Area Moment of Inertia Converter
Convert between Area Moment of Inertia units.
Area Moment of Inertia or Moment of Inertia of an Area - also known as Second Moment of Area - I, is a property of shape that is used to predict deflection, bending and stress in beams.
The general equation for Moment of Inertia for bending around an axis can be expressed as
Iaxis = ∫ y2 dA (1)
where
Iaxis = Area Moment of Inertia related to an axis (m4, mm4, in4, ft4)
y = the perpendicular distance from axis to the element dA (m, mm, in, ft)
dA = an elemental area (m2, mm2, in2, ft2)
Area Moment of Inertia Converter
Convert from | Multiply with | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convert to | |||||
| m4 | cm4 | mm4 | in4 | ft4 | |
| m4 | 1 | 108 | 1012 | 2.4×106 | 116.3 |
| cm4 | 10-8 | 1 | 104 | 2.4×10-2 | 1.2×10-6 |
| mm4 | 10-12 | 10-4 | 1 | 2.4×10-6 | 1.2×10-10 |
| in4 | 4.16×10-7 | 41.6 | 4.16×105 | 1 | 4.8225×10-5 |
| ft4 | 8.6×10-3 | 8.6×105 | 8.6×109 | 207346 | 1 |
Example - Convert between Area of Inertia Units
To convert from 160.6 cm4 to in4 multiply with 2.4×10-2 as
(160.6 cm4) 2.4×10-2 = 3.9 in4
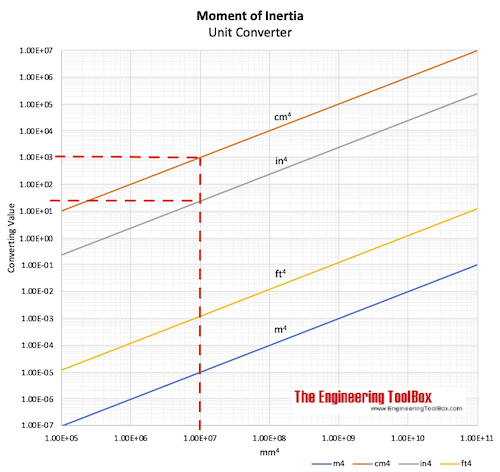
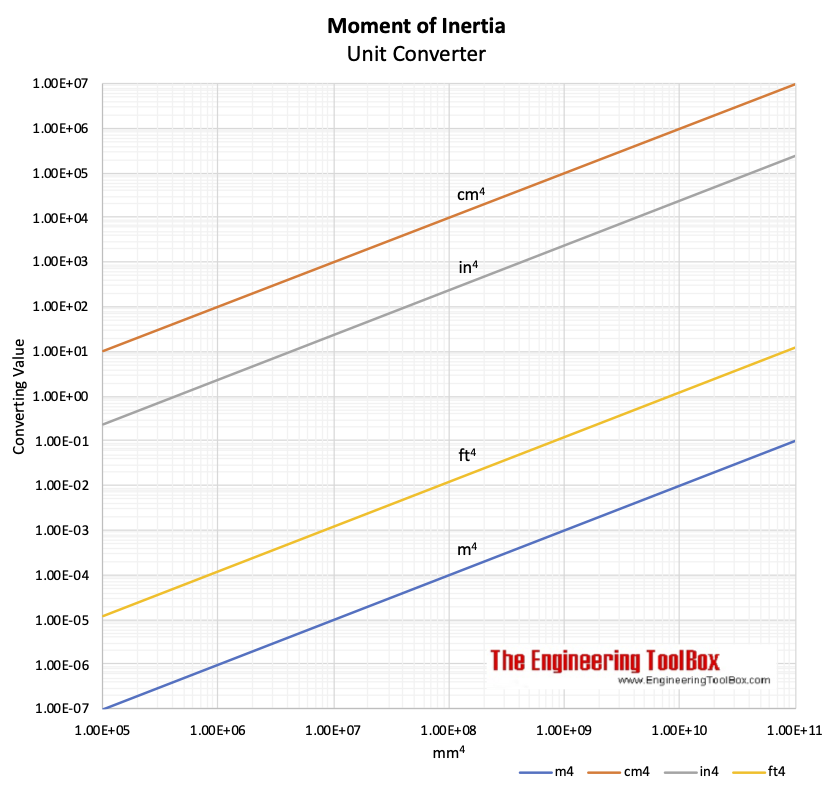
Moment of Inertia - Unit Converter Chart
Download and print Moment of Inertia - Unit Converting Chart
Moment of Inertia - Unit Converting Chart Example
100 cm4 (1.00×102 cm4) can be converted to 10000000 mm4 (1.00×107 mm4) or 24 in4 (2.4×101 in4) as indicated in the chart below: