Nitrogen - Prandtl number vs. Temperature and Pressure
Figures and tables showing Prandtl number of nitrogen at varying temperarure and pressure, SI and Imperial units.
The Prandtl Number - Pr - is a dimensionless number approximating the ratio of momentum diffusivity (kinematic viscosity) to thermal diffusivity - and is often used in heat transfer and free and forced convection calculations.
The Prandtl number can for calculations be expressed as
Pr = μ cp / k (1)
where
μ = absolute or dynamic viscosity (kg/(m s)), (lbm/(ft h))
cp = specific heat (J/(kg K)), (Btu/lbmoF)
k = thermal conductivity (W/(m K)), (Btu/(h ft2oF/ft))
Below, Prandtl numbers of nitrogen at varying temperatures and saturation pressure, as well as 1, 10 and 100 bara (14.5, 145 and 1450 psia) are given in figures and tables.
See also other properties of Nitrogen at varying temperature and pressure : Density and specific weight, Dynamic and kinematic viscosity, Specific heat (Heat capacity), Thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity, and thermophysical properties at standard conditions,
as well as Prandtl number of Air, Ammonia, Carbon dioxide, Methane, Propane and Water .
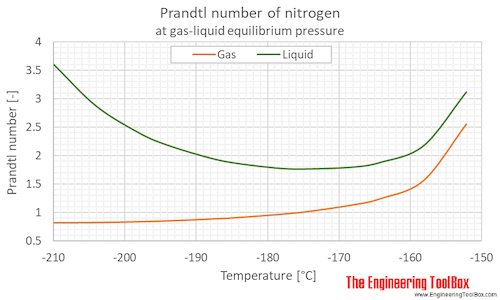
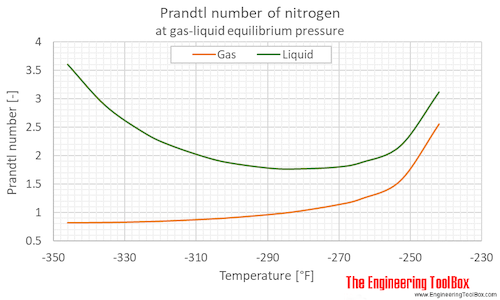
Prandtl number of nitrogen at gas-liquid equilibrium pressure, varying temperature given as °C or °F:
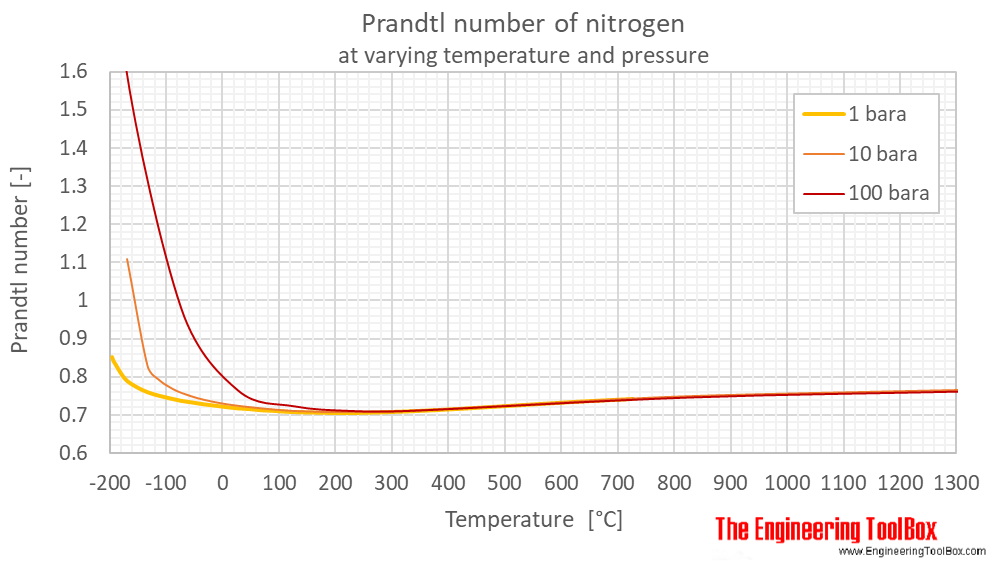
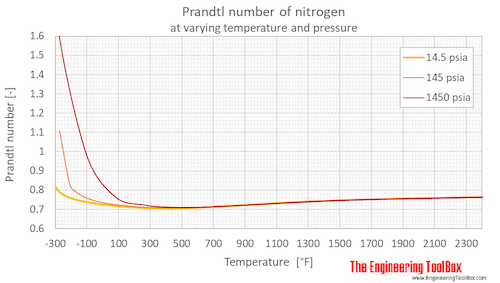
Prandtl number of nitrogen at 1, 10 and 100 bara (14.5, 145 and 1450 psia), varying temperature given as °C or °F:
Prandtl number of nitrogen at atmospheric pressure, temperature given as K, °C or °F:
| Temperature | Prandtl number | Temperature | Prandtl number | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (K) | (°C) | (-) | (K) | (°F) | (-) | |
| 78 | -195 | 0.847 | 78 | -320 | 0.849 | |
| 98 | -175 | 0.799 | 89 | -300 | 0.818 | |
| 123 | -150 | 0.769 | 116 | -250 | 0.775 | |
| 148 | -125 | 0.755 | 144 | -200 | 0.757 | |
| 173 | -100 | 0.746 | 172 | -150 | 0.746 | |
| 198 | -75 | 0.738 | 200 | -100 | 0.737 | |
| 223 | -50 | 0.731 | 228 | -50 | 0.730 | |
| 231 | -42 | 0.729 | 231 | -44 | 0.729 | |
| 248 | -25 | 0.726 | 244 | -20 | 0.726 | |
| 263 | -10 | 0.723 | 255 | 0 | 0.724 | |
| 268 | -5 | 0.722 | 266 | 20 | 0.723 | |
| 278 | 5 | 0.721 | 278 | 40 | 0.721 | |
| 283 | 10 | 0.720 | 283 | 50 | 0.720 | |
| 293 | 20 | 0.719 | 294 | 70 | 0.719 | |
| 298 | 25 | 0.718 | 300 | 80 | 0.718 | |
| 303 | 30 | 0.718 | 305 | 90 | 0.717 | |
| 323 | 50 | 0.714 | 311 | 100 | 0.716 | |
| 348 | 75 | 0.712 | 339 | 150 | 0.714 | |
