Drain Pipes and Vent Stacks
Drain pipes and vent stack sizing.
Vents transports sewer gas through the building to open air space. Properly installed the vents prevents traps siphoning and sewage gas to leak into the interior building.
Different codes in different jurisdictions exists and must be adhered to locally. In general we talk about
- individual vents
- relief vents
- circuit vents
- branch vents
- stack vents
Individual vents
Individual vents serve individual fixtures.
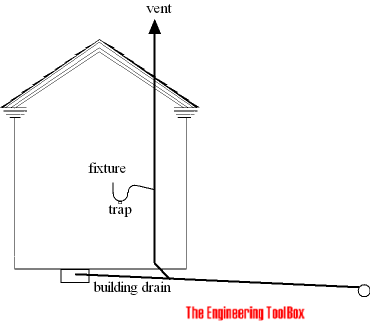
This vents only one fixture but may connect into an other vent that extends to open air.
- an individual vent should be at least one-half the size of the drain it vents (no less than 1 1/4", 32 mm)
Relief vents
Relief vents provide additional air to the drainage system where the primary vent is too far from the fixture.
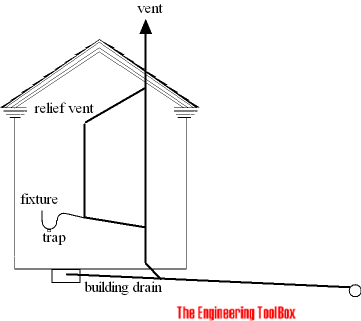
- an relief vent should be at least one-half the size of the drain it vents (no less than 1 1/4", 32 mm)
Circuit vents
Circuit vents are used with more than one fixtures. A circuit vent is installed before the last fixture extend up to open air or connects to an other vent that extend to the outside

- an circuit vent should be at least one-half the size of the drain it vents (no less than 1 1/4", 32 mm)
Branch vents
Branch vents are vents extending horizontally that connects multiple vents together.
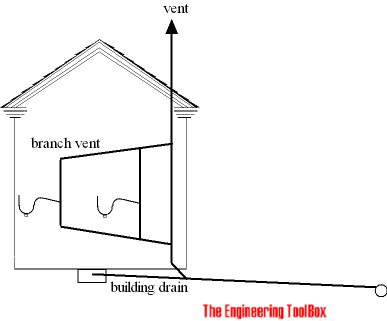
Stack vents
A vent stack is used only for the purpose of venting.

Vents are normally sized by using the "Developed Length" (total linear footage of pipe making up the vent) method.
Maximum length of vent stacks and relief vents
| Size of Soil Waste Stack (in) | Length | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixture Units Connected | Diameter of Required Vent Stack (in) | |||||||
| 1 1/4 | 1 1/2 | 2 | 2 1/2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 1 1/4 | 2 | 30 | ||||||
| 1 1/2 | 8 | 50 | 150 | |||||
| 10 | 30 | 100 | ||||||
| 2 | 12 | 30 | 75 | 200 | ||||
| 20 | 26 | 50 | 150 | |||||
| 2 1/2 | 42 | 30 | 100 | 300 | ||||
| 3 |
10 | 30 | 100 | 200 | 600 | |||
| 30 | 60 | 200 | 500 | |||||
| 60 | 50 | 80 | 400 | |||||
| 4 |
100 | 35 | 100 | 260 | 1000 | |||
| 200 | 30 | 90 | 250 | 900 | ||||
| 500 | 20 | 70 | 180 | 700 | ||||
| 5 |
200 | 35 | 80 | 350 | 1000 | |||
| 500 | 30 | 70 | 300 | 900 | ||||
| 1100 | 20 | 50 | 200 | 700 | ||||
Drainage and Vent Pipes
Materials used in drainage an vent pipes according U.S. standards.
| Piping Material | US Standards |
|---|---|
| Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) plastic pipe in IPS diameters, including Schedule 40, DR 22 (PS 200) and DR 24 (PS 140); with a solid, cellular core or composite wall | ASTM D2661; ASTM F628;ASTM F1488; CSA B181.1 |
| Cast-iron pipe | ASTM A74; ASTM A888; CISPI 301 |
| Copper or copper-alloy pipe | ASTM B42; ASTM B43; ASTM B302 |
| Copper or copper-alloy tubing (Type K, L, M or DWV) | ASTM B75; ASTM B88;ASTM B251; ASTM B306 |
| Galvanized steel pipe | ASTM A53 |
| Glass pipe | ASTM C1053 |
| Polyolefin pipe | ASTM F1412; CSA B181.3 |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic pipe in IPS diameters, inclu-ing Schedule 40, DR 22 (PS 200), and DR 24 (PS 140); with a solid, cellular core or composite wall | ASTM D2665; ASTM F891; ASTM F1488; CSA B181.2 |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic pipe with a 3.25-inchO.D. and a solid, cellularcore or composite wall | ASTM D2949, ASTM F1488 |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) plastic pipe | ASTM F1673; CSA B181.3 |
| Stainless steel drainage systems, Types 304 and 316L | ASME A112.3.1 |



