Bodies Moving on Inclined Planes - Acting Forces
Required forces to move bodies up inclined planes.
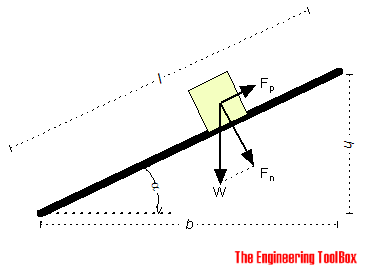
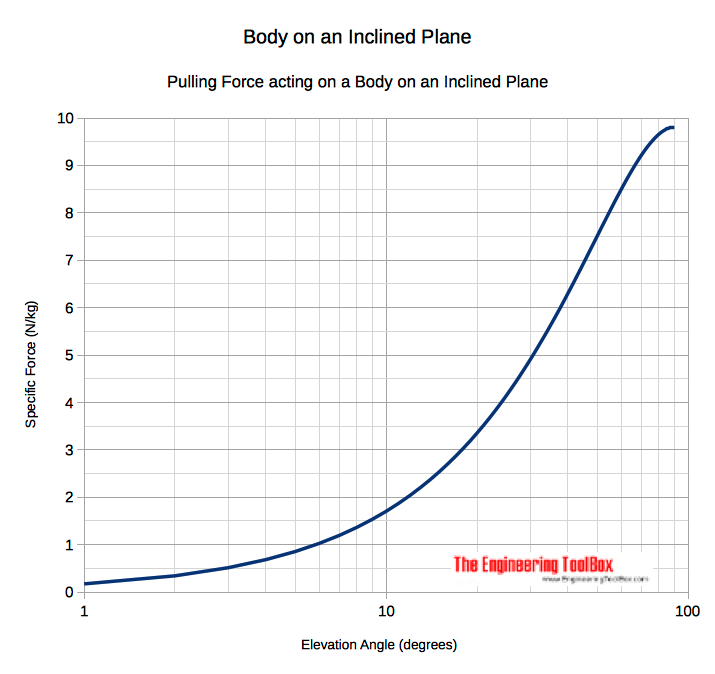
If we neglect friction between the body and the plane - the force required to move the body up an inclined plane can be calculated as
Fp = W h / l
= W sin(α)
= m ag sin(α) (1)
where
Fp = pulling force (N, lbf)
W = m ag
= gravity force - or weight of body (N, lbf)
h = elevation (m, ft)
l = length (m, ft)
α = elevation angle (degrees) (degrees vs. gradient vs. slopes)
m = mass of body (kg, slugs)
ag = acceleration of gravity (9.81 m/s2, 32.174 ft/s2)
By adding friction - (1) can be modified to
Fp = W (sin(α) + μ cos(α))
= m ag (sin(α) + μ cos(α)) (2)
where
Example - Pulling Force on Inclined Plane
A body with mass 1000 kg is located on a 10 degrees inclined plane. The pulling force without friction can be calculated as
Fp = (1000 kg) (9.81 m/s2) sin(10°)
= 1703 N
= 1.7 kN
Online Inclined Plane Force Calculator - SI Units
The calculator below can be used to calculate required pulling force to move a body up an inclined plane.
Online Inclined Plane Force Calculator - Imperial Units
Angle of Repose
A body resting on a plane inclined at at an angle α to the horizontal plane is in a state of equilibrium when the gravitational force tending to slide the body down the inclined plane is balanced by an equal and opposite frictional force acting up the inclined plane.
For equilibrium the "angle of response" α can be expressed as:
μ = F p / F n
= W sin(α) / (W cos(α))
= tan(α) (3)
Example - Gradient Force acting on a Car, Work Done and Power Required
The weight of an electric car is 2400 kg . The force acting on the car with 5% inclination can be calculated from (1) as
Fp_5% = (2400 kg) ( 9.81 m/s2) sin(5°)
= 2051 N
The force acting on the car with 10% inclination can be calculated as
Fp_10% = (2400 kg) ( 9.81 m/s2) sin(10°)
= 4088 N
If the car is moving along the inclined roads with the same speed - the work done by the forces after 1 km can be calculated as
W5% = (2051 N) (1000 m)
= 2051 kJ
W10% = (4088 N) (1000 m)
= 4088 kJ
If the speed of the car is 80 km/h (22.2 m/s) - the time to drive the distance can be calculated as
t80 = (1000 m) / (22.2 m/s)
= 45 s
The power required to move the vehicle (without rolling and air resistance) can be calculated as
P5% = (2051 kJ) / (45 s)
= 45.6 kW
P50% = (4088 kJ) / (45 s)
= 90.8 kW
If the speed of the car is reduced to 60 km/h (16.6 m/s) - the time to drive the distance can be calculated as
t60 = (1000 m) / (16.6 m/s)
= 60.2 s
The power required to move the vehicle (without rolling and air resistance) can be calculated as
P5% = (2051 kJ) / (60.2 s)
= 34.1 kW
P50% = (4088 kJ) / (60.2 s)
= 67.9 kW