Moist Air - Relative Humidity
Relative humidity in moist air is the ratio of partial vapor pressure to air pressure.
Humidity is the quantity of water vapor present in air. It can be expressed as an absolute, specific or relative value.
Relative humidity is expressed by
- partial vapor and air pressure,
- density of the vapor and air, or
- by the actual mass of the vapor and air
Relative humidity is usually expressed in per cent and abbreviated by φ or RH.
Relative Humidity and Vapor Partial Pressure
Relative humidity as the ratio of vapor partial pressure in the air - to the saturation vapor partial pressure if the air at the actual dry bulb temperature.
φ = pw / pws 100% (1)
where
φ = relative humidity [%]
pw = vapor partial pressure [mbar]
pws = saturation vapor partial pressure at the actual dry bulb temperature [mbar]. This is the vapour pressure at maximum content of water gas in air, before it starts to condense out as liquid water.
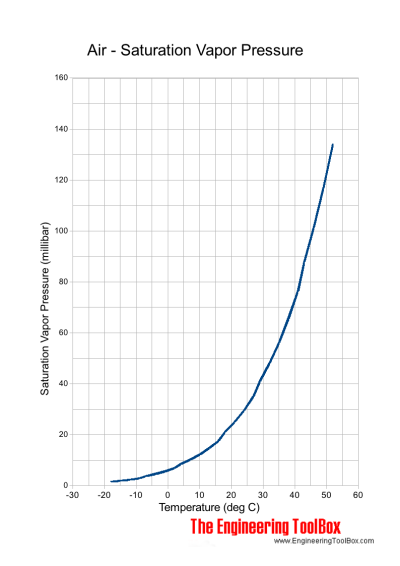
Vapor saturation pressures at different temperatures:
| Temperature | Saturation Vapor Pressure [10-3 bar] | |
|---|---|---|
| [oC] | [oF] | |
| -18 | 0 | 1.5 |
| -15 | 5 | 1.9 |
| -12 | 10 | 2.4 |
| -9 | 15 | 3.0 |
| -7 | 20 | 3.7 |
| -4 | 25 | 4.6 |
| -1 | 30 | 5.6 |
| 2 | 35 | 6.9 |
| 4 | 40 | 8.4 |
| 7 | 45 | 10.3 |
| 10 | 50 | 12.3 |
| 13 | 55 | 14.8 |
| 16 | 60 | 17.7 |
| 18 | 65 | 21.0 |
| 21 | 70 | 25.0 |
| 24 | 75 | 29.6 |
| 27 | 80 | 35.0 |
| 29 | 85 | 41.0 |
| 32 | 90 | 48.1 |
| 35 | 95 | 56.2 |
| 38 | 100 | 65.6 |
| 41 | 105 | 76.2 |
| 43 | 110 | 87.8 |
| 46 | 115 | 101.4 |
| 49 | 120 | 116.8 |
| 52 | 125 | 134.2 |
- 10-3 bar = 1 millibar
- 1 bar = 1000 mbar = 105 Pa (N/m2) = 0.1 N/mm2 = 10,197 kp/m2 = 10.20 m H2O = 0.9869 atm = 14.50 psi (lbf/in2) = 106 dyn/cm2 = 750 mmHg
If the water vapor pressure in the air is 10.3 mbar, the vapor saturates on a surface with 45oF (7oC).
Note! The atmospheric pressure of air is 1013 mbar (101.325 kPa, 760 mmHg). As we can see the maximum water vapor pressure - the saturation pressure - is relatively small.
Example: Relative Humidity and Vapor Pressure
From the table above the saturation pressure at 70oF (21oC) is 25.0 mbar. If the vapor pressure in the actual air is 10.3 mbar the relative humidity can be calculated as:
φ = 10.2 [mbar] / 25.0 [mbar]* 100[%]
= 41[%]
Relative Humidity and Vapor Density
Relative humidity can also be expressed as the ratio of the vapor density of the air - to the saturation vapor density at the the actual dry bulb temperature.
Relative humidity by density:
φ = ρw / ρws 100% (2b)
where
φ = relative humidity [%]
ρw = vapor density [kg/m3]
ρws = vapor density at saturation at actual dry bulb temperature [kg/m3]
A common unit for vapor density is g/m3.
Example: Relative humidity at a given temperature and known vapor density and saturation density
If the actual vapor density at 20oC (68oF) is 10 g/m3 and the saturation vapor density at this temperature is 17.3 g/m3, the relative humidity can be calculated as
φ = 10 [g/m3] / 17.3 [g/m3] *100 [%]
= 57.8 [%]
Relative Humidity and Vapor Mass
Relative humidity can also be expressed as the ratio at actual mass of water vapor in a given air volume - to the mass of water vapor required to saturate at this volume.
