Melting points of Hydrocarbons, Alcohols and Acids
Melting temperature (°C and °F) with carbon number up to C33.
The tables and figures below show how the melting point changes with increasing carbon number up to C 33 for different kinds of hydrocarbons, alcohols and carboxylic acids. More detailed definitions and examples of molecular structures of the different classes of organic compounds are given below the figures.
- Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid
- Boiling point - the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas
For hydrocarbons with the same carbon number the boiling point increases in the following order:
multisubstituted alkane < singelsubstituted alkane < singelsubstituted alkene < normal alkene < normal alkane < alkyl cyclohexane < alkylbenzene < cycloalkene < cycloalkane < 2-, 4- and 3-alkanol / 1-alkylnaphthalene < 1-alkanol < normal alkanoic acid
For melting points, the trends are more varying with increasing carbon number for the different types of hydrocarbons.
See also boiling points of hydrcarbons, alcohols and acids , densities for different kinds of organic compounds and density, boiling and melting points of nitrogen and sulfur compounds.
See also pKa values for phenols, alcohols and carboxylic acids .
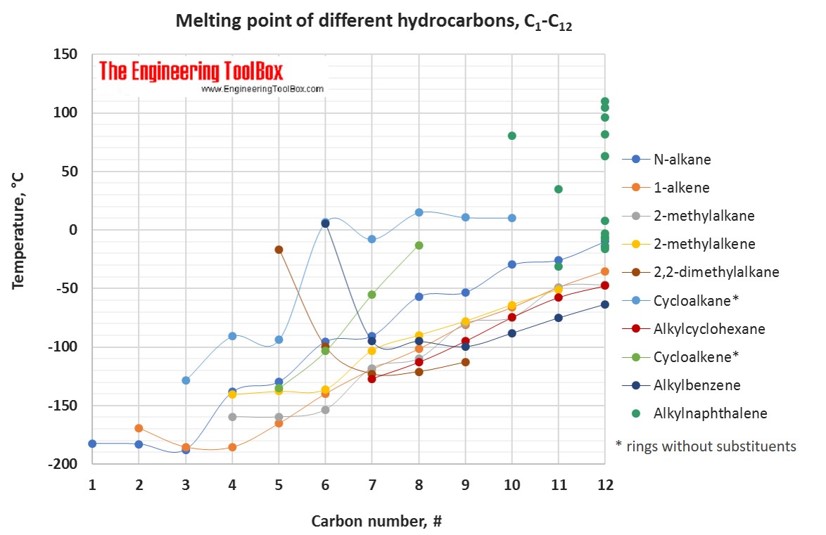
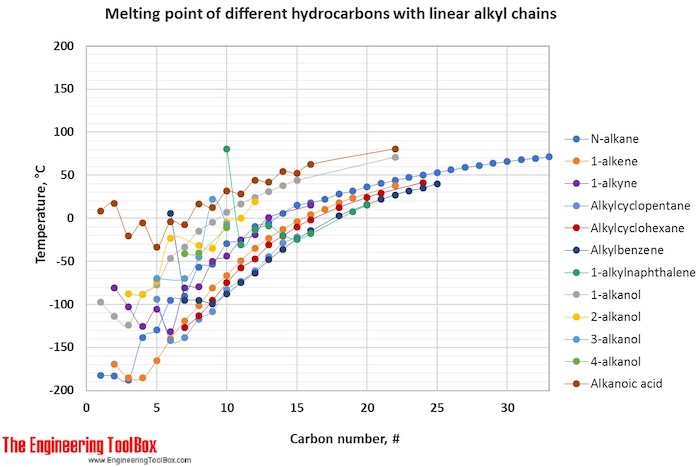

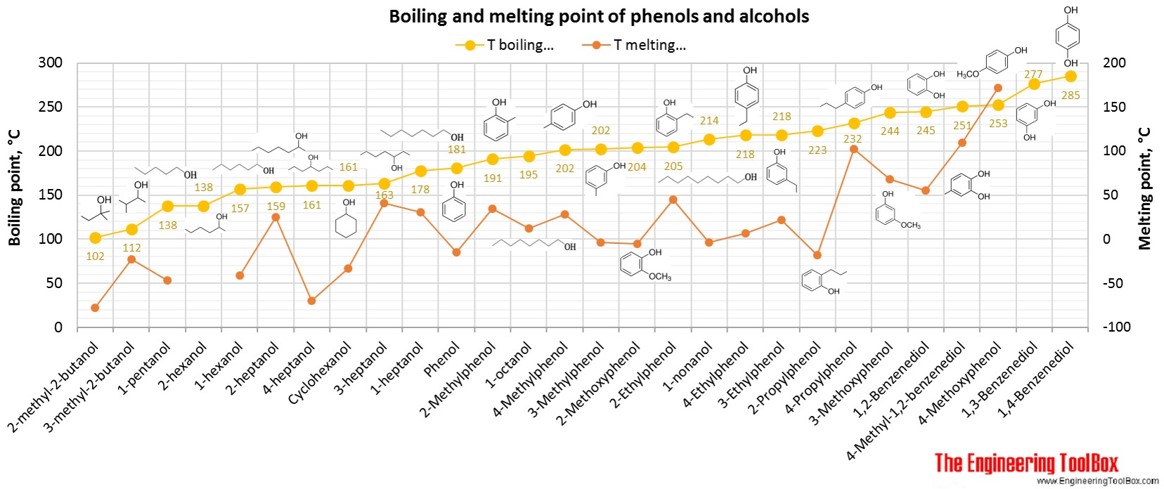
For full table - rotate the screen!
