Torque - Work done and Power Transmitted
The work done and power transmitted by a constant torque.
Work done
Work done is the force multiplied with the distance moved by the force - and can be expressed as
W = F s (1)
where
W = work done (J, Nm)
F = force (N)
s = distance moved by force (s)
For an angular motion
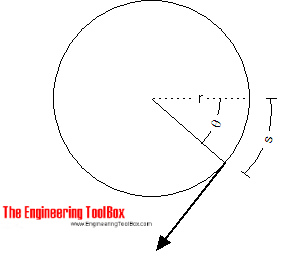
the work done can be expressed as
W = F θ r
= T θ (2)
where
W = work (Joules)
θ = angle (radians)
r = radius (m)
T = torque or moment (Nm)
Power transmitted
Power is the ratio between the work done and the time taken and can be expressed as
P = W / dt
= T θ / dt
= T ω
= 2 π n T
= 2 π (nrpm / 60) T
= 0.105 nrpm T (3)
where
P = power (Watts)
dt = time taken (s)
ω = θ / dt
= 2 π n
= angular velocity (rad/s)
n = speed (rev/s)
nrpm = speed (rev/min, rpm)
Note! - a machine must rotate to produce power! A machine with no rotation can deliver torque - like an electric motor - but since no distance is moved by force - no power is produced. As soon as the machine starts to rotate power is produced.
Example - required Torque to produce Power
A machine rotates with speed 3000 rev/min (rpm) and consumes 5 kW. The torque at the shaft can be calculated by modifying (3) to
T = P / 2 π n
= (5 kW) (1000 W/kW) / 2 π (3000 rev/min) / (60 sec/min)
= 15.9 Nm



