Center of Gravity
A body and the center of gravity.
The "center of gravity" for a volume, an area or a line - is the point at which the body - if suspended - would be in balance.
For a symmetrical body in a uniform material - the center of gravity would be in the geometric center.
Perimeter
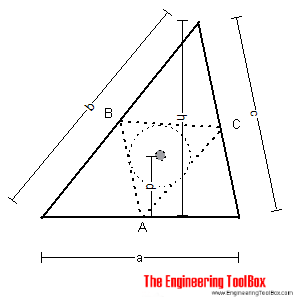
The center of gravity is the center of the circle inscribed in triangle ABC (middle points of the sides of the triangle).
The distance d can be calculated as
d = h (b + c) / 2 (a + b + c) (1)
Triangle
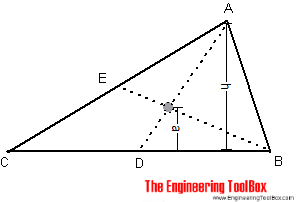
The center of gravity of a triangle is at the intersection of lines BE and AD. The distance a can be calculated as
a = h / 3 (2)
Parallelogram
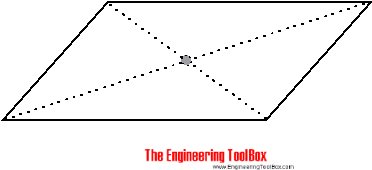
The center of gravity of a parallelogram is at the intersection of the diagonals.
Trapezoid
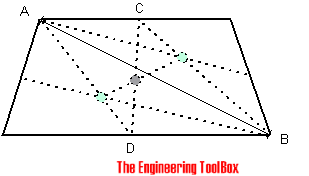
The center of gravity of a trapezoid can be estimated by dividing the trapezoid in two triangles. The center of gravity will be in the intersection between the middle line CD and the line between the triangles centers of gravity.
Two Bodies
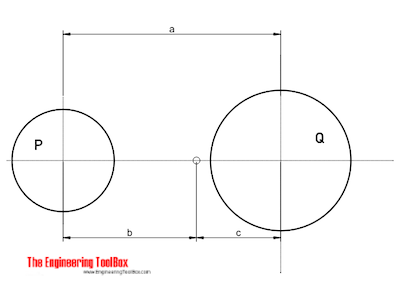
The center of gravity of two bodies can be calculated as
b = Q a / (P + Q) (3a)
c = P a / (P + Q) (3b)
where
Q, P = weight or mass of the bodies (N, kg, lb, slugs)



