Angular Motion - Power and Torque
Angular velocity and acceleration vs. power and torque.
- Work is the result of a force acting over some distance. Work is quantified in joules (Nm) or foot-pounds.
- Torque is a rotating force produced by a motor’s crankshaft. The more torque the motor produces, the greater is its ability to perform work. Since torque is a vector acting in a direction it is commonly quantified by the units Nm or pound-feet.
- Power is how rapidly work is accomplished - work in a given amount of time. Power is quantified in watts (J/s) or horse power.
Power and Torque of Body in Angular Motion
The power of a rotating body can be expressed as
P = T ω
= T 2 π nrps
= T π nrpm / 30 (1)
where
P = power (W)
T = torque or moment (Nm)
ω = angular velocity (rad/s)
π = 3.14...
nrps = rotations per second (rps, 1/s)
nrpm = rotations per minute (rpm, 1/min)
- 1 rad = 360o/ 2 π =~ 57.29578..o
Note! - an object - like an electric motor - can have an active moment without rotation, but without rotation (ω = 0) there is no power produced.
In imperial units
P = T nrpm / 5252 (1b)
where
P = power (hp)
T = torque (ft lbf)
Example - Torque created by Rotating Motor
An electric motor runs with 3600 rpm with an measured power consumption of 2000 W. The torque created by the motor (without losses) can be calculated by rearranging (1) to
T = 30 P / (π nrpm)
= 30 (2000 W) / (π (3600 rpm))
= 5.3 Nm
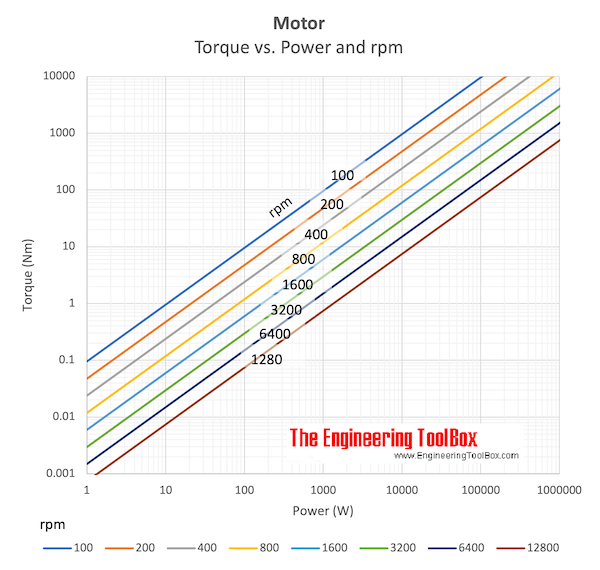
Torque Calculator
Download and print Motor - Torque vs. Power and rpm chart
Torque of a Body in Angular Motion
T = I α (2)
where
I = moment of inertia (kg m2, lbf ft s2)
α = angular acceleration (rad /s2)