Ammonia - Prandtl Number vs. Temperature and Pressure
Figures and table with changes in Prandtl number for ammonia with changes in temperature and pressure.
The Prandtl Number - Pr - is a dimensionless number approximating the ratio of momentum diffusivity (kinematic viscosity) to thermal diffusivity - and is often used in heat transfer and free and forced convection calculations.
The Prandtl number can for calculations be expressed as
Pr = μ Cp / k (1)
where
μ = absolute or dynamic viscosity (kg/m s, lbm/(ft h))
Cp = specific heat (J/kg K, Btu/lbmoF)
k = thermal conductivity (W/m K, Btu/(h ft2oF/ft))
Below, Prandtl numbers for ammonia at varying temperatures and pressures are given in figures and table.
See also other properties of Ammonia at varying temperature and pressure: Density and specific weight, Dynamic and kinematic viscosity, Prandtl Number, Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium pressure, Specific Heat (Heat Capacity) and Thermal Conductivity, and Thermophysical properties at standard conditions and Vapour pressure at gas-liquid equilibrium,
as well as Prandtl number of Air, Carbon dioxide, Methane, Nitrogen, Propane and Water.
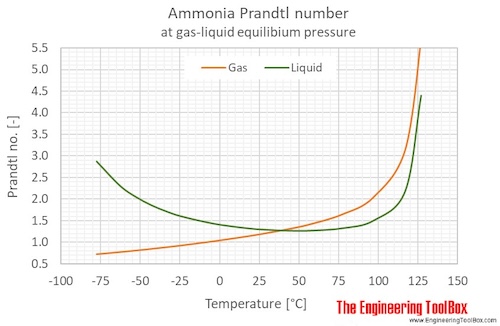
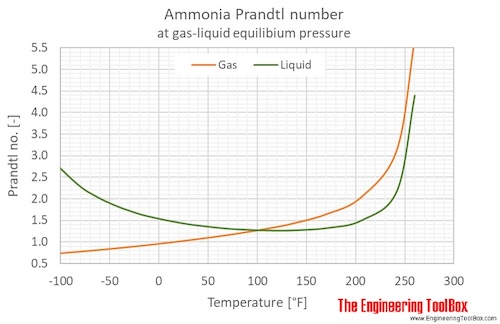
Ammonia Prandtl number at gas-liquid equilibrium pressure, temperature given as °C or °F:
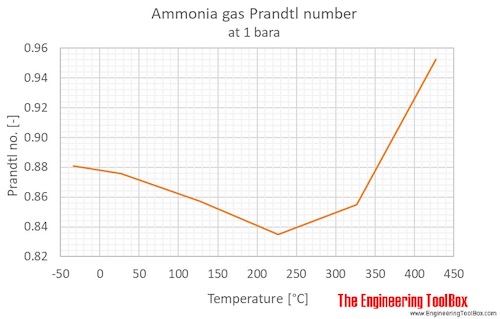
Ammonia Prandtl number at atmospheric pressure, temperature given as °C:
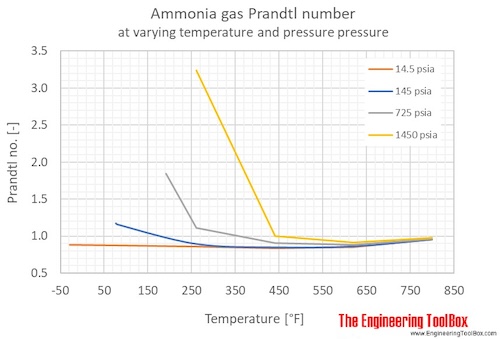
Ammonia Prandtl number at varying temperatures at given constant pressures, SI and Imperial units:

Ammonia Prandtl number at given temperatures and 1, 10, 50 and 100 bara presure:
| Temperature | Prandtl number at given pressures | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (K) | (°C) | (°F) | 1 bara | 10 bara | 50 bara | 100 bara |
| 200 | -73.2 | -8.6 | 2.67 | 2.67 | 2.69 | 2.72 |
| 239.56 | -33.6 | 13.3 | 1.71(liq) | |||
| 239.56 | -33.6 | 13.3 | 0.881(g) | |||
| 298.05 | 24.9 | 45.8 | 1.30 (liq) | |||
| 298.05 | 24.9 | 45.8 | 1.18 (g) | |||
| 300 | 26.9 | 46.9 | 0.876 | 1.16 | 1.29 | 1.29 |
| 362.03 | 88.9 | 81.4 | 1.41 (liq) | |||
| 362.03 | 88.9 | 81.4 | 1.84 (g) | |||
| 398.32 | 125 | 102 | 3.59 (liq) | |||
| 398.32 | 125 | 102 | 4.85 (g) | |||
| 400 | 127 | 102 | 0.857 | 0.894 | 1.11 | 3.24 |
| 500 | 227 | 158 | 0.835 | 0.846 | 0.903 | 0.998 |
| 600 | 327 | 214 | 0.855 | 0.860 | 0.883 | 0.913 |
| 700 | 427 | 269 | 0.952 | 0.955 | 0.965 | 0.976 |



