Air - Humidifying with Steam, SI units
Using steam to humidify air.
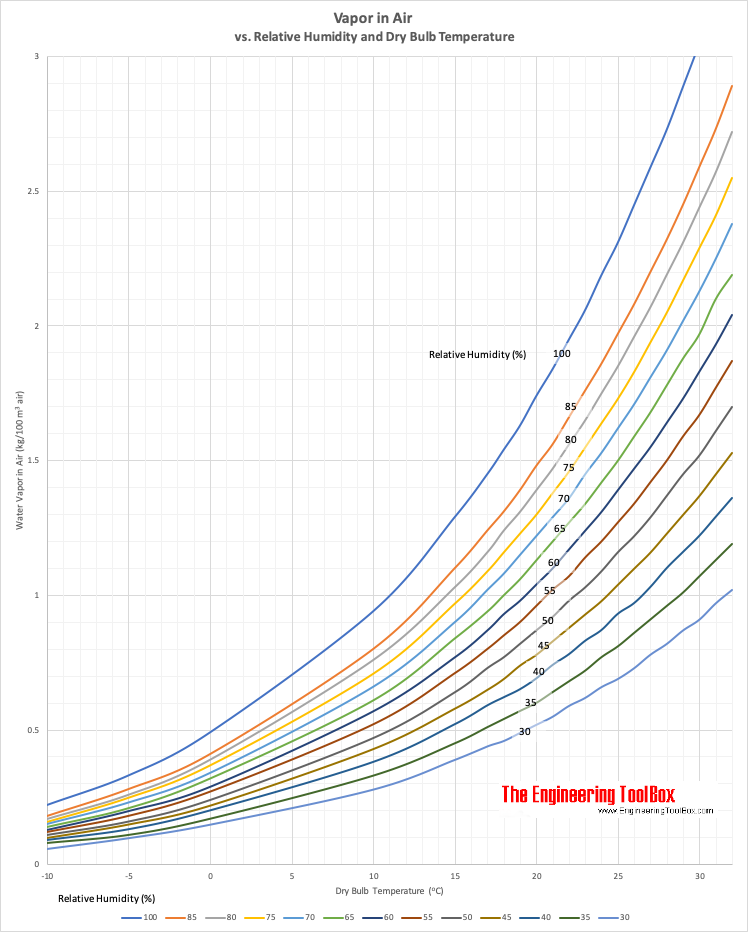
The amount of vapor in 100 m3 air volume is indicated below.
For full table - rotate the screen!
| Dry Bulb Temperature (oC) | Vapor in Air (kg per 100 m3air) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative Humidity (%) | |||||||||||||
| 100 | 85 | 80 | 75 | 70 | 65 | 60 | 55 | 50 | 45 | 40 | 35 | 30 | |
| 32 | 3.39 | 2.89 | 2.72 | 2.55 | 2.38 | 2.19 | 2.04 | 1.93 | 1.7 | 1.53 | 1.36 | 1.19 | 1.02 |
| 31 | 3.22 | 2.73 | 2.57 | 2.41 | 2.25 | 2.1 | 1.93 | 1.77 | 1.61 | 1.45 | 1.29 | 1.13 | 0.97 |
| 30 | 3.05 | 2.59 | 2.44 | 2.29 | 2.13 | 1.97 | 1.83 | 1.67 | 1.52 | 1.37 | 1.22 | 1.07 | 0.91 |
| 29 | 2.89 | 2.45 | 2.31 | 2.17 | 2.02 | 1.88 | 1.73 | 1.59 | 1.45 | 1.3 | 1.16 | 1.01 | 0.87 |
| 28 | 2.73 | 2.32 | 2.19 | 2.05 | 1.91 | 1.78 | 1.64 | 1.5 | 1.37 | 1.23 | 1.1 | 0.96 | 0.82 |
| 27 | 2.59 | 2.2 | 2.07 | 1.94 | 1.81 | 1.68 | 1.55 | 1.42 | 1.29 | 1.16 | 1.03 | 0.91 | 0.78 |
| 26 | 2.45 | 2.08 | 1.96 | 1.83 | 1.71 | 1.59 | 1.47 | 1.34 | 1.22 | 1.1 | 0.97 | 0.86 | 0.73 |
| 25 | 2.31 | 1.97 | 1.85 | 1.73 | 1.62 | 1.5 | 1.39 | 1.27 | 1.16 | 1.04 | 0.93 | 0.81 | 0.69 |
| 24 | 2.19 | 1.86 | 1.75 | 1.64 | 1.53 | 1.42 | 1.31 | 1.2 | 1.09 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.66 |
| 23 | 2.06 | 1.76 | 1.63 | 1.55 | 1.45 | 1.34 | 1.24 | 1.14 | 1.03 | 0.93 | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.62 |
| 22 | 1.95 | 1.66 | 1.56 | 1.46 | 1.36 | 1.27 | 1.17 | 1.07 | 0.98 | 0.88 | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.59 |
| 21 | 1.84 | 1.56 | 1.47 | 1.38 | 1.29 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.02 | 0.92 | 0.83 | 0.74 | 0.67 | 0.55 |
| 20 | 1.74 | 1.48 | 1.39 | 1.3 | 1.22 | 1.13 | 1.04 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.69 | 0.61 | 0.52 |
| 19 | 1.63 | 1.39 | 1.31 | 1.23 | 1.15 | 1.06 | 0.98 | 0.9 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.65 | 0.57 | 0.49 |
| 18 | 1.54 | 1.31 | 1.24 | 1.16 | 1.08 | 1 | 0.93 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.69 | 0.62 | 0.54 | 0.46 |
| 17 | 1.45 | 1.24 | 1.16 | 1.09 | 1.02 | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.8 | 0.73 | 0.65 | 0.59 | 0.51 | 0.44 |
| 15 | 1.29 | 1.1 | 1.03 | 0.97 | 0.9 | 0.84 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 0.58 | 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.39 |
| 10 | 0.94 | 0.8 | 0.76 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 0.61 | 0.57 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.43 | 0.38 | 0.33 | 0.28 |
| 0 | 0.49 | 0.41 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.2 | 0.17 | 0.15 |
| -5 | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.2 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.1 |
| -10 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.06 |
Note! In a psychrometric chart or in a Mollier diagram the amount of vapor humidity ratio - x - is indicated in kg/kgdry air (kg vapor per kg dry air). The values above can be transformed to kg/kgdry air by dividing the values with the air density at the actual temperature.
Example - Humidifying Air with Steam
Air at 20 oC and 30% relative humidity are humidified to 20 oC and 80% relative humidity.
From the table above it can be estimated that air at 20 oC and 30% relative humidity contains 0.52 kg water vapor per 100 m3 air volume. Air at 20 oC and 80% relative humidity contains 1.39 kg per 100 m3 air volume.
The amount of water vapor required per 100 m3 air volume can be calculated like
Amount of Water Vapor
= (1.39 kg/100 m3 air volume) - (0.52 kg/100 m3 air volume)
= 0.87 (kg/100 m3 air volume)