Buoyancy
Buoyancy is the resultant force acting on a submerged body.
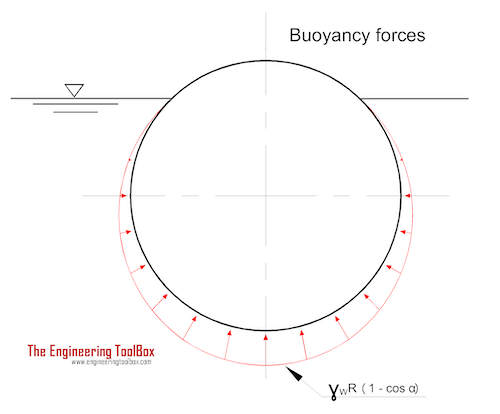
Buoyancy is defined as the tendency of a body to float or rise when submerged in a fluid. The resultant force acting on a submerged body by the fluid is called the buoyant force and can be expressed as
F = V γ
= V ρ g (1)
where
F = buoyant force (N)
V = body volume (m3)
γ = ρ g = specific weight of fluid (N/m3)
ρ = density of fluid (kg/m3)
g = acceleration of gravity (= 9.81 m/s2)
The buoyant force acts upwards.
Archimedes' principle indicates that
"the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body fully or partially submerged in a fluid - equals to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces"
- if the body weighs more than the fluid - it sinks
- if the body weighs less than the fluid - it floats
Example - Buoyant Force acting on a Floating Box
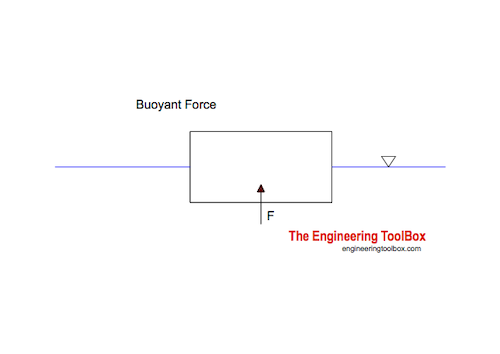
A plastic box with length 0.3 m and width 0.4 m is submerged 0.1 m into water. The water density is 1000 kg/m 3.
The buoyant force acting on the box can be calculated with (1)
F = (0.3 m) (0.4 m) (0.1 m) ( 1000 kg/m3) ( 9.81 m/s2)
= 119 N



