Power
Power is the rate at which work is done or energy converted.
Work done
Power is a measure of the rate at which work is done - work done per unit time - and can be expressed as
P = Work / time
= W / dt (1)
where
P = power (W, ft lb/s)
W = work done (J, ft lb)
dt = time taken (s)
Work can be expressed as
W = F s (1b)
where
F = force (N, lb)
s = distance (m, ft)
Since work is the product of the applied force and the distance, power (1) can be modified to
P = F v (1c)
where
F = force (N, ft)
v = velocity (m/s, ft/s)
Energy converted
Power is also a measure of the rate at which energy is converted from one form to another and can be expressed as
P = E / dt (2)
where
P = power (W, ft lb/s)
E = energy converted (J, ft lb)
dt = time taken (s)
Example - Power needed to lift a Mass
A mass of 1000 kg is lifted 10 m in 10 seconds.
The work done can be calculated as
W = (1000 kg) (9.81 m/s2) (10 m)
= 98100 J (Nm)
The power required is work done per unit time
P = (98100 J) / (10 s)
= 9810 W (J/s)
= 9.8 kW
Example - Work done by an Electric Motor
The work done by a 1 kW electric motor in 1 hour can be calculated by modifying (1) to
W = P dt
= (1 kW) (1000 W/kW) (1 h) (3600 s/h)
= 3600000 J
= 3600 kJ
Example - Electric Winch lifting a Mass
An electric winch is lifting a mass of 100 kg 10m above the ground. The electric motor in the winch is 500 W. The force (weight) acting on the mass due to the acceleration of gravity can be calculated as
F = m g
= (100 kg) (9.81 m/s2)
= 981 N
= 0.98 kN
The work done by the winch can be calculated with (1b) as
W = F s
= (981 N) (10 m)
= 9810 Nm (J)
The time required for the winch with the actual motor to lift the mass can be calculated by modifying (1)
dt = W / P
= (9810 J) / (500 W)
= 19.6 s
Power - kW versus Horsepower

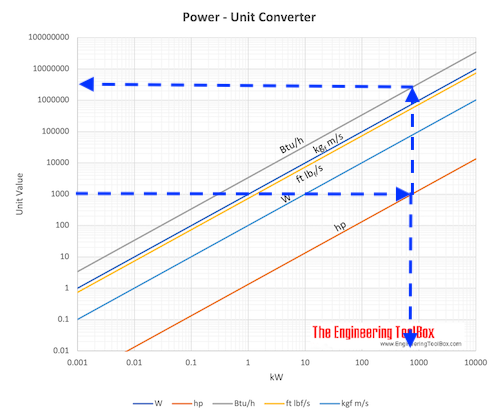
Download and print Power - Unit Converting Chart
Power can also be expressed in horsepower (hp):
1 kW = 1.341 hp
1 hp = 0.7457 kW
- 1 kW = 1000 W = 3412 Btu/h = 737.6 ft lbf/s = 1.3596 hp(M) (ps) = 1.341 hp(I) (bhp) = 101.97 kgf m/s = 737.6 ft lbf/s
- 1 hp (English horse power, bhp) = 745.7 W = 0.746 kW = 550 ft lb/s = 2545 Btu/h = 33000 ft lb/m = 1.0139 ps (metric horse power) ~= 1.0 KVA
PS (Pferdestärke, horse strength in German) referred to as 'metric horsepower' is replaced by kW as the legal EU measurement of engine power.
Comparative Power Outputs
Comparative power outputs are indicated below:
- human sound - normal speech : 10-8 kW
- human output: 0.1 kW (daily average), 0.2 kW (walking), 1 kW (running), 1.7 kW (sprinting)
- small scooter : 4 kW
- family car : 40 kW
- light aircraft : 150 kW
- sports car : 240 kW
- helicopter : 400 kW
- formula 1 car : 600 kW
- locomotive : 1500 kW
- cargo vessel : 6000 kW
- military aircraft : 30000 kW
- warship : 60000 kW
- airliner : 80000 kW
- launch rocket : 400000 kW
Example - 1000 hp
1000 hp can be converted to aprox. 745 kW or 2500000 Btu/h as indicated in the chart below.