| 373 | 100 | 0.710 | 366 | 200 | 0.710 | |
| 398 | 125 | 0.707 | 394 | 250 | 0.708 | |
| 423 | 150 | 0.706 | 422 | 300 | 0.706 | |
| 448 | 175 | 0.705 | 478 | 400 | 0.705 | |
| 473 | 200 | 0.705 | 533 | 500 | 0.706 | |
| 573 | 300 | 0.708 | 644 | 700 | 0.712 | |
| 623 | 350 | 0.711 | 700 | 800 | 0.717 | |
| 673 | 400 | 0.714 | 755 | 900 | 0.721 | |
| 773 | 500 | 0.723 | 811 | 1000 | 0.726 | |
Prandtl number of nitrogen at given temperatures and pressures:
| State | Temperature | Pressure | Prandtl number | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (K) | (°C) | (°F) | (bara) | (psia) | (-) | |
| Liquid at equilibrium |
63.15 | -210.0 | -346.0 | 0.125 | 1.82 | 3.598 |
| 69 | -204 | -335 | 0.332 | 4.82 | 2.876 | |
| 75 | -198 | -325 | 0.760 | 11.0 | 2.402 | |
| 79 | -194 | -317 | 1.22 | 17.8 | 2.183 | |
| 85 | -188 | -307 | 2.29 | 33.2 | 1.956 | |
| 89 | -184 | -299 | 3.31 | 47.9 | 1.857 | |
| 95 | -178 | -289 | 5.41 | 78.4 | 1.771 | |
| 99 | -174 | -281 | 7.26 | 105 | 1.762 | |
| 105 | -168 | -271 | 10.8 | 157 | 1.793 | |
| 109 | -164 | -263 | 13.8 | 201 | 1.878 | |
| 115 | -158 | -253 | 19.4 | 281 | 2.170 | |
| 121 | -152 | -242 | 26.4 | 383 | 3.113 | |
| Gas at equilibrium |
63.15 | -210.0 | -346.0 | 0.125 | 1.82 | 0.8240 |
| 69 | -204 | -335 | 0.332 | 4.82 | 0.8295 | |
| 75 | -198 | -325 | 0.760 | 11.0 | 0.8433 | |
| 79 | -194 | -317 | 1.22 | 17.8 | 0.8578 | |
| 85 | -188 | -307 | 2.29 | 33.2 | 0.8887 | |
| 89 | -184 | -299 | 3.31 | 47.9 | 0.9168 | |
| 95 | -178 | -289 | 5.41 | 78.4 | 0.9738 | |
| 99 | -174 | -281 | 7.26 | 105 | 1.025 | |
| 105 | -168 | -271 | 10.8 | 157 | 1.136 | |
| 109 | -164 | -263 | 13.8 | 201 | 1.249 | |
| 115 | -158 | -253 | 19.4 | 281 | 1.565 | |
| 121 | -152 | -242 | 26.4 | 383 | 2.553 | |
| Liquid | 63.17 | -210.0 | -346.0 | 1 | 14.5 | 3.596 |
| 77.24 | -195.9 | -320.6 | 1 | 14.5 | 2.272 | |
| Gas | 77.24 | -195.9 | -320.6 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.8508 |
| 80 | -193 | -316 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.8401 | |
| 100 | -173 | -280 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7944 | |
| 120 | -153 | -244 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7732 | |
| 140 | -133 | -208 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7593 | |
| 160 | -113 | -172 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7503 | |
| 180 | -93.2 | -136 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7430 | |
| 200 | -73.2 | -100 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7366 | |
| 220 | -53.2 | -63.7 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7322 | |
