Steam Entropy
Basic steam thermodynamics - entropy diagram.
The entropy diagram for steam shows the relationships between
- Pressure
- Temperature
- Dryness Fraction
- Entropy
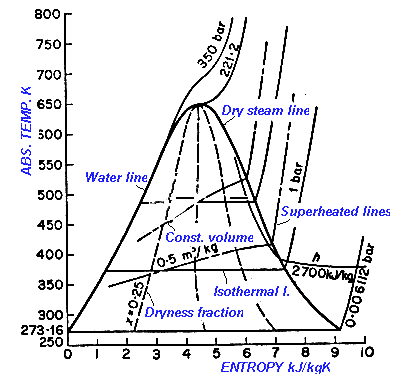
With two factors given - the others can be found in the diagram. The ordinates in the diagram represents the Entropy and the Absolute temperature.
The diagram consist of the following lines
- Isothermal line
- Pressure lines
- Lines of dryness fraction
- Waterline between water and steam
- Dry steam lines
- Constant volume lines
The total heat is given by the area enclosed by absolute zero base water line and horizontal and vertical line from the respective points.
An adiabatic expansion is a vertical line. An adiabatic process is expansion at constant entropy with no transfer of heat.
- Critical temperature of steam is 375 to 3,380 oC
- Critical pressure is 217.8 atm
Total Entropy of Steam
Entropy of Water
The change of entropy can be expressed as:
dS = loge(T1/T) (1)
where
T = absolute temperature (K)
The entropy of water above freezing point can be expressed as:
dS = loge(T1/273) (2)
Entropy of Evaporation
Change of Entropy during evaporation
dS = dL/T (3)
where
L = latent heat (J)
Entropy of wet steam
The entropy of wet steam can be expresses as:
dS = loge(T1/273) +ζ(L1/T1) (4)
where
ζ = dryness fraction
Entropy of superheated steam
Change of entropy during super-heating can be expressed as
dS = cp loge( T/T1) (5)
where
cp= specific heat capacity at constant pressure for steam (kJ/kgK)
The entropy of superheated steam can be expressed as:
dS = loge( T1/273) + L1/T1 + cp loge( Ts/T1) (6)
where
Ts = absolute temperature of superheated steam
T1 = absolute temperature of evaporation
Water and Steam Entropy - Imperial Units
| Temperature (oF) | Absolute Pressure (psia) | Entropy (Btu/lb oF) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Steam | ||
| 0 | 0.0185 | -0.3243 | 2.330 |
| 10 | 0.0309 | -0.3141 | 2.283 |
| 20 | 0.0505 | -0.3038 | 2.238 |
| 30 | 0.0809 | -0.2936 | 2.195 |
| 32 (0 oC) | 0.0887 | 0.0000 | 2.187 |
| 40 | 0.1217 | 0.0162 | 2.159 |
| 50 | 0.1718 | 0.0361 | 2.126 |
| 60 | 0.2564 | 0.0555 | 2.094 |
| 70 | 0.3633 | 0.0746 | 2.064 |
| 80 | 0.5074 | 0.0933 | 2.035 |
| 90 | 0.6989 | 0.1116 | 2.008 |
| 100 | 0.9503 | 0.1296 | 1.982 |
| 110 | 1.277 | 0.1473 | 1.957 |
| 120 | 1.695 | 0.1647 | 1.933 |
| 130 | 2.226 | 0.1817 | 1.911 |
| 140 | 2.893 | 0.1985 | 1.889 |
| 150 | 3.723 | 0.2151 | 1.868 |
| 160 | 4.747 | 0.2314 | 1.848 |
| 170 | 5.999 | 0.2474 | 1.829 |
| 180 | 7.519 | 0.2632 | 1.811 |
| 190 | 9.350 | 0.2787 | 1.793 |
| 200 | 11.54 | 0.2941 | 1.776 |
| 210 | 14.12 | 0.3092 | 1.760 |
| 212 (100 oC) | 14.70 | 0.3122 | 1.756 |
| 220 | 17.20 | 0.3241 | 1.744 |
| 230 | 20.80 | 0.3389 | 1.729 |
| 240 | 24.99 | 0.3534 | 1.714 |
| 250 | 29.85 | 0.3678 | 1.700 |
- 1 psi (lb/in2) = 6894.8 Pa (N/m2)
- 1 Btu/lbmoF = 4186.8 J/ (kg K)