| Carbon number | Melting point of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids, C1-C16, given in °C | |||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
| Alkylcyclohexane* | -127 | -113 | -95 | -78 | -58 | -48 | -31 | -20 | -10 | -2 | ||||||
| 2,2-dimetylalkane | -17 | -100 | -123 | -121 | -113 | |||||||||||
| 3-methylalkane | -118 | -119 | -121 | -108 | -85 | -80 | -58 | |||||||||
| Alkylbenzene* | 6 | -95 | -95 | -100 | -88 | -75 | -63 | -48 | -36 | -24 | -14 | |||||
| Alkylcyclopentane | -142 | -138 | -117 | -108 | -83 | -73 | -61 | -45 | -29 | -22 | ||||||
| 2-methylalkane | -160 | -160 | -154 | -118 | -110 | -80 | -75 | -49 | -47 | |||||||
| 1-alkene | -169 | -185 | -185 | -165 | -140 | -119 | -102 | -81 | -66 | -49 | -35 | -23 | -13 | -4 |
4 |
|
| 2-methylalkene | -140 | -138 | -136 | -103 | -90 | -78 | -64 | -51 | ||||||||
| N-alkane | -183 | -183 | -188 | -138 | -130 | -95 | -91 | -57 | -53 | -30 | -26 | -10 | ||||
| 1-alkyne | -81 | -103 | -126 | -106 | -132 | -81 | -79 | -50 | -44 | -25 | -19 | 1 | 15 | |||
| 3-alkanol | -70 | -70 | -45 | 22 | -8 | |||||||||||
| Cycloalkene** | -135 | -104 | -55 | |||||||||||||
| 4-alkanol | -41 | -41 | -11 | |||||||||||||
| 2-alkanol | -88 | -88 | -73 | -23 | -32 | -35 | -5 | 0 | 19 | |||||||
| 1-alkanol | -98 | -114 | -124 | -89 | -78 | -46 | -33 | -15 | -5 | 7 | 17 | 24 | 31 | 38 | 44 | |
| Cycloalkane** | -129 | -91 | -94 | 7 | -8 | 15 | 11 | 10 | ||||||||
| Alkanoic acid | 8 | 17 | -21 | -5 | -34 | -4 | -7 | 17 | 12 | 31 | 29 | 44 | 42 | 63 | ||
| 1-alkylnaphthalene | 80 | -31 | -14 | -9 | -20 | -25 | -18 | |||||||||
| Carbon number | Melting point of hydrocarbons, alcohols and acids, C1-C16, given in °F | |||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
| Alkylcyclohexane* | -197 | -171 | -139 | -108 | -72 | -54 | -24 | -5 | 14 | 29 | ||||||
| 2,2-dimetylalkane | 2 | -148 | -189 | -186 | -171 | |||||||||||
| 3-methylalkane | -180 | -182 | -186 | -162 | -121 | -112 | -72 | |||||||||
| Alkylbenzene* | 42 | -139 | -139 | -147 | -126 | -103 | -82 | -54 | -33 | -11 | 6 | |||||
| Alkylcyclopentane | -224 | -217 | -179 | -162 | -117 | -99 | -78 | -48 | -20 | -8 | ||||||
| 2-methylalkane | -255 | -256 | -245 | -180 | -166 | -112 | -103 | -56 | -53 | |||||||
| 1-alkene | -273 | -302 | -302 | -265 | -220 | -182 | -151 | -114 | -87 | -56 | -31 | -10 | 9 | 25 | 40 | |
| 2-methylalkene | -221 | -216 | -213 | -153 | -130 | -108 | -83 | -60 | ||||||||
| N-alkane | -297 | -297 | -306 | -217 | -201 | -140 | -131 | -70 | -64 | -21 | -14 | 15 | ||||
| 1-alkyne | -113 | -153 | -194 | -158 | -205 | -114 | -111 | -58 | -47 | -13 | -2 | 34 | 59 | |||
| 3-alkanol | -94 | -94 | -49 | 72 | 19 | |||||||||||
| Cycloalkene** | -211 | -154 | -67 | |||||||||||||
| 4-alkanol | -42 | -41 | 12 | |||||||||||||
| 2-alkanol | -126 | -127 | -99 | -9 | -25 | -31 | 23 | 32 | 66 | |||||||
| 1-alkanol | -144 | -173 | -192 | -127 | -108 | -52 | -28 | 6 | 23 | 45 | 62 | 76 | 88 | 100 | 111 | |
