Sound - Frequency, Wavelength and Octave
An introduction to the nature of sound with frequencies, wave-lengths and octaves.
Sound energy is transmitted through air (or other particles) as a traveling pressure wave. In air the displacement wave amplitude may range from 10-7 mm to a few mm per second.
Frequency
The frequency - cycles per second - of a sound is expressed in hertz (Hz). The frequency can be expressed as
f = 1 / T (1)
where
f = frequency (s-1, 1/s, Hz)
T = time for completing one cycle (s)
Example - Frequency
The time for completing one cycle for a 500 Hz tone can be calculated as
T = 1 / (500 Hz)
= 0.002 s
The frequency range for the human hearing is 20 to 20.000 Hz. By age the upper limit for many is reduced to 12-13.000 Hz.
Example - Parallel to Alternating Current
An alternating current completes 5 cycles in 100 ms.
The time for completing one cycle can be calculated
T = (100 ms/cycle) / (5 cycles)
= 20 ms
The frequency of the alternating current can be calculated as
f = 1 / ((20 ms) (10-3 s/ms))
= 50 Hz
Wavelength
The wavelength of sound is the distance between the analogous points of two successive waves.
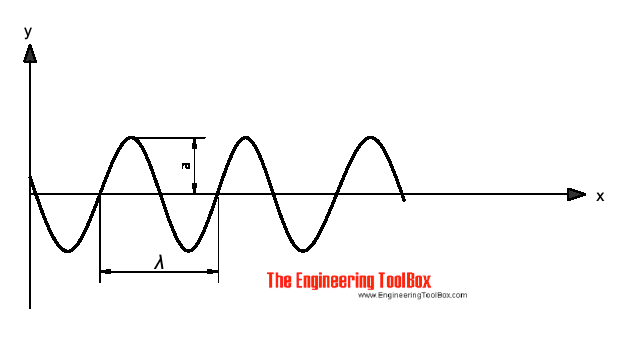
λ = c / f (2)
where
λ = wavelength (m)
c = speed of sound (m/s)
f = frequency (s-1, Hz)
Example - the Wavelength of a Tone
In air at normal atmosphere and 0 oC the speed of sound is 331.2 m/s. The wavelength of a 500 Hz tone can be calculated as
λ = (331.2 m/s) / (500 Hz)
= 0.662 m
Octave
An octave is the interval between two points where the frequency at the second point is twice the frequency of the first. The fundamental frequencies behaves in ratio (f1, f2) of 1:2. The mean frequency of the octave is
fm = (f1 f2)1/2 (3)
| Octave Center Frequency (Hz) | 31.25 | 62.5 | 125 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 4000 | 8000 | 16000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength in air (70oF, 21oC) (ft) |
17.92 | 9.03 | 4.52 | 2.26 | 1.129 | 0.56 | 0.28 | 0.14 | ||
| Wavelength in air (70oF, 21oC) (m) |
5.46 | 2.75 | 1.38 | 0.69 | 0.34 | 0.17 | 0.085 | 0.043 |
Although the octave is the eighth note of a series in any key - an octave is separated by 5 whole notes and 2 half notes.
- only six whole notes separates an octave



