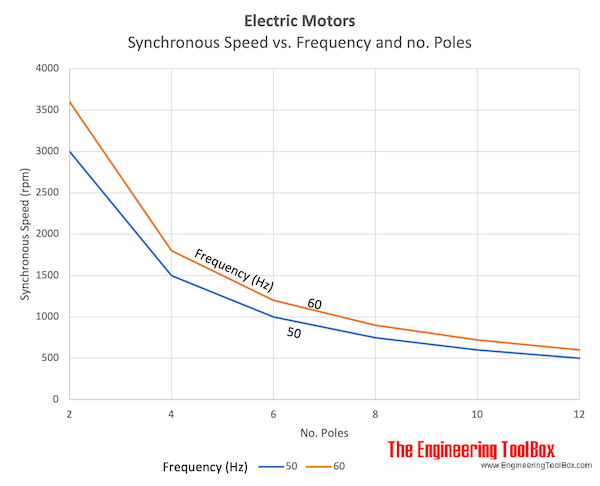
Induction Motors - No. of Poles and Synchronous vs. Full Load Speed
Synchronous and full load speed of amplitude current (AC) induction motors.
Synchronous and approximate full load speed of AC synchronous electrical induction motors:
| Number of Poles | Speed (rpm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (Hz, cycles/sec) | ||||
| 60 | 50 | |||
| Synchronous | Full Load | Synchronous | Full Load | |
| 2 | 3600 | 3500 | 3000 | 2900 |
| 4 | 1800 | 1770 | 1500 | 1450 |
| 6 | 1200 | 1170 | 1000 | 960 |
| 8 | 900 | 870 | 750 | 720 |
| 10 | 720 | 690 | 600 | 575 |
| 12 | 600 | 575 | 500 | 480 |
| 14 | 515 | 490 | 429 | 410 |
| 16 | 450 | 430 | 375 | 360 |
| 18 | 400 | 380 | 333 | 319 |
| 20 | 360 | 340 | 300 | 285 |
| 22 | 327 | 310 | 273 | 260 |
| 24 | 300 | 285 | 240 | 230 |
| 26 | 277 | 265 | 231 | 222 |
| 28 | 257 | 245 | 214 | 205 |
| 30 | 240 | 230 | 200 | 192 |
Example - Speed of Electric Motor
A motor with 4 poles runs with frequency 50 Hz. The synchronous speed is 1500 rpm and the typical full load speed is 1450 rpm. The slip is the difference between synchronous and load speed - 50 rpm.