Relative humidity can be expressed as:
φ = mw / mws 100% (2c)
where
φ = relative humidity [%]
mw = mass of water vapor in the given air volume [kg]
mws = mass of water vapor required to saturate at this volume [kg]
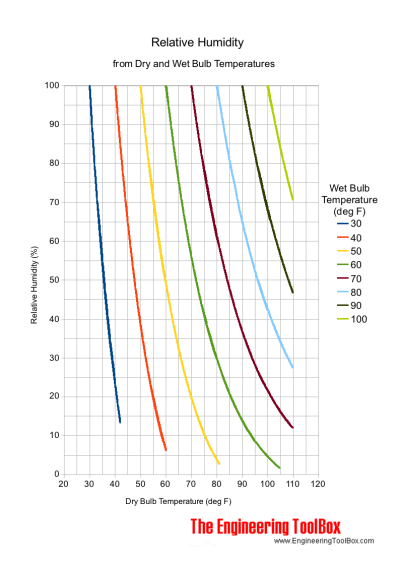
Relative Humidity Chart - degrees Fahrenheit
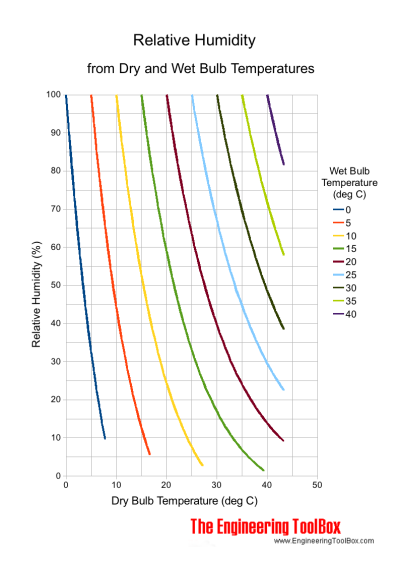
Relative Humidity Chart - degrees Celsius
Altitude and Correction Factors
| Barometric Altitude [mbar] | Abs. Altitude | Correction Factor for φ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| [m] | [ft] | ||
| 1013 | 0 | 0 | 1.000 |
| 1000 | 108 | 354 | 0.987 |
| 989 | 200 | 656 | 0.976 |
| 966 | 400 | 1312 | 0.953 |
| 943 | 600 | 1996 | 0.931 |
| 921 | 800 | 2624 | 0.909 |
| 899 | 1000 | 3281 | 0.887 |
| 842 | 1500 | 4922 | 0.831 |
| 795 | 2000 | 6562 | 0.785 |
Related Topics
-
Air Psychrometrics
Moist and humid air calculations. Psychrometric charts and Mollier diagrams. Air-condition systems temperatures, absolute and relative humidities and moisture content in air.
Related Documents
-
Air - Drying Force
The drying force of air depends on the air moisture holding capacity and the water surface to air evaporation capacity. -
Air - Humidity Measurement from Dry and Wet Bulb Temperature
Relative humidity in moist air can estimated by measuring the dry and wet bulb temperature. -
Air - Humidity Ratio
The mass of water vapor present in moist air - to the mass of dry air. -
Air - Maximum Moisture Carrying Capacity
Maximum water content in humid air vs. temperature. -
Air - Moisture Holding Capacity vs. Temperature
The moisture holding capacity of air increases with temperature. -
Air - SCFM versus ACFM and ICFM
Actual air compressor capacity (ACFM) vs. standard air capacity (SCFM) and inlet air capacity (ICFM). -
Dry Bulb, Wet Bulb and Dew Point Temperatures
Dry Bulb, Wet Bulb and Dew Point temperatures can be used to determine the state of humid air. -
Health and Relative Humidity of Air
The optimum relative humidity ranges for bacteria, viruses, fungi, mites, asthma. -
Indoor Relative Humidity vs. Outdoor Relative Humidity and Temperature
Recommended indoor relative humidity vs. outdoor relative humidity and temperature. -
Moist Air - Cooling and Dehumidifying
Cooling and dehumidifying processes of moist and humid air - sensible and latent cooling. -
Moist Air - Degree of Saturation
Humidity ratio of moist air to humidity ratio of saturated moist air. -
Moist Air - Density vs. Pressure
Density of moist air vs. pressure ranging 75 - 1000 mmHg. -
Moist Air - Partial Pressure and Daltons Law
The pressure in a mixture of dry air and water vapor - humid or moist air - can be estimated by using Daltons Law of partial pressures. -
Moist Air - Psychrometric Table for Pressure 29.92 inHg
Dry and wet bulb temperatures, saturation pressure, water vapor weight, specific volume, heat and more. -
Moist Air - Psychrometric Terms
Dry and wet bulb temperature, specific volume, relative humidity, enthalpy and more. -
Moist Air - Specific vs. Relative Humidity
Specific humidity of moist air vs. relative humidity, water vapor and air density. -
Moist Air - Vapor Pressure
Vapor pressures vs. dry and wet bulb temperatures in moist air. -
Relative Humidity in Production and Process Environments
Recommended relative humidity in production and process environments - like libraries, breweries, storages and more. -
Removing Heat with Air
Calculating heat removed with air by measuring the wet bulb temperature. -
Saturated Salt Solutions - Controlling Air Humidity
A salt solutions can be used maintain a particular value of relative humidity. -
Water - Saturation Pressure vs. Temperature
Online calculator, figures and tables with water saturation (vapor) pressure at temperatures ranging 0 to 370 °C (32 to 700°F) - in Imperial and SI Units. -
Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT)
The Wet Bulb Globe Temperature can be used to measure the general Heat-Stress index.