Conn-Rod Mechanism
The connecting rod mechanism.
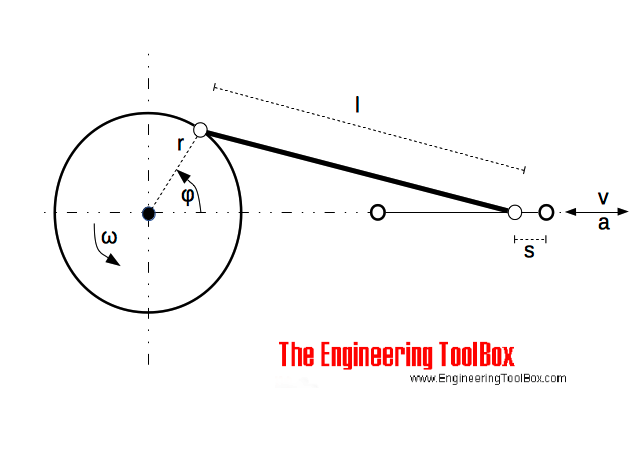
A connecting rod - conn-rod - mechanism converts rotating motion to reciprocating motion - or vice versa.
The position of the rod can be expressed as
s = r (1 - cos(φ)) + (λ / 2) r sin2(φ) (1)
where
s = position of the rod (m)
r = radius of crank (m)
φ = ω t
= 2 π ns t
= angular position of crank (rad)
ω = crank angular velocity (rad/s)
t = time (s)
ns = revolution per second (1/s)
λ = r / l
= crank ratio
l = length of rod (m)
The velocity of the rod can be expressed as
v = ω r sin(φ) (1 + λ cos(φ)) (2)
where
v = velocity of rod (m/s)
The acceleration of the rod can be expressed as
a = ω2 r (cos(φ) + λ cos(2φ)) (3)
where
a = acceleration of rod (m/s2)



