyl sulfide | 16 | 34 | 1 | 258.51 | -1 | 338* | 0.844 |
| Branched sulfide | Isopropyl methyl sulfide | 4 | 10 | 1 | 90.19 | -101 | 85 | 0.829 | |
| Branched sulfide | Tert-butyl methyl sulfide | 5 | 12 | 1 | 104.21 | 99 | 0.830 | ||
| Branched sulfide | Ethyl isopropyl sulfide | 5 | 12 | 1 | 104.21 | -122 | 107 | 0.825 | |
| Branched sulfide | Diallyl sulfide | 6 | 10 | 1 | 114.21 | -85 | 138 | 0.893 | |
| Branched sulfide | Diisopropyl sulfid | 6 | 14 | 1 | 118.24 | -78 | 120 | 0.814 | |
| Branched sulfide | Tert-butyl ethyl sulfide | 6 | 14 | 1 | 118.24 | -86 | 120 | 0.820 | |
| Branched sulfide | Isopropyl propyl sulfid | 6 | 14 | 1 | 118.24 | 132 | 0.827 | ||
| Branched sulfide | Methyl tert-pentyl sulfide | 6 | 14 | 1 | 118.24 | 150 | 0.840 | ||
| Branched sulfide | Methyl phenyl sulfide | Methyl thiobenzene, Thianisole | 7 | 8 | 1 | 124.20 | -15 | 188 | 1.057 |
| Branched sulfide | Phenyl vinyl sulfide | (Phenylthio)ethylene | 8 | 8 | 1 | 136.21 | 180 | 1.044 | |
| Branched sulfide | Ethyl phenyl sulfide | Ethyl thiobenzene | 8 | 10 | 1 | 138.23 | 204 | 1.023 | |
| Branched sulfide | Di-tert-butyl sulfide | 8 | 18 | 1 | 146.29 | -9 | 152 | 0.819 | |
| Branched sulfide | Di-sec-butyl sulfide | 8 | 18 | 1 | 146.29 | 167 | 0.835 | ||
| Branched sulfide | Diisobutyl sulfid | 8 | 18 | 1 | 146.29 | -106 | 173 | 0.829 | |
| Branched sulfide | Allyl phenyl sulfide | 9 | 10 | 1 | 150.24 | 224 | 1.024 | ||
| Branched sulfide | Diisopentyl sulfid | 10 | 22 | 1 | 174.35 | -75 | 211 | 0.832 | |
| Branched sulfide | Diphenyl sulfide | Phenyl sulfide | 12 | 10 | 1 | 186.27 | -15 | 294 | 1.114 |
| Branched sulfide | Dibenzyl sulfide | Benzyl sulfide | 14 | 14 | 1 | 214.33 | 48 | 335 | 1.058 |
| Disulfid | Dimethyl disulfide | DMDS | 2 | 6 | 2 | 94.20 | -85 | 110 | 1.063 |
| Disulfid | Diethyl disulfide | 4 | 10 | 2 | 122.25 | -102 | 154 | 0.993 | |
| Disulfid | Diallyl disulfide | DADS Garlicin | 6 | 10 | 2 | 146.27 | 180 | 1.010 | |
| Disulfid | Diisopropyl disulfid | 6 | 14 | 2 | 150.31 | -69 | 177 | 0.944 | |
| Disulfid | Dipentyl disulfide | 10 | 22 | 2 | 206.41 | ||||
| Disulfid | Dihexyl disulfide | 12 | 26 | 2 | 234.46 | ||||
| Disulfid | Diheptyl disulfide | 14 | 30 | 2 | 262.52 | ||||
| Disulfid | Dioctyl disulfide | 16 | 34 | 2 | 290.57 | ||||
| Disulfid | Dipropyl disulfide | 6 | 14 | 2 | 150.31 | -85 | 196 | 0.960 | |
| Disulfid | Di-tert-butyl disulfide | 8 | 18 | 2 | 178.36 | -3 | 180* | 0.923 | |
| Disulfid | Dibutyl disulfide | 8 | 18 | 2 | 178.36 | 236 | 0.938 | ||
| Disulfid | Di-phenyl disulfide | 12 | 10 | 2 | 218.34 | 60 | 310 | 1.353 | |
| Disulfid | Di-cyclohexan disulfide | 12 | 22 | 2 | 230.43 | 340* | 1.049 | ||
| Disulfid | Di-2-napthyl disulfide | 20 | 14 | 2 | 318.46 | 139 | 1.144 | ||
| Thiophene | Thiophene | Thiofurane | 4 | 4 | 1 | 84.14 | -38 | 84 | 1.065 |
| Thiophene | 2,3-Dihydrothiopene | 4 | 6 | 1 | 86.16 | 112 | |||
| Thiophene | 2,5-Dihydrothiopene | 4 | 6 | 1 | 86.16 | 122 | |||
| Thiophene | Tetrahydrothiophene | Thiolane, Thiophane, Thiacyclopentane | 4 | 8 | 1 | 88.17 | -96 | 121 | 0.999 |
| Thiophene | 2-Methylthiophene | 5 | 6 | 1 | 98.17 | -63 | 113 | 1.019 | |
| Thiophene | 3-Methylthiophene | 5 | 6 | 1 | 98.17 | -69 | 115 | 1.022 | |