| Cycloalkane** | -199 | -131 | -137 | 44 | 18 | 59 | 51 | 51 | ||||||||
| Alkanoic acid | 47 | 63 | -5 | 23 | -28 | 25 | 19 | 62 | 54 | 89 | 83 | 111 | 107 | 145 | ||
| 1-alkylnaphthalene | 177 | -24 | 7 | 17 | -3 | -12 | 0 | |||||||||
| * C#(N-alkyl)=0-10 | ||||||||||||||||
| ** rings without substituents | ||||||||||||||||
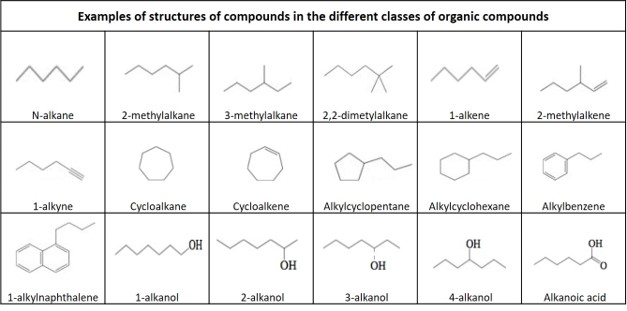
Definitions of organic compounds
Hydrocarbon: An organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon.
Main groups of hydrocarbons:
Alkane: An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula C n H 2n+2 . Also called paraffin .
Alkene: An unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond, with the general formula C n H 2n . Also called olefine .
Alkyne : An unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond, with the general formula C n H 2n-2 . Also called acetylene .
Cycloalkane: A one-ring (monocyclic) saturated hydrocarbon, with the general formula C n H 2n . Also called naphthene .
Cycloalkene: An alkene hydrocarbon which contains a closed ring of carbon atoms, but has no aromatic character, with the general formula C n H 2n-2 . Also called cycloolefin .
Aromatic hydrocarbon : A cyclic (ring-shaped), planar (flat) molecule with a ring of resonance bonds that exhibits more stability than other geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms. The simplest of the aromatics have 6 carbon atoms and contains 3 double bounds. A one ring aromatic without any substituents is called benzene, with the formula C6 H6.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons : hydrocarbon that are composed of multiple aromatic rings. A two ring aromatic without any substituents is called naphthalene, with the formula C 10 H 8 .
Some under-groups of hydrocarbons given in this document:
Alkyl: An alkane substituent missing one hydrogen, with general formula C n H 2n+1
2-Methylalkane: A branched alkane, with a methyl group connected to the second carbon atom in the main carbon chain.
3-Methylalkane: A branched alkane, with a methyl group connected to the third carbon atom in the main carbon chain.
2-Methylalkene: A branched alkene, with a methyl group connected to the second carbon atom in the main carbon chain.
Alkylcycklohexane: A monosubstituted cyclohexane with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of the cyclohexane ring, with the general formula C n H (2n+1) C6 H 11 .
Alkylcycklopentane : A monosubstituted cyclopentane with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of the cyclohexane ring, with the general formula C n H 2n+1 C5 H 9 .
Alkylbenzene: A monosubstituted benzene with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of the benzene ring, with the general formula C n H (2n+1) C6 H5.
Alkylnaphthalene: A monosubstituted naphthalene with one branching via the attachment of one alkyl group on one carbon of one of the aromatic rings, with the general formula C n H (2n+1) C 10 H 7 .
