Pollution Concentration in Rooms
Concentration of a pollution in a limited space as a room depends on the amount of polluted material spread in the room, supply of fresh air, outlets positions and construction, principles used for supply and outlet from the space.
The concentration of a pollution in a limited space as a room, container, tank etc. depends on
- amount of polluted material spread in the room or space
- amount of fresh supply air or fluid
- the outlet positions and constructions
- the principles used for supply and outlet from the space
- fluid flow in the space
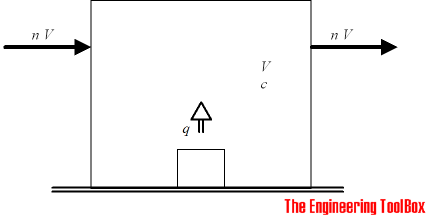
The generic equation for pollution concentration (amount of polluting product to amount of fluid in space (like air a room)) can be calculated
c = q / n V (1 - e-nt) + (c1 - c2) e-nt + c2 (1)
where
c = concentration in the space (or in the room) at perfect mix (m3/m3) (kg/kg)
q = amount of pollution added to the space (m3/h) (kg/h)
n = volume changes per hour (h-1)
V = volume or mass of the space (m3) (kg)
e = the number 2.72..
t = time (h)
c1 = concentration in the space at start (m3/m3) (kg/kg)
c2 = concentration in the supply fluid (m3/m3) (kg/kg)
If the start concentration (t = 0) of the space and the concentration in the supply fluid is zero, equation (1) can be reduced to
c = q / n V (1 - e-nt) (2)
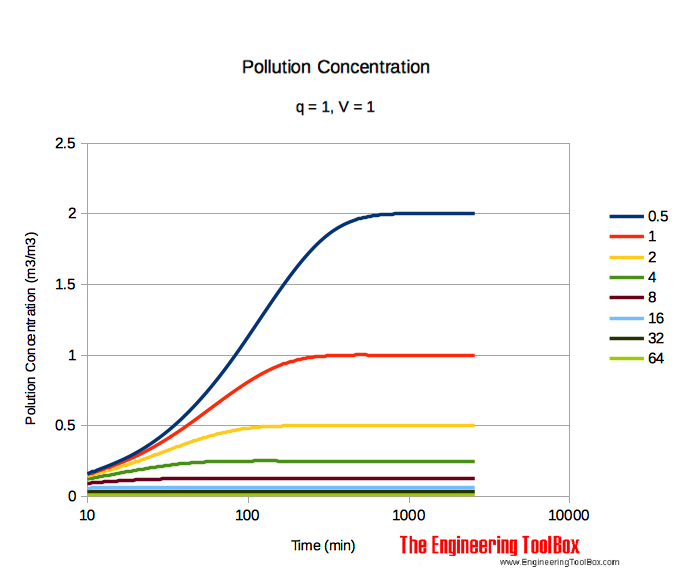
Note! After some time the concentration in the room will stabilize. The table below shows the value of c when the amount of pollution q = 1, and the volume of the space V = 1.
For full table - rotate the screen!
| Volume changes per hour (1/h) | Concentration of pollution - c - (m3/m3) (kg/kg) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time - t - (min) | |||||||||
| 10 | 20 | 40 | 80 | 160 | 320 | 640 | 1280 | 2560 | |
| 0.5 | 0.1599 | 0.3070 | 0.5669 | 0.9732 | 1.4728 | 1.8610 | 1.9903 | 2.0000 | 2.0000 |
| 1 | 0.1535 | 0.2835 | 0.4866 | 0.7364 | 0.9305 | 0.9952 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 2 | 0.1417 | 0.2433 | 0.3682 | 0.4653 | 0.4976 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 |
| 4 | 0.1216 | 0.1841 | 0.2326 | 0.2488 | 0.2500 | 0.2500 | 0.2500 | 0.2500 | 0.2500 |
| 8 | 0.0921 | 0.1163 | 0.1244 | 0.1250 | 0.1250 | 0.1250 | 0.1250 | 0.1250 | 0.1250 |
| 16 | 0.0582 | 0.0622 | 0.0625 | 0.0625 | 0.0625 | 0.0625 | 0.0625 | 0.0625 | 0.0625 |
| 32 | 0.0311 | 0.0312 | 0.0312 | 0.0313 | 0.0313 | 0.0313 | 0.0313 | 0.0313 | 0.0313 |
| 64 | 0.0156 | 0.0156 | 0.0156 | 0.0156 | 0.0156 | 0.0156 | 0.0156 | 0.0156 | 0.0156 |