Air - Diffusion Coefficients of Gases in Excess of Air
Diffusion coefficients (D12) for gases in large excess of air at temperatures ranging 0 - 400 °C.
Fick's first law states that a substance will flow from a region with high concentration to a region of low concentration. Fick's law can be expressed as
J = -D dφ/dx (1)
where
J = diffusion flux - the amount of substance that flows through an unit area per unit time (mass or mol/(m2s))
D = diffusion coefficient (m2/s)
dφ = change in concentration of substance (mass or mol/m3)
dx = change in length (m)
For simple one-dimensional transport, the diffusion coefficient describes the time–rate of change of concentration. The diffusion coefficient varies from substance to substance and with temperature and pressure.
Figure and table below shows the diffusion coefficients, D12 , for binary gas mixtures where air is in large excess.
See also Air Composition and molecular weight, Density at varying pressure, Density and specific weight at varying temperature, Diffusion coefficients for gases in air, Dynamic (absolute) and kinematic viscosity, Prandtl Number, Specific heat at varying temperature and Specific heat at varying pressure, Thermal conductivity, Thermal diffusivity, Properties at gas-liquid equilibrium conditions and Air properties, for other properties of air, as well as Diffusion coefficients of gases in water and Carbon dioxide concentrations in rooms with people
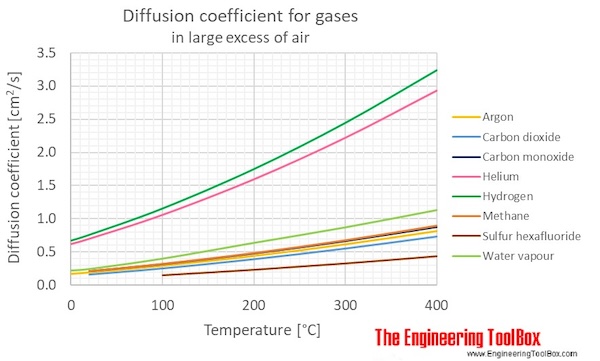
| Gases in large excess of air | Diffusion coefficient, D12 , (cm2/s) at atmospheric pressure and given temperatures | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 °C | 20 °C | 100 °C | 200 °C | 300 °C | 400 °C | ||
| Name | Formula | 32 °F | 68 °F | 212 °F | 392 °F | 572 °F | 752 °F |
| Argon | Ar | 0.167 | 0.189 | 0.289 | 0.437 | 0.612 | 0.81 |
| Methane | CH4 | 0.21 | 0.321 | 0.485 | 0.678 | 0.899 | |
| Carbon monoxide | CO | 0.208 | 0.315 | 0.475 | 0.662 | 0.875 | |
| Carbon dioxide | CO2 | 0.16 | 0.252 | 0.39 | 0.549 | 0.728 | |
| Hydrogen | H2 | 0.668 | 0.756 | 1.153 | 1.747 | 2.444 | 3.238 |
| Water vapour | H2O | 0.219 | 0.242 | 0.399 | 0.638 | 0.873 | 1.135 |
| Helium | He | 0.617 | 0.697 | 1.057 | 1.594 | 2.221 | 2.933 |
| Sulfur hexafluoride | SF6 | 0.15 | 0.233 | 0.329 | 0.438 | ||



