Hydrostatic Pressure vs. Depth
Depth and hydrostatic pressure.
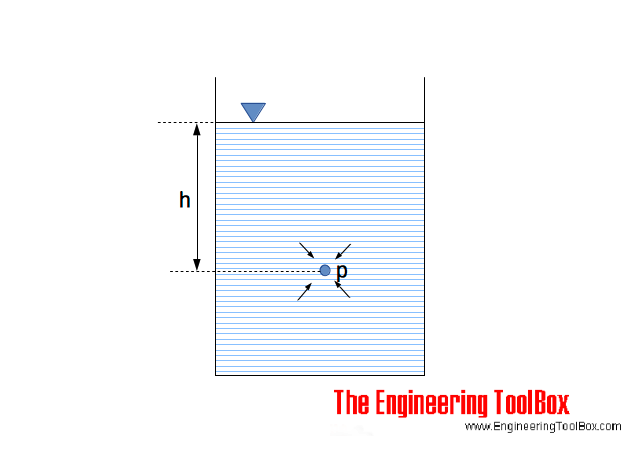
Hydrostatic pressure in a liquid can be calculated as
p = ρ g h (1)
where
p = pressure in liquid (N/m2, Pa, lbf/ft2, psf)
ρ = density of liquid (kg/m3, slugs /ft3)
g = acceleration of gravity (9.81 m/s2, 32.17405 ft/s2)
h = height of fluid column - or depth in the fluid where pressure is measured (m, ft)
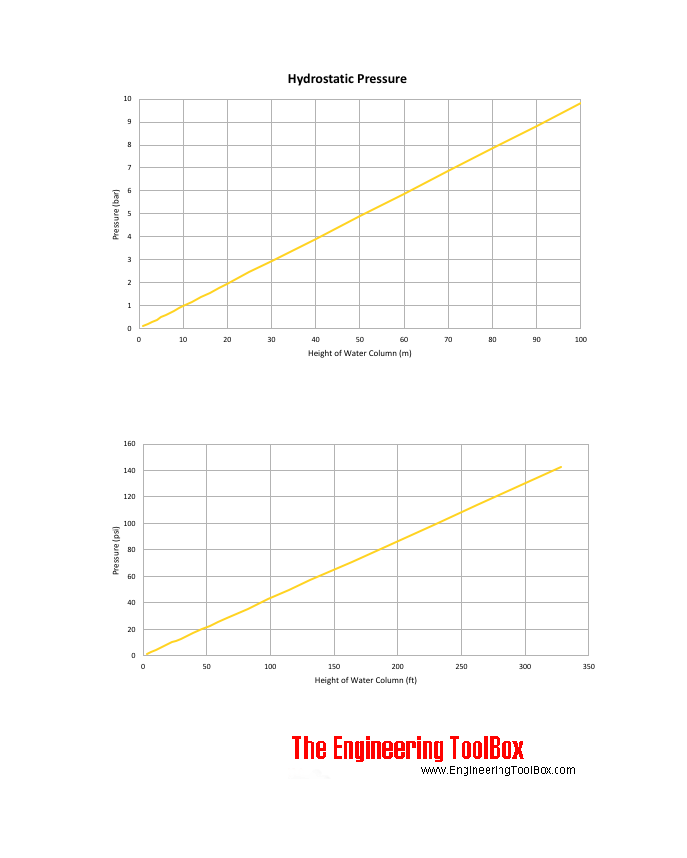
Hydrostatic pressure in a water column - or depth ( density of water 1000 kg/m3):
| Height of Water Column | Pressure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (ft) | (kPa) | (bar) | (atm) | (psi) |
| 1 | 3.28 | 9.81 | 0.098 | 0.097 | 1.42 |
| 2 | 6.56 | 19.6 | 0.196 | 0.194 | 2.85 |
| 3 | 9.84 | 29.4 | 0.294 | 0.290 | 4.27 |
| 4 | 13.1 | 39.2 | 0.392 | 0.387 | 5.69 |
| 5 | 16.4 | 49.1 | 0.491 | 0.484 | 7.11 |
| 6 | 19.7 | 58.9 | 0.589 | 0.581 | 8.54 |
| 7 | 23.0 | 68.7 | 0.687 | 0.678 | 10.0 |
| 8 | 26.2 | 78.5 | 0.785 | 0.775 | 11.4 |
| 9 | 29.5 | 88.3 | 0.883 | 0.871 | 12.8 |
| 10 | 32.8 | 98.1 | 0.981 | 0.968 | 14.2 |
| 12 | 39.4 | 118 | 1.18 | 1.16 | 17.1 |
| 14 | 45.9 | 137 | 1.37 | 1.36 | 19.9 |
| 16 | 52.5 | 157 | 1.57 | 1.55 | 22.8 |
| 18 | 59.0 | 177 | 1.77 | 1.74 | 25.6 |
| 20 | 65.6 | 196 | 1.96 | 1.94 | 28.5 |
| 25 | 82.0 | 245 | 2.45 | 2.42 | 35.6 |
| 30 | 98.4 | 294 | 2.94 | 2.90 | 42.7 |
| 35 | 115 | 343 | 3.43 | 3.39 | 49.8 |
| 40 | 131 | 392 | 3.92 | 3.87 | 56.9 |
| 50 | 164 | 491 | 4.91 | 4.84 | 71.1 |
| 60 | 197 | 589 | 5.89 | 5.81 | 85.4 |
| 70 | 230 | 687 | 6.87 | 6.78 | 100 |
| 80 | 262 | 785 | 7.85 | 7.75 | 114 |
| 90 | 295 | 883 | 8.83 | 8.71 | 128 |
| 100 | 328 | 981 | 9.81 | 9.68 | 142 |