Some other groups of organic compounds:
Alcohol: an organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom
Alkanol: An alcohol where the hydroxyl group is connected to an alkane
Carboxylic acid: an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group (C(=O)OH). The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R–COOH, with R referring to the rest of the molecule.
Alkanoic acid: A carboxylic acid where the R is an alkane.
Related Topics
-
Material Properties
Properties of gases, fluids and solids. Densities, specific heats, viscosities and more. -
Melting and Freezing Points
Melting and freezing points of elements and chemical species at varying conditions.
Related Documents
-
Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids - Physical Data
Molweight, melting and boiling point, density, pKa-values, as well as number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in molecules are given for 150 different alcohols and acids. -
Boiling Fluids - Max Suction Flow Velocities
Recommended max suction flow velocity when pumping boiling fluids. -
Crude Oil - Density vs. Temperature
Variations in crude oil density are shown as function of temperatur, together with volume correction factors. -
Elements - Melting Points
Melting points of elements. -
Elements of the Periodic System
The elements of the periodic system with names, symbols, atomic numbers and weights, melting and boiling points, density, electronegativity and electron affinity, and electron configuration. -
Ethanol - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables showing dynamic and kinematic viscosity of ethanol, C2H5OH, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units. -
Ethanol Freeze Protected Water Solutions
Freezing temperature and flash points for ethanol based water solutions or brines. -
Ethylene Glycol Heat-Transfer Fluid Properties
Properties like freezing point, viscosity, specific gravity and specific heat of ethylene glycol based heat-transfer fluids, or brines. -
Glycerine - Boiling and Freezing Points
Boiling and freezing points of glycerine aqueous solutions. -
Hydrocarbons - Physical Data
Molweight, melting and boiling point, density, flash point and autoignition temperature, as well as number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in each molecule for 200 different hydrocarbons. -
Hydrocarbons - Melting Point vs. Molecular Weight
Calculate melting point of hydrocarbons from molecular weight (molar mass). -
Hydrocarbons, Alcohols and Acids - Boiling points
Boiling temperatures (°C and °F) with varying carbon numbers up to C33. -
Hydrocarbons, Linear Alcohols and Acids - Densities
Density of hydrocarbons like alcohols and acids as function of carbon number at 20°C / 68°. -
Inorganic Compounds in Water - Melting and Boiling Temperature, Density and Solubility
Physical constants for more than 280 common inorganic compounds. Density is given for the actual state at 25°C and for liquid phase at melting point temperature. -
Jet Fuel - Density vs. Temperature
Variations in jet fuel density as function of temperatur, together with volume correction factors. -
Liquids - Freezing and Melting Points
Common fluids and their freezing and melting points. -
Liquids and Gases - Boiling Points
Boiling temperatures for common liquids and gases - acetone, butane, propane and more. -
Lubricating Oil - Densities vs. Temperature
Variations in lubricating oil density as function of temperatur, together with volume correction factors. -
Melting and Boiling Temperatures - Evaporation and Melting Heats common Materials
Melting and boiling point temperatures, latent heat of evaporation, and melting heat of common substances like copper, gold, lead and more - SI units. -
Metal Alloys - Melting Points
Alloys and their melting points. -
Metals and Alloys - Melting Temperatures
The melting temperatures for some common metals and alloys. -
Methane - Dynamic and Kinematic Viscosity vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables showing dynamic and kinematic viscosity of methane, CH4, at varying temperature and pressure - Imperial and SI Units. -
Molybdenum Binary Eutectic Alloys - Melting Points
Mo - Molybdenum - binary eutectic alloys and melting points. -
Naming of Organic Compounds
Nomenclature rules for different groups of organic compounds and functional groups, together with examples of use of the rules. -
Organic Nitrogen Compounds - Physical Data
Boiling and melting points of amines, diamines, pyrroles, pyridines, piperidines and quinolines shown together with their molecular structures, as well as molweights and density. -
Organic Sulfur Compounds - Physical Data
Boiling and melting points of thoils, sulfides, disulfides and thiophenes shown together with molecular structures, as well as molweights and density. -
Phenols, Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids - pKa Values
For oxygen containing organic compounds this is given: pKa (the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant), molecular structures, molar weights, density and melting and boiling points. -
Propylene Glycol based Heat-Transfer Fluids
Freezing points of propylene glycol based heat-transfer fluids suitable for the food processing industry. -
Refrigerants - Physical Properties
Physical properties of refrigerants - molecular weight, boiling, freezing and critical points.




