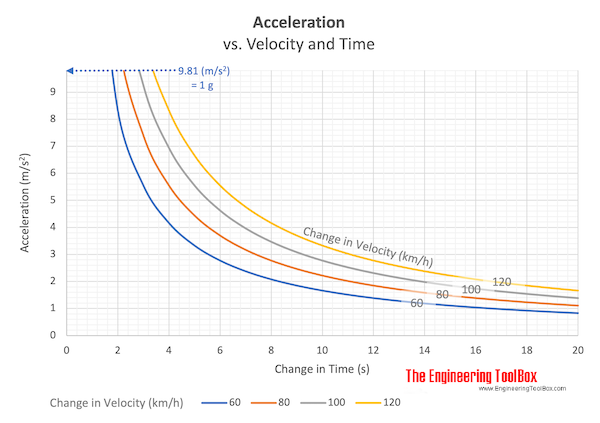
Acceleration
Change in velocity vs. time used.
Acceleration is the ratio change in velocity to time used and can be expressed as
a = dv / dt
= (v1 - v0) / (t1 - t0) (1)
where
a = acceleration (m/s2, ft/s2)
dv = change in velocity (m/s, ft/s)
v1 = final speed (m/s, ft/s)
v0 = initial speed (m/s, ft/s)
dt = time taken (s)
t1 = final time (s)
t0 = initial time (s)
Example - Motorcycle Acceleration
If a motorcycle accelerates from 0 km/h to 100 km/h in 3 seconds , the acceleration can be calculated as
a = ((100 km/h) - (0 km/h)) (1000 m/km) / (3600 s/h)) / (3 s)
= 9.26 m/s2
or close to acceleration of gravity 1 g = 9.81 (m/s2) .
The time from 0 - 100 km/h for an acceleration equal to gravity can be calculated by modifying the equation above to
(9.81 m/s2) = ((100 km/h) - (0 km/h)) (1000 m/km) / (3600 s/h)) / dt
or
dt = ((100 km/h) - (0 km/h)) (1000 m/km) / (3600 s/h)) / (9.81 m/s2)
= 2.83 s
Acceleration Calculator
The calculator below can be used to calculate acceleration:
Download and print Acceleration vs. Change in Velocity and Time chart