Polyurethane Insulation
Thermal conductivity - k-values - vs. temperature.
Polyurethane is an organic polymer formed by reacting a polyol (an alcohol with more than two reactive hydroxyl groups per molecule) with a diisocyanate or a polymeric isocyanate in the presence of suitable catalysts and additives.
Polyurethanes are flexible foams used in mattresses, chemical-resistant coatings, adhesives and sealants, insulation for buildings and technical applications like heat exchangers, cooling pipes and much more.
Thermal conductivity vs. temperature are indicated in the charts below:
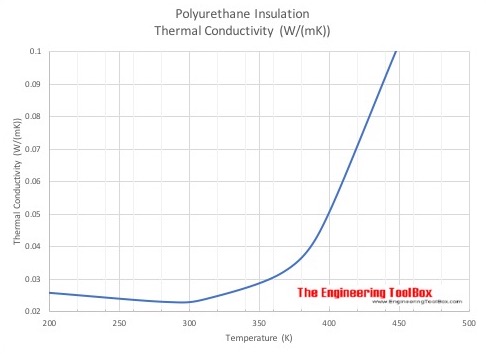
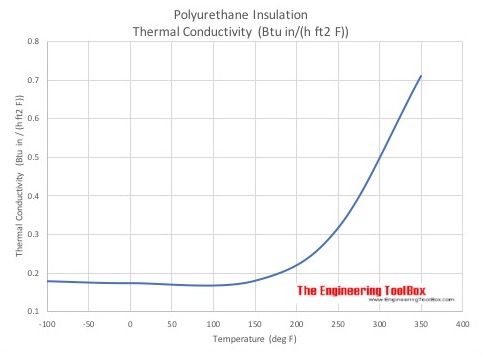
- T (oC) = 5/9 (T (oF) - 32)
- 1 W/(m K) = 6.935 (Btu in)/(h ft² °F)