Example - Pressure acting in water at depth 1 m
The density of water at 4 oC is 1000 kg/m3. The pressure acting in water at 1 m can be calculated as
p = ρ g h
= ( 1000 kg/m3) ( 9.81 m/s2) (1 m)
= 9810 Pa
Example - Pressure acting in water at depth 3 ft
The density of water at 32 oF is 1.940 slugs/ft3. The pressure acting in water at 3 ft can be calculated as
p = ρ g h
= ( 1.940 slugs/ft3) ( 32.17405 ft/s2) (3 ft)
= 187.3 lbf/ft2(psf)
= 1.3 lbf/in2(psi)
Ocean Pressure - Depth and Latitude
Ocean pressure varies with depth and position (latitude) on earth.
Depth (m) | Ocean Pressure (MPa) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude (degrees) | |||||||
| 0 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 60 | 75 | 90 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1000 | 10.080 | 10.083 | 10.093 | 10.106 | 10.120 | 10.130 | 10.133 |
| 2000 | 20.208 | 20.215 | 20.234 | 20.261 | 20.288 | 20.308 | 20.315 |
| 3000 | 30.383 | 30.394 | 30.424 | 30.464 | 30.505 | 30.535 | 30.545 |
| 4000 | 40.606 | 40.620 | 40.660 | 40.714 | 40.768 | 40.808 | 40.823 |
| 5000 | 50.874 | 50.892 | 50.942 | 51.010 | 51.079 | 51.129 | 51.147 |
| 6000 | 61.188 | 61.210 | 61.270 | 61.352 | 61.434 | 61.495 | 61.517 |
| 7000 | 71.547 | 71.572 | 71.643 | 71.739 | 71.835 | 71.906 | 71.932 |
| 8000 | 81.949 | 81.979 | 82.059 | 82.170 | 82.280 | 82.361 | 82.391 |
| 9000 | 92.395 | 92.428 | 92.519 | 92.644 | 92.769 | 92.861 | 92.894 |
| 10000 | 102.880 | 102.917 | 103.019 | 103.157 | 103.296 | 103.398 | 103.436 |
- 1 Pa = 10-6 MPa = 10-3 kPa = 10-6 N/mm2 = 10-5 bar = 0.1020 kp/m2 = 1.020×10-4 m H2O at 4°C/39°F = 9.869×10-6 atm = 0.004 in H2O= 1.450×10-4 psi (lbf/in2) = 0.02089 lbf/ft2(psf)



