Geometric Shapes - Areas
Areas, diagonals and more - of geometric figures like rectangles, triangles, trapezoids ..
Square
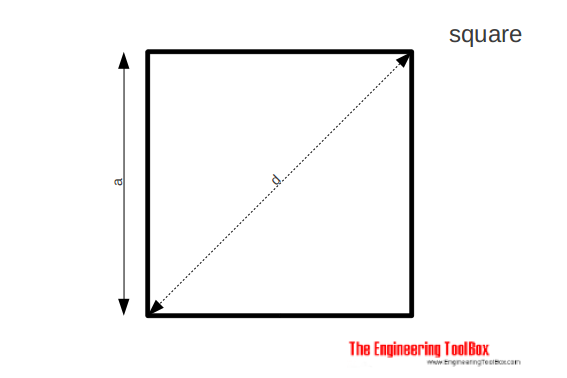
The area of a square can be calculated as
A = a2 (1a)
The side of a square can be calculated as
a = A1/2 (1b)
The diagonal of a square can be calculated as
d = a 21/2 (1c)
Rectangle
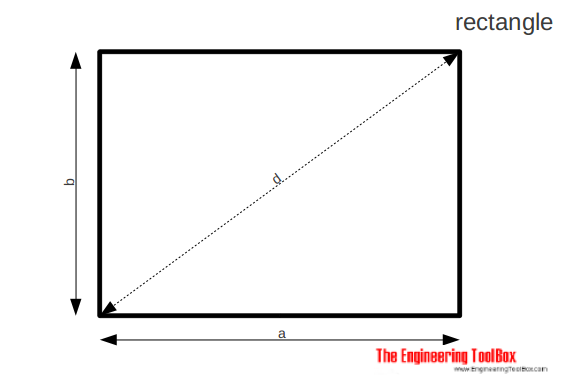
The area of a rectangle can be calculated as
A = a b (2a)
The diagonal of a rectangle can be calculated as
d = (a2 + b2)1/2 (2b)
Parallelogram
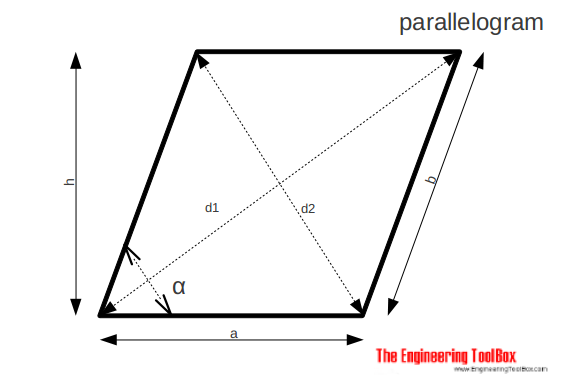
The area of a parallelogram can be calculated as
A = a h
= a b sin(α) (3a)
The diameters of a parallelogram can be calculated as
d1 = ((a + h cot(α))2 + h2)1/2 (3b)
d2 = ((a - h cot(α))2 + h2)1/2 (3b)
Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are equal.
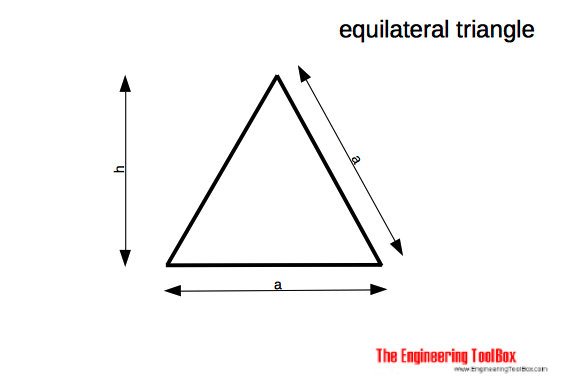
The area of an equilateral triangle can be calculated as
A = a2 / 3 31/2 (4a)
The area of an equilateral triangle can be calculated as
h = a / 2 31/2 (4b)
Triangle
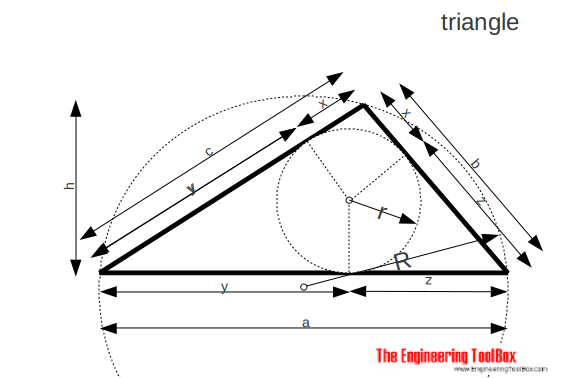
The area of a triangle can be calculated as
A = a h / 2
= r s (5a)
r = a h / 2s (5b)
R = b c / 2 h (5c)
s = (a + b + c) / 2 (5d)
x = s - a (5e)
y = s - b (5f)
z = s - c (5g)
