Air - Heating, Cooling, Mixing, Humidifying or Dehumidifying Processes
Basic air changing state processes - heating, cooling, mixing, humidifying and dehumidifying by adding steam or water - psychometric diagrams and the Mollier charts.
The most common air condition processes are
- heating air
- mixing air
- cooling and dehumidifying air
- humidifying air by adding steam and/or water
Heating Air
The process of heating air can be visualized in the Mollier diagram as:
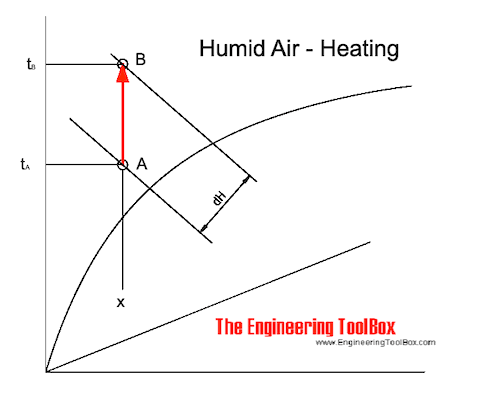
The heating process moves the air condition from state A to state B along a constant specific humidity - x - line. The specific heat supplied - dH - to the air is as indicated in the diagram.
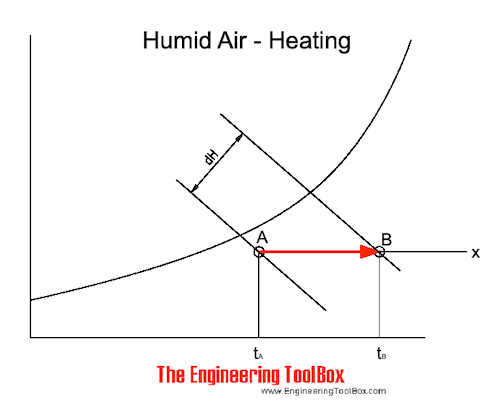
The air heating process can also be expressed in the psychrometric chart:
Mixing Air of different States
When mixing air of state A and state C - the mixing point will be on the straight line between the two states - in point B.
The position of point B depends on the volume of the air at state A related to the volume of the air at state C.
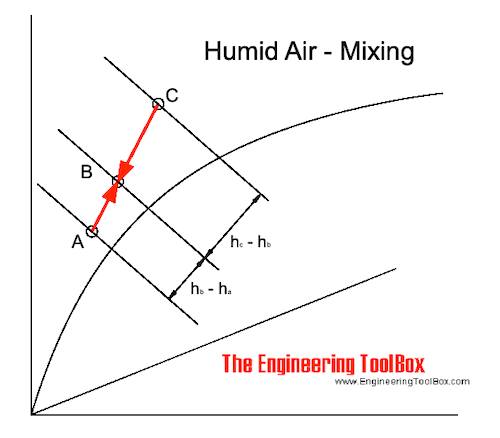
A heat balance for the mixture can be expressed as
mA hA + mC hC = (mA + mC) hB (1)
where
m = mass of the air (kg)
h = heat of the air (J/kg)
The moisture balance for the mixture can be expressed as:
mA xA + mC xC = (mA + mC) xB (2)
where
x = specific humidity in the air (kgh2o/kgdry_air)
When hot air is mixed with cold air it results in fog if the mixing point is below the saturation line of the air. When there is fog parts of the moisture in the air condense to small droplets floating in the air. The "fog process" can be expressed in the Mollier diagram as
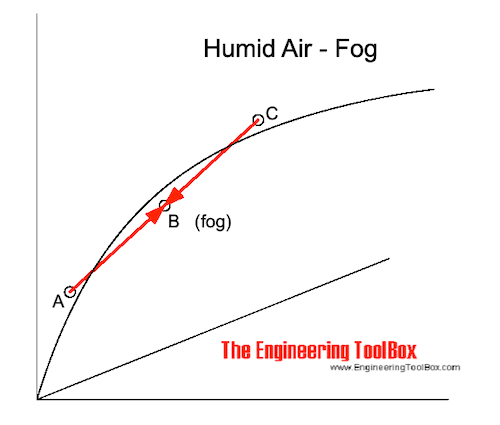
Cooling and Dehumidifying Air
With a cold surface exposed to moist air the air close to the surface may be cooled down below the saturation line. Humidity in the air close to the surface will then condensate on the surface and the air as a whole will be dehumidified.
If the temperature on the cooling surface is higher than the Dew Point Temperature - tDP - air cools along a constant specific humidity - x - line.
The cooling process of air can be expressed in the Mollier diagram as
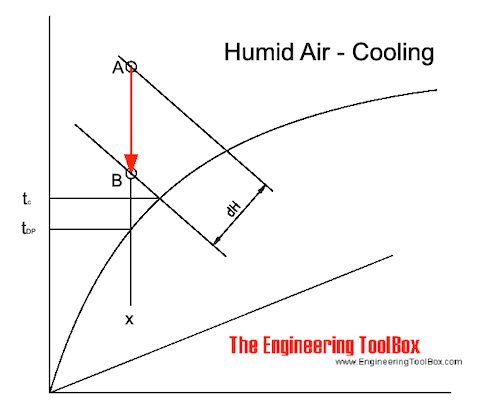
It the temperature on the cooling surface is lower than the Dew Point Temperature - tDP, air cools in the direction of a point C as indicated below.
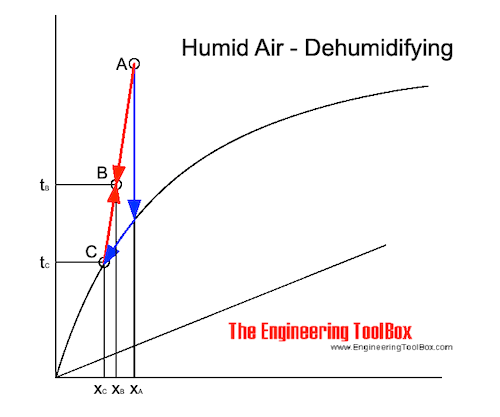
Vapor in the air condensates on the surface, and the the amount of water condensated will be xA - xB.
Humidifying, Adding Steam or Water
If water is added to air without any heat supply, the air condition changes adiabatic along a constant enthalpy line - h. The dry temperature of the air decreases as shown in the Mollier diagram below.
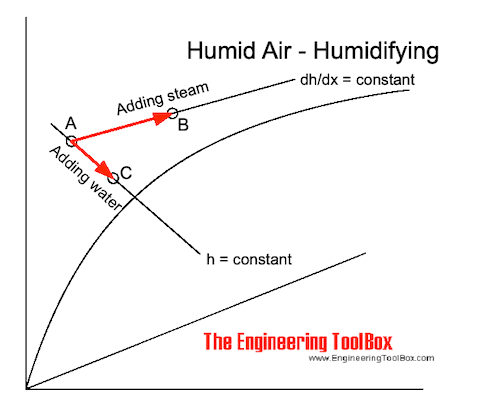
If steam is added to the air, air condition changes along a constant dh/dx line as shown above.
When adding saturated steam at atmospheric pressure the temperature rise is very small - in general less than 1 oC. For practical purposes the process of adding saturated steam at atmospheric pressure approximates the horizontal temperature line in the Mollier diagram.



