Sewer Pipes - Capacities vs. Slope
Carrying capacities of sewer and wastewater pipes - gpm and liter per second.
The diagrams below can be used for design of sewage and wastewater gravity conveying systems.
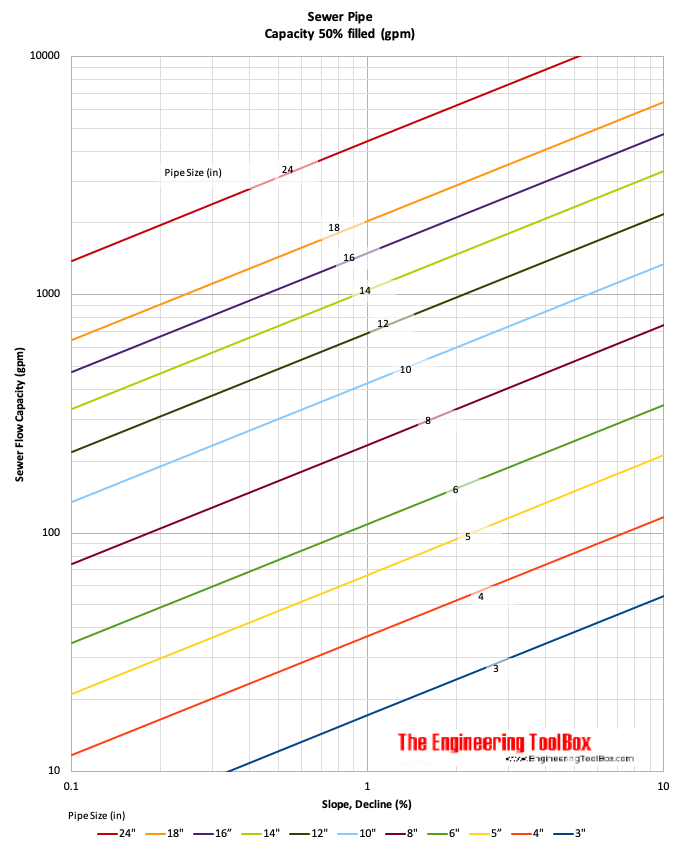
Sewage Pipe Capacity - Imperial units - gpm
Sewage Pipe Capacity - SI Units - liter per second
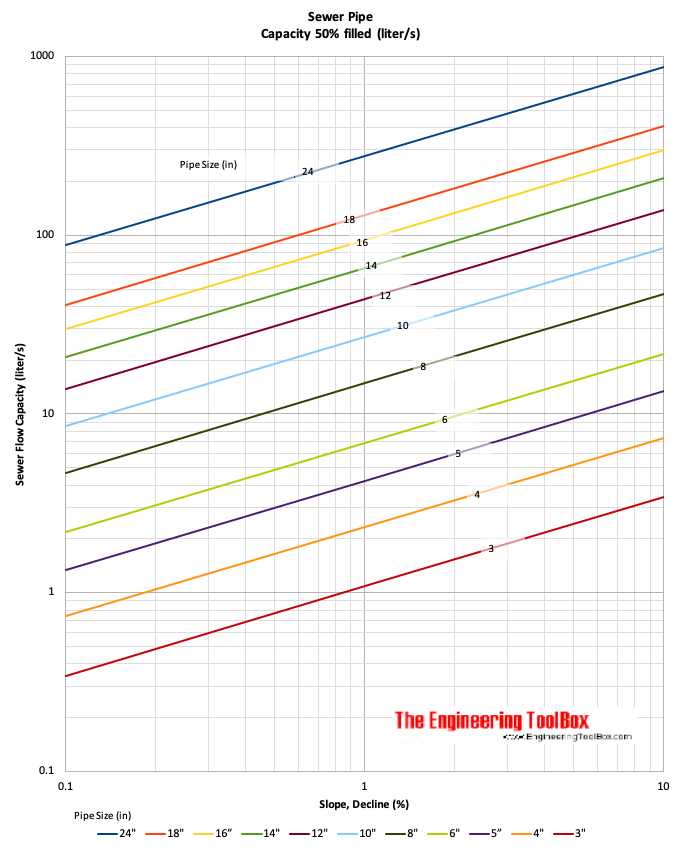
Note! - the charts are based on clean plastic pipes - calculated with the Manning formula, roughness coefficient 0.015 and fill 50%.
@Example - Capacity of a Sewer Pipe
The capacity of a 4 inch sewer pipe with decline 0.5% is aprox. 25 gpm (1.6 liter/s).
- 1 gal (US)/min = 6.30888×10-5 m3/s = 0.227 m3/h = 0.06309 dm3(liter)/s = 2.228×10-3 ft3/s = 0.1337 ft3/min = 0.8327 Imperial gal (UK)/min
Decline and Slope
Calculate between decline and slope units
d = 8.33 s(in/ft)
= 100 s(ft/ft)
= 100 s(m/m)
= s(ft/100ft) (1)
where
d = decline (%)
s = slope
Example - % Decline
1/8 in/ft slope can be transformed to % decline as
d = 8.33 (1/8 in/ft)
= 1.04 %



