Sound Intensity, Power and Pressure Levels
Introduction to decibel, sound power, intensity and pressure.
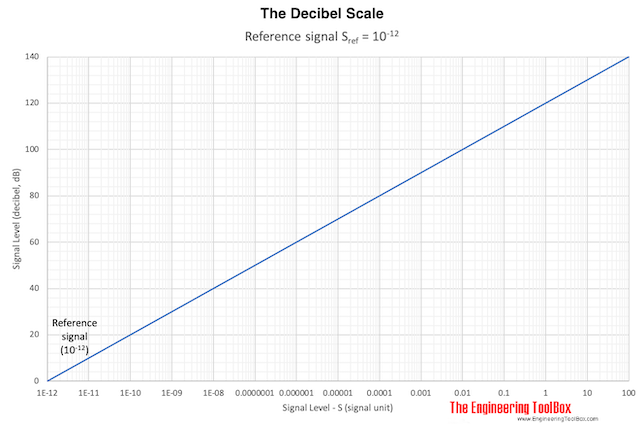
The Decibel
Decibel is a logarithmic unit used to describe ratios of physical values like - like power, sound pressure, voltage, intensity and more.
The decibel can be expressed as:
L = 10 log(S / Sref) (1)
where
L = signal level (dB)
S = signal (signal unit)
Sref = signal reference (signal unit)
Sound Power Level
Sound power is the energy rate - the energy of sound per unit of time (J/s, W in SI-units) from a sound source.
Sound power can more practically be expressed in a logarithmic scale named Sound Power Level as the ratio of sound power to the sound power at the threshold of hearing - 10-12 W:
LN = 10 log(N / Nref) (2)
where
LN = Sound Power Level (decibel, dB)
N = sound power (W)
Nref = reference sound power (10-12 W)
- The lowest sound power persons with excellent hearing can discern is about 10-12 W - defined as 0 dB in the decibel scale
- The loudest sound power generally possible to encounter is that of a jet aircraft with a sound power of 105 W - 170 dB
Sound Intensity Level
Sound intensity is the ratio acoustic or sound power to area. The SI-unit for Sound Intensity is W/m2.
The Sound Intensity Level can be expressed as:
LI = 10 log(I / Iref) (3)
where
LI = sound intensity level (dB)
I = sound intensity (W/m2)
Iref = 10-12 - reference sound intensity (W/m2)
Sound Pressure Level
The sound pressure is the force (N) of a sound on a surface area (m2) perpendicular to the direction of the sound. The SI-unit for the Sound Pressure is N/m2 or Pa.
The Sound Pressure Level in decibel can be expressed as
Lp = 10 log(p2 / pref2)
= 10 log(p / pref)2
= 20 log(p / pref) (4)
where
Lp = sound pressure level (dB)
p = sound pressure (Pa)
pref = 2×10-5 - reference sound pressure (Pa)
- If the pressure is doubled the sound pressure level is increased with 6 dB (20 log(2))