Flowmeters - Turndown Ratios
Turndown ratio (Rangeability) can be used to compare flow measurement devices like orifices, venturi meters etc.
Turndown ratio - rangeability - is often used to compare the span - the range - of flow measurement devices.
Turndown Ratio - Rangeability
Turndown ratio can be expressed as:
TR = qmax / qmin (1)
where
TR = Turndown Ratio
qmax = maximum flow
qmin = minimum flow
Maximum and minimum flow is stated within a specified accuracy and repeatability for the device.
Example - Turndown Ratio for an Orifice Meter
The turndown ratio - TR - for an orifice meter with maximum flow of 12 kg/s and a minimum flow of 3 kg/s can be calculated as:
TR = (12 kg/s) / (3 kg/s)
= 4
- normally expressed as turndown ratio of 4:1
This is a typical turndown ratio for a orifice plate. In general a orifice plates has turndown ratio between 3:1 and 5:1.
Turndown Ratio and Measured Signal
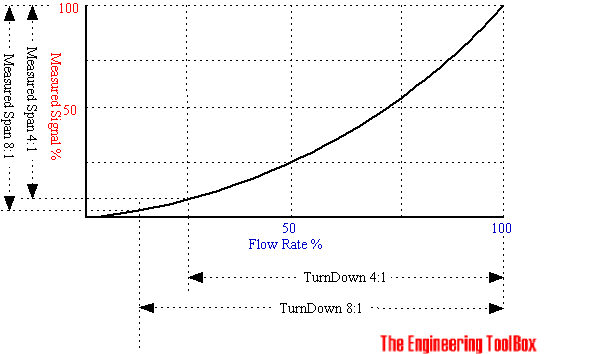
In a flow meter based on the orifice or venturi principle the differential pressure upstream and downstream of an obstruction in the flow is used to indicate the flow. According the Bernoulli Equation the differential pressure increases with the square of flow velocity. A large turndown ratio will cramp the measurement signal at low flow rate.



