Electrical Induction Motors - Synchronous Speed
Operating speed of an induction motor depends on the input power frequency and the number of magnetic poles in the motor.
The synchronous speed for an electric induction motor is determined by
- the power supply frequency, and
- the number of poles in the motor winding.
The synchronous speed can be calculated as:
n = f (2 / p) 60 (1)
where
n = shaft rotation speed (rev/min, rpm)
f = frequency of electrical power supply (Hz, cycles/sec, 1/s)
p = number of poles
Note - an induction motor will never reach its synchronous speed. If it did - the rotor would appear to be stationary to the rotating stator field since it would rotate with the same speed. With no relative motion between stator and rotor field no voltage will be induced in the motor. The speed of an induction motor is therefore limited to a speed below synchronous speed and the difference between synchronous speed and actual speed is called slip.
Example - Synchronous Speed of Electric Motor with Two Poles
A motor with two poles is supplied with power with frequency 50 Hz (1/s). The rotation speed can be calculated as
n = (50 1/s) (2 / 2) (60 s/min)
= 3000 rpm (1/min)
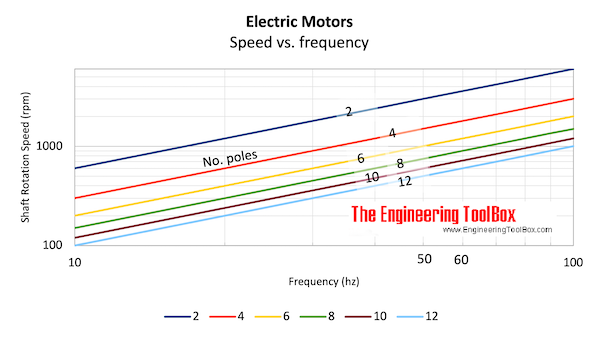
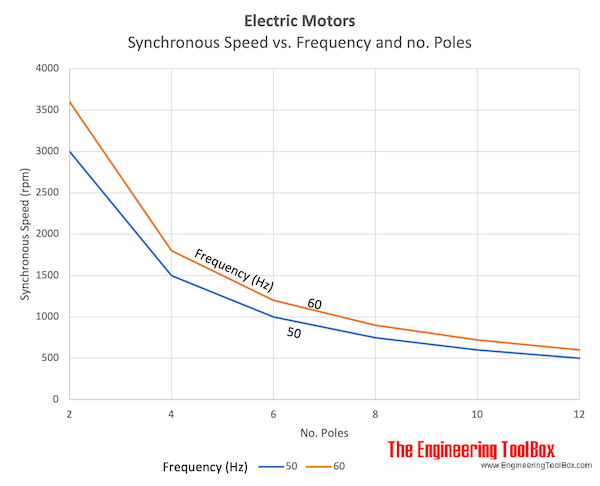
Synchronous rotation speed at different frequencies and number of poles
| Shaft rotation - n - (rev/min, rpm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency - f - (Hz) | Number of poles - p - | |||||
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | |
| 10 | 600 | 300 | 200 | 150 | 120 | 100 |
| 20 | 1200 | 600 | 400 | 300 | 240 | 200 |
| 30 | 1800 | 900 | 600 | 450 | 360 | 300 |
| 40 | 2400 | 1200 | 800 | 600 | 480 | 400 |
| 501) | 3000 | 1500 | 1000 | 750 | 600 | 500 |
| 602) | 3600 | 1800 | 1200 | 900 | 720 | 600 |
| 70 | 4200 | 2100 | 1400 | 1050 | 840 | 700 |
| 80 | 4800 | 2400 | 1600 | 1200 | 960 | 800 |
| 90 | 5400 | 2700 | 1800 | 1350 | 1080 | 900 |
| 100 | 6000 | 3000 | 2000 | 1500 | 1200 | 1000 |
- Motors designed for 50 Hz are most common outside U.S
- Motors designed for 60 Hz are most common in U.S
Variable Frequency Drive
A variable frequency drive modulates the speed of an electrical motor by changing the frequency of the power supply.