Trapezoid
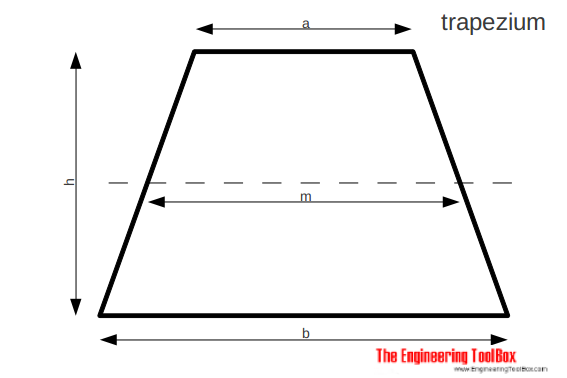
The area of a trapezoid can be calculated as
A = 1/2 (a + b) h
= m h (6a)
m = (a + b) / 2 (6b)
Hexagon
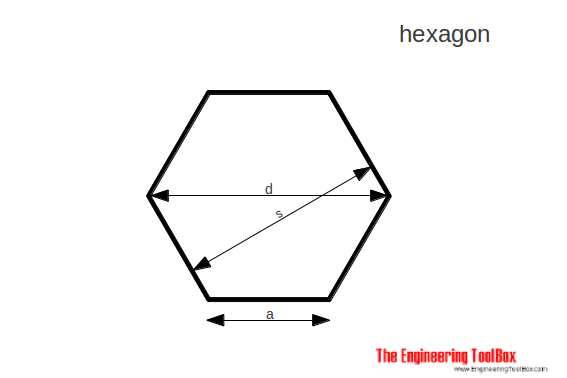
The area of a hexagon can be calculated as
A = 3/2 a2 31/2 (7a)
d = 2 a
= 2 / 31/2 s
= 1.1547005 s (7b)
s = 31/2/ 2 d
= 0.866025 d (7c)
Circle
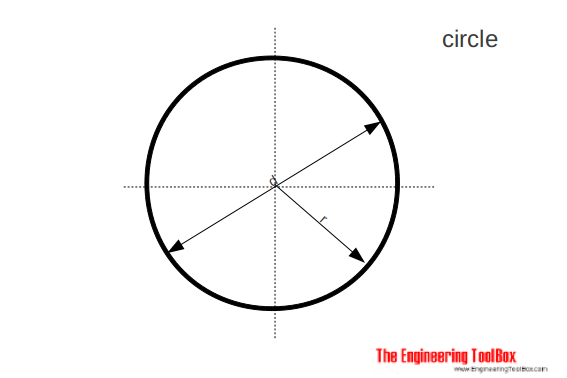
The area of a circle can be calculated as
A = π/4 d2
= π r2
= 0.785.. d2 (8a)
C = 2 π r
= π d (8b)
where
C = circumference
Sector and Segment of a Circle
Sector of Circle
Area of a sector of circle can be expressed as
A = 1/2 θr r2 (9)
= 1/360 θd π r2
where
θr = angle in radians
θd = angle in degrees
Segment of Circle
Area of a segment of circle can be expressed as
A = 1/2 (θr - sin(θr)) r2
= 1/2 (π θd / 180 - sin(θd)) r2 (10)
Right Circular Cylinder
Lateral surface area of a right circular circle can be expressed as
A = 2 π r h (11)
where
h= height of cylinder (m, ft)
r = radius of base (m, ft)
Right Circular Cone
Lateral surface area of a right circular cone can be expressed as
A = π r l
= π r (r2 + h2)1/2 (12)
where
h= height of cone (m, ft)
r = radius of base (m, ft)
l = slant length (m, ft)
Sphere
Lateral surface area of a sphere can be expressed as
A = 4 π r2 (13)



