Compressed Air vs. Free Air - Compression Ratio
The ratio of compressed air pressure to free air pressure.
Free air is air at ambient conditions at a specific location where
- ambient temperature
- moisture content
- barometric pressure
are stated.
Compression Ratio
Compression Ratio is based on the Ideal Gas Law and is the ratio between Discharge Pressure Absolute and Suction Pressure Absolute.
CR = pd / ps (1)
where
CR = compression ratio
pd = discharge absolute pressure (bar abs, psia)
ps = suction absolute pressure (bar abs, psia)
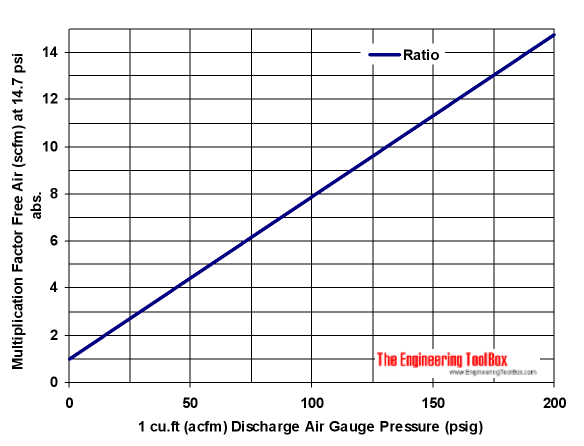
The compression ratio of free air - to compressed air, is indicated in the diagram below.
Compression Ratio - Pressure (psi)
- 1 psi = 6.9 kPa = 0.069 bar
- 1 ncfm = 0.5 nl/s
Converting Compressed Air Volume Flow to Free Air Volume Flow
A compressed air volume flow can be converted to a free air volume flow by using the equation
qF = CR qC (2)
where
qF = free air flow (m3/s, cfm)
qC = compressed air flow (m3/s, cfm)
Example - Converting Compressed Air Volume Flow to Free Air Volume Flow
A compressed air volume flow of 10 acfm (actual cfm) at 100 psig must be multiplied with Compression Ratio approximately 8 to estimate the volume of free air at atmospheric pressure.
qF = 8 (10 acfm)
= 80 scfm (standard cfm)
Compression Ratio - Pressure (bar)
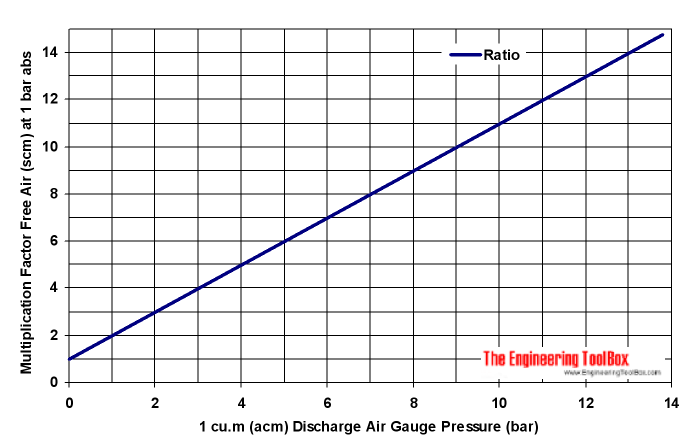
Example - Converting Free Air Volume Flow to Compressed Air Volume Flow
A free air volume flow of 1 m3/s is compressed to 10 bar (gauge) and must be divided with Compression Ratio approximately 11 to estimate the volume of compressed air.
qC = (1 m3/s) / 11
= 0.091 m3/s



