Restricted Thermal Expansion - Force and Stress
Stress and force when thermal expansion a pipe, beam or similar is restricted.
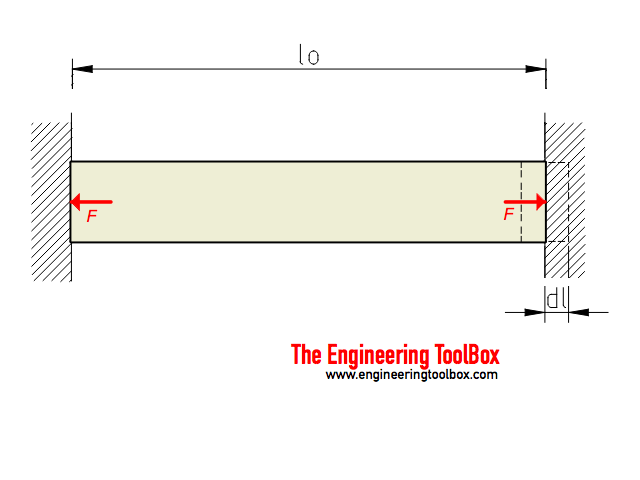
Linear expansion due to change in temperature can be expressed as
dl = α lo dt (1)
where
dl = elongation (m, in)
α = temperature expansion coefficient (m/mK, in/in oF)
lo = initial length (m, in)
dt = temperature difference (oC, oF)
The strain - or deformation - for an unrestricted expansion can be expressed as
ε = dl / lo (2)
where
ε = strain - deformation
The Elastic modulus (Young's Modulus) can be expressed as
E = σ / ε (3)
where
E = Young's Modulus (Pa (N/m2), psi)
σ = stress (Pa (N/m2), psi)
Thermal Stress
When restricted expansion is "converted" to stress - then (1), (2) and (3) can be combined to
σdt = E ε
= E dl / lo
= E α lo dt / lo
= E α dt (4)
where
σdt = stress due to change in temperature (Pa (N/m2), psi)
Axial Force
The axial force acted by the restricted bar due to change in temperature can be expressed as
F = σdt A
= E α dt A (5)
where
F = axial force (N)
A = cross-sectional area of bar (m2, in2)
Example - Heated Steel Pipe - Thermal Stress and Force with Restricted Expansion
A DN150 Std. (6 in) steel pipe with length 50 m (1969 in) is heated from 20 oC (68 oF) to 90 oC (194 oF). The expansion coefficient for steel is 12×10-6 m/mK (6.7×10-6 in/inoF). The modulus of elasticity for steel is 200 GPa (109 N/m2) (29×106 psi (lb/in2)).
make 3D models with The Engineering ToolBox Sketchup Extension
Expansion of unrestricted pipe:
dl = (12×10-6 m/mK) (50 m) ((90 oC) - (20 oC))
= 0.042 m
If the expansion of the pipe is restricted - the stress created due to the temperature change can be calculated as
σdt = (200×109 N/m2) (12×10-6 m/mK) ((90 oC) - (20 oC))
= 168 106 N/m2 (Pa)
= 168 MPa
Note! - if there is pressure in the pipe - the axial and circumferential (hoop) stress may be added to restricted temperature expansion stress by using vector addition.
The outside diameter of the pipe is 168.275 mm (6.63 in) and the wall thickness is 7.112 mm (0.28 in). The cross-sectional area of the pipe wall can then be calculated to
A = π ((168.275 mm) / 2)2 - π ((168.275 mm) - 2 (7.112 mm)) / 2)2
= 3598 mm2
= 3.6 10-3 m2
The force acting at the ends of the pipe when it is restricted can be calculated as
F = (168×106 N/m2) (3.6×10-3 m2)
= 604800 N
= 604 kN
The calculation in Imperial units
Expansion of unrestricted pipe:
dl = (6.7×10-6 in/inoF) (1669 in) ((194 oF) - (68 oF))
= 1.4 in
Stress in restricted pipe:
σdt = (29×106 lb/in2) (6.7×10-6 in/inoF) ((194 oF) - (68 oF))
= 24481 lb/in2 (psi)
Cross sectional area:
A = π ((6.63 in) / 2)2 - π ((6.63 in) - 2 (0.28 mm)) / 2)2
= 5.3 in2
Axial force acting at the ends:
F = (24481 lb/in2) (5.3 in2)
= 129749 lb
Example - Thermal Tensions in Reinforced or Connected Materials
When two materials with different temperature expansion coefficients are connected - as typical with concrete and steel reinforcement, or in district heating pipes with PEH insulation etc. - temperature changes introduces tensions.
This can be illustrated with a PVC plastic bar of 10 m reinforced with a steel rod.
The free expansion of the PVC bar without the reinforcement - with a temperature change of 100 oC - can be calculated from (1) to
dlPVC = (50.4×10-6 m/mK) (10 m) (100 oC)
= 0.054 m
The free expansion of the steel rod with a temperature change of 100 oC - can be calculated from (1) to
dlsteel = (12×10-6 m/mK) (10 m) (100 oC)
= 0.012 m
If we assume that the steel rod is much stronger than the PVC bar (depends on the Young's modulus and the areas of the materials) - the tension in the PVC bar can be calculated from the difference in temperature expansion with (4) as
σPVC = (2.8×109 Pa) (0.054 m - 0.012 m) / (10 m)
= 11.8 106 Pa
= 11.8 MPa
The Tensile Yield Strength of PVC is approximately 55 MPa.
Thermal Expansion Axial Force Calculator
This calculator can be used to calculate the axial force caused by an object with restricted temperature expansion. The calculator is generic and can be used for both metric and imperial units as long as the use of units are consistent.



