Piping Materials - Temperature Expansion Coefficients
Temperature expansion coefficients for materials used in pipes and tubes like aluminum, carbon steel, cast iron, PVC, HDPE and more.
Expansion coefficients that can be used to calculate temperature expansion of pipes and tubes - are indicated in the table below:
| Material | Expansion Coefficients | |
|---|---|---|
| 10-6 in/in oF | 10-6m/m oC | |
| Aluminum | 12.8 | 23.1 |
| Carbon Steel | 6.5 | 11.7 |
| Cast Iron | 5.9 | 10.6 |
| Copper | 9.3 | 16.8 |
| Stainless Steel | 9.9 | 17.8 |
| ABS Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | 35.0 | 63.0 |
| HDPE High density polyethylene | 67.0 | 120.0 |
| PE Polyethylene | 83.0 | 150.0 |
| CPVC Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride | 44.0 | 79.0 |
| PVC Polyvinyl chloride | 28.0 | 50.4 |
- in/in oF = 1200 in/100ft oF = 1.8 m/moC
Note! The higher expansion coefficients for plastic materials makes plastic pipes and tubes extremely sensitive to temperature changes. Always pay attention to plastic pipes and tubes when temperature varies.
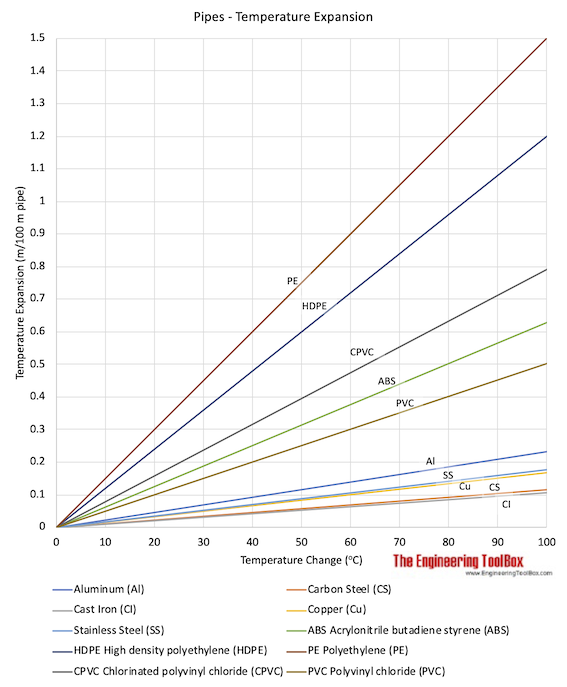
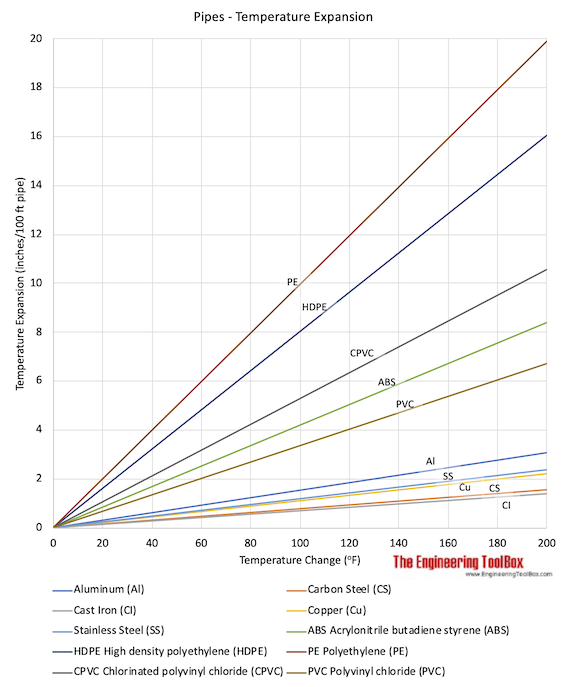
Example - Thermal Expansion of a PVC Pipe
A PVC pipe with length 6 m is heated from 0 oC to 60 oC.
Expansion of the pipe can be calculated as
dl = (50.4×10-6 m/m oC) (6 m) ((60 oC) - (0 oC))
= 0.018 m
= 1.8 cm



