Logarithms
The rules of logarithms - log10 and loge for numbers ranging 1 to 1000.
The logarithm (log) is the inverse operation to exponentiation - and the logarithm of a number is the exponent to which the base - another fixed value - must be raised to produce that number.
The expression
ay = x (1)
can be expressed as the "base a logarithm of x " as
loga(x) = y (1b)
where
a = base
x = antilogarithm
y = logarithm (log)
Example - Logarithm with base 10
Since
103 = 1000
- then the base 10 logarithm of 1000 can be expressed as
log10(1000) = 3
Natural Logarithm - Logarithm with base e (2.7182...)
ey = x
where
e = 2.7182.... - e constant or Euler's number
Base e logarithm of x can be expressed as
loge(x) = ln(x) = y
| System | Log to the base of | Terminology |
|---|---|---|
| loga | a | log to base a |
| log10 = lg | 10 | common log |
| loge = ln | e = 2.718281828459.. | natural log |
| log2= lb | 2 | log to base 2 |
Rules for Logarithmic Calculations
loga(x y) = loga(x) + loga(y) (2)
loga(x / y) = loga(x) - loga(y) (3)
loga(xp) = p loga(x) (4)
loga(1 / x) = - loga(x) (5)
loga(b) = 1 (6)
loga(1) = 0 (7)
loga(0) = undefined (8)
loga(x < 0) = undefined (9)
loga(x) = logc(x) / logc(a) (10)
loga(x → ∞) = ∞ (11)
Example - Logarithm Product Rule
log10((5) (6)) = log10(5) + log10(6)
= 0.6990 + 0.7782
= 1.4772
Conversion of Logarithms
lg(x) = lg(e) ln(x)
= 0.434294 ln(x) (12)
ln(x) = lg(x) / lg(e)
= 2.302585 lg(x) (13)
lb(x) = 1.442695 ln(x)
= 3.321928 lg(x) (15)
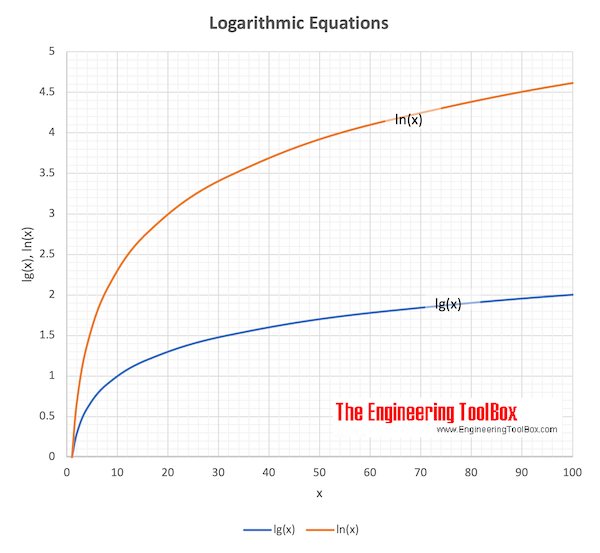
Log10 (x) and Loge (x) for x ranging 1 to 1000




