Distance Traveled vs. Speed and Time - Calculator and Chart
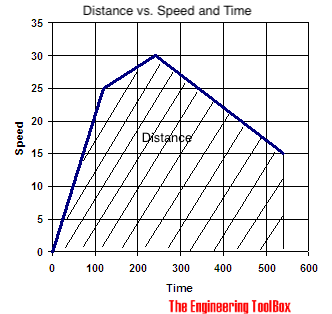
Velocity plotted in time used diagram.
For a graph with velocity vs. time - the area under the graph is distance traveled:
You can use the calculator below to summarize traveled distance:
Distance traveled: (m, ft, km, miles - depending on the units used)
Example
A car travels intervals with constant speed:
- 25 m/s in 120 s
- 30 m/s in 220 s
- 15 m/s in 300 s
The total distance traveled by the car can be calculated as
(25 m/s) (120 s) + (30 m/s) (220 s) + (15 m/s) (300 s)
= 14100 m
Related Topics
-
Dynamics
Motion of bodies and the action of forces in producing or changing their motion - velocity and acceleration, forces and torque. -
Miscellaneous
Engineering related topics like Beaufort Wind Scale, CE-marking, drawing standards and more.
Related Documents
-
Angular Motion - Power and Torque
Angular velocity and acceleration vs. power and torque. -
Centripetal and Centrifugal Acceleration Force
Forces due to circular motion and centripetal / centrifugal acceleration. -
Dynamic Pressure
Dynamic pressure is the kinetic energy per unit volume of a fluid in movement. -
Formulas of Motion - Linear and Circular
Linear and angular (rotation) acceleration, velocity, speed and distance. -
Impulse and Impulse Force
Forces acting a very short time are called impulse forces. -
Kinetic Energy
Energy possessed by an object's motion is kinetic energy. -
Piston Engines - Displacement
Calculate piston engine displacement. -
Projectile Range
Calculate the range of a projectile - a motion in two dimensions. -
Torque - Work done and Power Transmitted
The work done and power transmitted by a constant torque. -
Wind Load vs. Wind Speed
Wind load on surface - Wind load calculator.




