Air and Steam Mixtures
Air in the steam will lower the surface temperatures in heat exchangers - and less heat will be transferred.
Air in the steam will cause the temperatures on heat-exchangers surfaces to be lower than expected due to the saturation temperatures in the steam tables. The heat transfer will be reduced and the system efficiency will be decreased.
Air in steam can be described with the "Daltons Law of Partial Pressure".
Daltons Law of Partial Pressure
The total pressure of a mixture of gases is made up by the sum of the partial pressures of the components in the mixture as known from Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures:
| The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases! |
The total pressure in a mixture of steam and air can be expressed as:
p = pa + ps (1)
where
pa = partial pressure of air (Pa, bar, psi)
ps = partial pressure of steam (Pa, bar, psi)
The Partial Pressure in a Mixture
The partial pressure is the pressure exerted by each component as if it was occupying the same volume of the mixture. The effective partial pressure of the steam can be expressed as:
ps_effective = vs / V p (2)
where
ps_ effective = effective steam pressure, absolute (Pa, bar, psi)
vs = volume of steam (m3, in3)
V = volume of mixture (m3, in3)
p = absolute pressure (Pa, bar, psi)
Reducing the part of steam reduces the effective steam pressure. Increasing the part of steam (until 100%) increases the effective pressure.
Example - Mix of Air and Steam
The effective pressure in a steam/air mixture made up by 3 parts steam and 1 part air, with total pressure 5 bar absolute, can be expressed as:
ps_effective = (3 parts) / (3 parts + 1 part) (5 bar abs)
= 3.75 bar absolute
Important! Since the steam has an effective pressure of 3.75 bar instead of the pressure of 5 bar a, the mixture would have a temperature of approximately 139 oC rather than the expected saturation temperature of 152 oC. This has a major effect on the heat transfer capability of an heat exchanger.
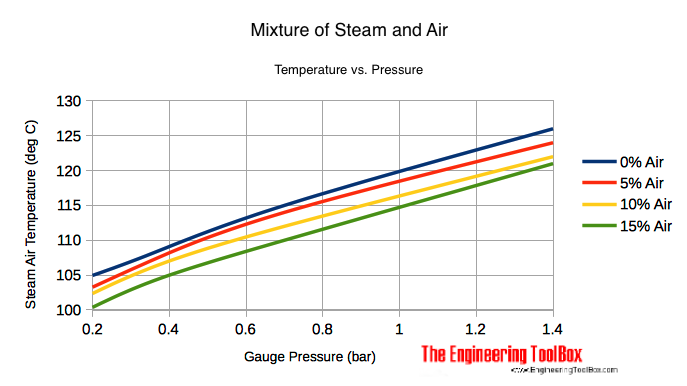
Mixing Air and Steam - Result Temperature
| Mixture Pressure | 0% Air (Pure Steam) | 5% Air | 10% Air | 15% Air | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (psig) | (bar) | (oF) | (oC) | (oF) | (oC) | (oF) | (oC) | (oF) | (oC) |
| 2 | 0.15 | 219 | 104 | 216 | 102 | 213 | 101 | 210 | 99 |
| 5 | 0.35 | 227 | 108 | 225 | 107 | 222 | 106 | 219 | 104 |
| 10 | 0.7 | 239 | 115 | 237 | 114 | 233 | 112 | 230 | 110 |
| 20 | 1.4 | 259 | 126 | 256 | 124 | 252 | 122 | 249 | 121 |
Related Topics
-
Steam and Condensate
Design of steam & condensate systems with properties, capacities, sizing of pipe lines, system configuration and more. -
Thermodynamics
Calculate heat, work, temperature and energy. The thermodynamics of steam and condensate systems. Water and Ice properties.
Related Documents
-
Air - Heating, Cooling, Mixing, Humidifying or Dehumidifying Processes
Basic air changing state processes - heating, cooling, mixing, humidifying and dehumidifying by adding steam or water - psychometric diagrams and the Mollier charts. -
Air - Humidifying by Adding Steam or Water
Air can be humidified by adding water or steam. -
Air - Humidifying with Steam - Imperial Units
Estimate the amount of steam required (lb/h in 100 cfm) in humid air. -
Air - Humidifying with Steam, SI units
Using steam to humidify air. -
Air - Moisture Holding Capacity vs. Temperature
The moisture holding capacity of air increases with temperature. -
Dalton's Law
Gibbs' Dalton's law of the total pressure of a mixture of gases. -
Humidifiers
Sprayed coils, spinning discs and steam humidifiers. -
Mixing of Humid Air
The change in state wwhen mixing moist air - enthalpy, heat, temperature and specific humidity. -
Moist Air - Density vs. Water Content and Temperature
Density of the mix of dry air and water vapor - moist humid air. -
Moist Air - Partial Pressure and Daltons Law
The pressure in a mixture of dry air and water vapor - humid or moist air - can be estimated by using Daltons Law of partial pressures. -
Steam Heating Air
Calculate steam heated air systems. -
Steam Heating Processes - Load Calculating
Calculating the amount of steam in non-flow batch and continuous flow heating processes. -
Vapor and Steam
An introduction to vapor and steam.




