Carbon Monoxide and Health Effects
Exposure to Carbon Monoxide - CO and health effects.
Carbon monoxide - CO - is an odorless, tasteless, colorless and toxic gas.
Carbon Monoxide poisoning symptoms
Low to moderate poisoning
- headache
- fatigue
- shortness of breath
- nausea
- dizziness
Severe poisoning
- confusion
- vomiting
- loss of muscle coordination
- unconsciousness
Carbon monoxide is a by-product from combustion processes. Any combustion process, fuel burning appliance, vehicle or other device has the potential to produce toxic carbon monoxide gas.
Carbon monoxide is dangerous because it inhibits the blood's ability to carry oxygen to vital organs such as the heart and brain. Inhaled CO will combine with the oxygen carrying hemoglobin in the blood and will form carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) which is not usable for oxygen transport.
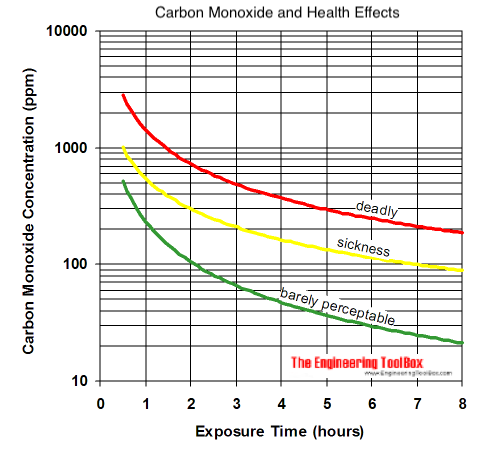
Health effects of Carbon Monoxide
| Exposure (hours) | CO Concentration (ppm)1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Perceptible | Sickness3) | Deadly4) | |
| 0.5 | 600 | 1000 | 2000 |
| 1 | 200 | 600 | 1600 |
| 2 | 100 | 300 | 1000 |
| 4 | 50 | 150 | 400 |
| 6 | 25 | 120 | 200 |
| 8 | 252) | 100 | 150 |
1) ppm - parts per million - is defined as the mass of the component in solution divided by the total mass of the solution multiplied by 106 (one million)
2) The maximum exposure allowed by OSHA in the workplace over an eight hour period is 35 ppm.
3) Typical sickness symptoms are mild headache, fatigue, nausea and dizziness.
4) A CO concentration of 12-13000 ppm is deadly after 1-3 minutes. A CO concentration of 1600 ppm is deadly after one hour.
| Concentration of CO in air (ppm) | Inhalation Time | Toxic Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| 9 | Short term exposure | ASHRAE recommended maximum allowable concentration in living area. |
| 35 | 8 hours | The maximum exposure allowed by OSHA in the workplace over an eight hour period. |
| 200 | 2-3 hours | Slight headache, tiredness, fatigue, nausea and dizziness. |
| 400 | 1-2 hours | Serious headache-other symptoms intensify. Life threatening after 3 hours. |
| 800 | 45 minutes | Dizziness, nausea and convulsions. Unconscious within 2 hours. Death after 2-3 hours. |
| 1600 | 20 minutes | Headache, dizziness and nausea. Death within 1 hour. |
| 3200 | 5-10 minutes | Headache, dizziness, nausea. Death within 1 hour. |
| 6400 | 1-2 minutes | Headache, dizziness, nausea. Death within 25-30 minutes. |
| 12800 | 1-3 minutes | Death within 1-3 minutes |
Related Topics
-
Environment
Climate, meteorology, solar, wind, emissions and environmental related engineering resources. -
Physiology
Human physiology vs. air quality, comfort temperatures, activity and metabolic rates. Health effects of gases adn polutions like carbon monoxide and more. -
Ventilation Systems
Design of systems for ventilation and air handling - air change rates, ducts and pressure drops, charts and diagrams and more.
Related Documents
-
Air Contaminants - Exposure Limits
Exposure limits for various air contaminants. -
Air Supply to a Boiler House
Incomplete boiler combustion may generate carbon monoxide - CO - and re-ignition may cause disastrous effects on personnel and property. -
Ammonia - NH3 - Concentration in Air and Health Effects
Ammonia and health symptoms - smell and threat to life. -
Blood Sugar Units
Convert between blood sugar units. -
Carbon Dioxide Concentration in Rooms Occupied with People
Carbon dioxide concentration in a room may indicate air quality and ventilation system efficiency. -
Carbon Monoxide - CO - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, Physical and Thermal Properties of Carbon Monoxide - CO. -
Carbon Monoxide Gas - CO - Specific Heat vs. Temperature
Carbon Monoxide Gas - CO - specific heat of at temperatures ranging 175 - 6000 K. -
Chemicals Hazard Rating System
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) hazard system for chemical materials. -
Concentration of Carbon Dioxide in the Atmosphere
The atmospheric Carbon Dioxide concentration year 1959 - 2015. -
Garage Ventilation
Exhaust ventilation from garages and workshops. -
Gases - Dangerous Concentration Levels
Dangerous vs. tolerable concentration levels for some industrial gases. -
Human Life Expectancy
Age and life expectancy for men and women. -
Human Need of Air
Fresh air is required for respiration and for transport of heat and vapor emitted from the human body. -
Water Supply Systems - Impurity Limits
Typiclal limits for impurities in drinking water.