| Thiophene | 2,5-Dimethtylthiophene | 6 | 8 | 1 | 112.19 | 134 | 0.987 | ||
| Thiophene | 2-Ethylthiophene | 6 | 8 | 1 | 112.19 | 76 | 136 | 0.993 | |
| Thiophene | 2,3-Dimethtylthiophene | 6 | 8 | 1 | 112.19 | -49 | 142 | 1.007 | |
| Thiophene | Tetrahydro-2,5-dimethyl-thiophene | 6 | 12 | 1 | 116.22 | -89 | 143 | 0.922 | |
| Thiophene | 2-Propylthiophene | 7 | 10 | 1 | 126.22 | 158 | 0.984 | ||
| Thiophene | Benzothiophene | Thianaphthene | 8 | 6 | 1 | 134.20 | 31 | 221 | 1.156 |
| Thiophene | 3-Methylbenzothiophene | 8 | 6 | 1 | 134.20 | 233* | 1.108 | ||
| Thiophene | 2-Butylthiophene | 8 | 12 | 1 | 140.25 | 179 | 0.954 | ||
| Thiophene | 2-Methylbenzo(b)thiophene | 2-Methylthianaphthene | 9 | 8 | 1 | 148.22 | 49 | ||
| Thiophene | 2-Phenylthiophene | 10 | 8 | 1 | 160.24 | 35 | 256 | ||
| Thiophene | Dibenzothiophene | 12 | 8 | 1 | 184.26 | 99 | 332 | 1.252 | |
| Thiophene | 4-Methyldibenzothiophene | 13 | 10 | 1 | 198.28 | 65 | 298 | ||
| Thiophene | 4,6-Dimethyldibenzothiophene | 14 | 12 | 1 | 212.31 | 153 | |||
| Thiophene | Benzonaphtho(2,1-d)thiophene | 16 | 10 | 1 | 234.32 | 189 | |||
| Thiophene | 4,6-Diethyldibenzothiophene | 16 | 16 | 1 | 240.36 | 49 | |||
| * Values estimated for 1 atm from low pressure measurements | |||||||||
Definition of organic compounds
Hydrocarbon: An organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon.
Alkane: An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula CnH2n+2. Also called paraffin.
Alkyl: An alkyl group is an alkane substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula CnH2n+1
Phenyl: An phenyl group is a benzene substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula C6H5.
Organic sulfur compounds:
Thiol: An organosulfur compound that contains a carbon-bonded sulfhydryl group (-SH), with the general formula R–SH (where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent). For thiols in this document the R represents an alkyl group, and in a 1-thiol the -SH group is located at the end of the alkyl chain. In a 2-thiol and a 3-thiol the -SH group is located at the second and third carbon atom in the alkyl chain, respectively. Also called mercaptan.
Sulfide: An organic compound of the form R’–S–R’’ (where R’ and R’’ represents an alkyl or other organic substituent).
Dialkyl sulfide: A sulphide where R’ and R’’ are linear alkyl groups, and of the same length.
Methyl alkyl sulfide: A sulphide where R’ is a methyl group and R’’ are any alkyl group.
Ethyl alkyl sulfide: A sulphide where R’ is an ethyl group and R’’ are any alkyl group.
Isopropyl alkyl sulphide: A sulphide where R’ is an isopropyl group and R’’ are any alkyl group.
Diisoalkyl sulphide: A sulphide where R’ and R’’ are isoalkyl groups, and of the same length.
Disulfide: An organic compound of the form R’–S-S–R’’ (where R’ and R’’ represents an alkyl or other organic substituent).
Thiophene: A heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a stable, flat five-membered ring.
Alkylthiophene: A monosubstituted thiophene with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of the thiophene ring, with the general formula CnH(2n+1)C4H3S
Benzothiophene: A polycyclic aromatic compound consisting of a benzene ring connected to a thiophene ring, with the formula C8H6S.