| 240 | -33.2 | -27.7 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7277 | |
| 260 | -13.2 | 8.3 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7241 | |
| 280 | 6.9 | 44.3 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7203 | |
| 300 | 26.9 | 80.3 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7171 | |
| 320 | 46.9 | 116 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7152 | |
| 340 | 66.9 | 152 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7123 | |
| 360 | 86.9 | 188 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7109 | |
| 400 | 127 | 260 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7074 | |
| 500 | 227 | 440 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7049 | |
| 600 | 327 | 620 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7092 | |
| 700 | 427 | 800 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7165 | |
| 800 | 527 | 980 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7254 | |
| 900 | 627 | 1160 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7343 | |
| 1000 | 727 | 1340 | 1 | 14.5 | 0.7417 | |
| Liquid | 63.37 | -210 | -346 | 10 | 145 | 3.583 |
| 80 | -193 | -316 | 10 | 145 | 2.143 | |
| 100 | -173 | -280 | 10 | 145 | 1.747 | |
| 103.8 | -169.4 | -273 | 10 | 145 | 1.777 | |
| Gas | 103.8 | -169.4 | -273 | 10 | 145 | 1.109 |
| 140.0 | -133.2 | -208 | 10 | 145 | 0.8276 | |
| 160 | -113 | -172 | 10 | 145 | 0.7918 | |
| 180 | -93.2 | -136 | 10 | 145 | 0.7715 | |
| 200 | -73.2 | -100 | 10 | 145 | 0.7574 | |
| 240 | -33.2 | -28 | 10 | 145 | 0.7391 | |
| 300 | 26.9 | 80.3 | 10 | 145 | 0.7234 | |
| 400 | 127 | 260 | 10 | 145 | 0.7097 | |
| 500 | 227 | 440 | 10 | 145 | 0.7067 | |
| 600 | 327 | 620 | 10 | 145 | 0.7098 | |
| 800 | 527 | 980 | 10 | 145 | 0.7258 | |
| 1100 | 827 | 1520 | 10 | 145 | 0.7485 | |
| 1600 | 1327 | 2420 | 10 | 145 | 0.7658 | |
| Liquid | 100 | -173 | -280 | 50 | 725 | 1.670 |
| Supercritical phase |
600 | 327 | 620 | 50 | 725 | 0.7113 |
| 1100 | 827 | 1520 | 50 | 725 | 0.7480 | |
| 1600 | 1327 | 2420 | 50 | 725 | 0.7652 | |
| Liquid | 65.32 | -208 | -342 | 100 | 1450 | 3.466 |
| 80 | -193 | -316 | 100 | 1450 | 2.202 | |
| 100 | -173 | -280 | 100 | 1450 | 1.634 | |
| Supercritical phase | 200 | -73.2 | -100 | 100 | 1450 | 0.9808 |
| 300 | 26.9 | 80.3 | 100 | 1450 | 0.7660 | |
| 400 | 127 | 260 | 100 | 1450 | 0.7237 | |
| 500 | 227 | 440 | 100 | 1450 | 0.7115 | |
| 600 | 327 | 620 | 100 | 1450 | 0.7114 | |
| 1100 | 827 | 1520 | 100 | 1450 | 0.7468 | |
| 1600 | 1327 | 2420 | 100 | 1450 | 0.7630 | |



