Dynamic Pressure
Dynamic pressure is the kinetic energy per unit volume of a fluid in movement.
Dynamic pressure is the kinetic energy of a flowing fluid - liquid or gas - per unit volume - and can be expressed as
pd = 1/2 ρ v2 (1)
where
pd = dynamic pressure (N/m2(Pa), lbf/ft2(psf))
ρ = density of fluid (kg/m3, slugs /ft3)
v = velocity (m/s, ft/s)
Dynamic Pressure Calculator - SI Units
The default values below are for water with density of 1000 kg/m3 .
- 1 N/m2= 1 Pa = 1.4504×10-4 lbf/in2(psi) = 0.02089 lbf/ft2(psf) = 1×10-5 bar = 4.03×10-3 in water = 0.336×10-3 ft water = 0.1024 mm water = 0.295×10-3 in mercury = 7.55×10-3 mm mercury = 0.1024 kp/m2 = 0.993×10-5atm
Dynamic Pressure Calculator - Imperial Units
The default values below are for water with density of 1.940 slugs .
Some common densities at atmospheric pressure:
- Water - 0 oC - 1000 kg/m3
- Water - 32 oF - 1.940 slugs/ft3
- Air - 20 oC - 1.2 kg/m3
- Air - 60 oF - 2.373×10-3 slugs/ft3
Example - The Dynamic Pressure in a Water Flow
The dynamic pressure in water with - temperature 20 oC - density 1000 kg/m3 and velocity 5 m/s - can be calculated as
pd = 1/2 (1000 kg/m3) (5 m/s)2
= 12500 Pa
= 12.5 kPa
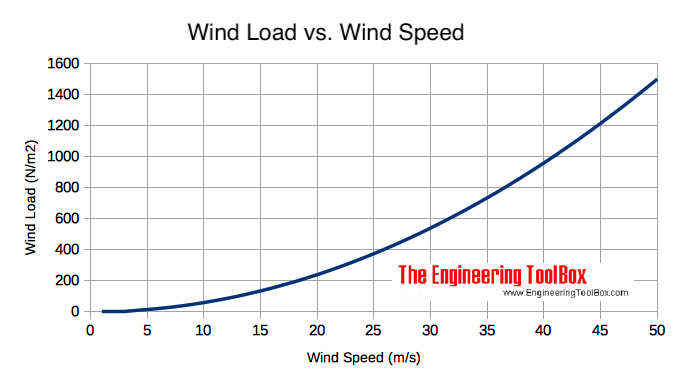
Example - Hurricane and Force acting on a Wall
The dynamic pressure in a hurricane with air temperature 20 oC, density of air 1.2 kg/m3 and wind speed 37 m/s can be calculated as
pd = 1/2 (1.2 kg/m3) (37 m/s)2
= 821 Pa (N/m2)
The force acting directly on a wall with area 10 m2 can be calculated as
F = pd A
= (821 N/m2) (10 m2)
= 8210 N
= 8.2 kN
- almost the weight of a small car.
Note! - the real force acting on the wall - or an other obstruction in the wind - is in general more complicated to calculate due to drag, turbulence and other effects.